![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
53 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
A gelatinous substance responsible for detecting linear & vertical acceleration |
Otoconia |
|
|
an illusion of being off balance |
disequilibrium |
|
|
an illusion of movement |
Vertigo |
|
|
bony labyrinth of the vestibular system is line by the~ |
perilymph |
|
|
Part of the semicircular canal that is oriented 30° upward |
Horizontal SCC |
|
|
Gelatinous barrier that contains sensory hair cells; within ampula |
cupula |
|
|
aka "Scarpa's Fluid"; it fills the ampulla & moves in response to the direction of the angular head rot |
endolymph |
|
|
Most important management for Vestibular Hypofunction to improve motion sensitivity |
Habituatiin Exercises |
|
|
Romberg test is (+) in closed eyes if _____ is affected a. proprioception b. cerebellum c. CNS |
A. B is for + in eyes open |
|
|
Inner Ear Test is (+) when applied cold stimulus near the ear eyes~ a. deviate towards b. deviate away c. stays the same |
B. |
|
|
Explain pathophyisology of Vestibular Hypofunction |
CN8 is damaged> info cannot travel up from CN8 to brain > eyes are fast enough for brain to react to mov't which results to dizziness/ disequilibrium> info is incorrect when sent to the retina; info is sent to brain & perceived as mov't |
|
|
tx for Vestibular Hypofunction |
promote inner ear adaptation and to challenge the balance component of the vestibular system.; Gaze Stability Exercise, Postural Stab, Habituation Exercises (Motion sensitivity) |
|
|
2 types of vestibular hypofunction |
Unilat & Bilat |
|
|
abnormal bone growth in the middle ear that cause hearing loss (idiopathic) |
Bilat Vestibular Hypofunction |
|
|
BBPPV is short for~ |
Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo |
|
|
test for BBPPV |
Dix-Hallpike Maneuver |
|
|
Vestibular d/o that has inner ear problems that causes short periods of dizziness when head is moved |
BPPV |
|
|
Occurs mostly when lying fown, turning over in bed & looking up a. Perilymphatic Fistula b. BPPV c. Vestibular Schwannoma |
B |
|
|
Hallmark of Meniere's dse |
htv • hearing loss • tinnitus • vertigo |
|
|
medical management for Meniere's dse |
Habituation Exercises (Motion Sensitivity): HEP |
|
|
explain Meniere's dse (any idea about the dse/ how can u differentiate it with other vestib dse) |
d/o of the inner ear marked by an INCREASED ENDOLYMPHATIC FLUID in the ear membranes results to > LOW FREQUENCY HEARING LOSS (due to inc. fluid P° & decrease hair cell mov't), VERTIGO, TINNITUS (auditory afferent nerves fire due to inc. P°) |
|
|
tell if it's PERIPHERAL Vestibular d/o or CENTRAL Vestibular d/o: •with heating loss |
Peripheral |
|
|
tell if it's PERIPHERAL Vestibular d/o or CENTRAL Vestibular d/o:• severe ataxia |
Central |
|
|
tell if it's PERIPHERAL Vestibular d/o or CENTRAL Vestibular d/o:• no hearing loss |
Central |
|
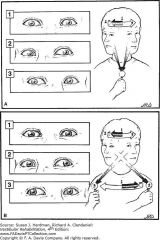
this management is called what? |
Gaze Stability/Stabilization Exercise |
|
|
tell if it's PERIPHERAL Vestibular d/o or CENTRAL Vestibular d/o:• Pendulum Nystagmus |
C |
|
|
tell if it's PERIPHERAL Vestibular d/o or CENTRAL Vestibular d/o:• Nystagmus occuring matagal na~ |
P |
|
|
tell if it's PERIPHERAL Vestibular d/o or CENTRAL Vestibular d/o:• + Ocular Tilt Reaction |
C |
|
|
Pseudoexacerbation that lasts for <24hrs & triggered by exposure to heat in Multiple Sclerosis |
Uthoff's Phenomenon |
|
|
aka Epley's Manuever |
Canalith Repositioning Maneuver |
|
|
BPPV due to canalithiasis |
Canalith Repositioning Manuever |
|
|
how to test for Dix-Hallpike Manuever? |
pt is sitting & passively ROT 45°, head is maintained & quickly moved to supine c cervical E 30° |
|
|
BPPV due to cupulolithiasis |
Liberatory/ Semont Manuever |
|
|
what is Cervicogenic Dizziness (any idea...) |
presence of dizziness, imbalance or unsteadiness related to the mov'ts or position of the CERVICAL SPINE or occuring with a STIFF or PAINFUL NECK |
|
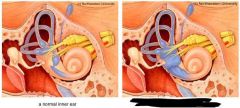
pic on right is what vestibular dse? |
Meniere's Dse |
|
|
tx for both cupulolithiasis & canalithiasis |
Brandt-Daroff Exercise |
|
|
Golden Standard for Vestibulat Schwannoma |
Gadolinium-enhanced MRI |
|
|
explain Perilympgatic Fistula |
occurs due to a rupture of the oval & round windows that result to leakage of Perilymph from inner ear to the middle ear |
|
|
Clinical Manifestation in Vestibular Schwannoma are the ff except: a. Emesis b. Tic Douloureux c Bell's Palsy d. Tinnitus e. hearing loss |
A. |
|
|
Tic Douloureux is~? |
Facial Hyperesthesia (CN5: Maxillary Division affectation; also seen in Herpes Zoster) |
|
|
all are true in Multiple System Atrophy except: a. increase in Alpha-synuclein protein b. it is a progressive degenarative dse of the NS c 4 clinical domains: Autonomic dysfx, Parkinsonism dse-lime Sxs, Cerebellar ataxia & Corticospinal Dysfx c. Hallmark of MSA is Gliosis>Papp-Lantos bodies/scars d. MSA c predominat parkinsonism includes Striagnigral Degeneration e. None of the above |
e |
|
|
tell if it's Palleocrebellum, Archicerebellum or Neocerebellum: • fx Spinocerebellum (trunk) |
Paleocrebellum |
|
|
tell if it's Palleocrebellum, Archicerebellum or Neocerebellum:• Clinical findings is balance problems |
Archicerebellum |
|
|
tell if it's Palleocrebellum, Archicerebellum or Neocerebellum:• Anatomic is located in Floculonodular |
Archicerebellum |
|
|
tell if it's Palleocrebellum, Archicerebellum or Neocerebellum:• Sx is Nystagmus |
Arc |
|
|
tell if it's Palleocrebellum, Archicerebellum or Neocerebellum:• Anatomic structure located in Posterior lobe |
Neo |
|
|
tell if it's Palleocrebellum, Archicerebellum or Neocerebellum:• Sx is Hypotonia / Ataxia |
Paleo |
|
|
tell if it's Palleocrebellum, Archicerebellum or Neocerebellum:• Sx is Dysmetria |
Neo |
|
|
tell if it's Palleocrebellum, Archicerebellum or Neocerebellum:• fx in fine mov't & coordination |
Neo |
|
|
It forwards efferent signal to ciliary ganglion of both sides for direct and consensual light responses |
Edinger–Westphal nucleus |
|
|
is the parasympathetic pre-ganglionic nucleus that innervates the iris sphincter muscle and the ciliary muscle. |
Edinger–Westphal nucleus |
|
|
What component of the macula causes the membrane to shift? |
Otoconia (calcium carbonate crystals) |
|
|
Explain how Otoliths work? |
Change in head position --> Force of gravity causes displacement of otoconia --> Hair cells bend. Stimulation = depolarization. Inhibiting = hyperpolarization. |

