![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
41 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Self Esteem (SE) |
-our sense of self made it comparison to those around us -a state; can change over time |
|
|
High SE |
-satisfied with self -feel you have good qualities -able to do things as well as most other people -positive attitude |
|
|
Low SE |
-don't feel good -have nothing to be proud of -useless -failure |
|
|
Individualist self |
-define themselves with personal traits -priority to own goals -who am i? smart, funny, outgoing -centre of universe; I am separate from my parents, siblings, etc. |
|
|
Collectivist self |
-define themselves in terms of relationship with other people -priority to group goals -who am i? a daughter, Japenese -overlap with relationships |
|
|
3 pieces of evidence for individualist self |
1. most people have high SE 2. most people engage in cognitive biases to enhance/maintain SE 3. most people do whatever it takes to maintain their positive SE |
|
|
1. most people have high SE -what are correlation between SE and success? |
-small correlations between SE and actual success, LARGE correlations between SE and self-perceived success -even larger correlations between SE and self-perceived success on SE-relevant tasks (for me, hockey) |
|
|
-what bias does this show? -when is this bias not true? |
-shows people use their own perceptions of how they're doing for SE, rather than reality -COGNITIVE BIAS --> i.e see ourselves more successful than we really are -don't have this bias when depressed -depressed = no SE |
|
|
2. Cognitive biases -what are these for? -what a 6 cognitive biases? |
-to enhance + maintain our SE -Encoding/RecallBiases -Definitional Biases -Self-Serving Attributional Bias (SSAB) -Unrealistically positive self-views (“Positivity Bias”) -Unrealistic Optimism -Illusory Control over good events |
|
|
encoding/recall bias? |
ex: encode all the times you did well driving, instead of all thebad things if you have a high self-esteem |
|
|
definitional bias? |
ex: helpfulness for your self-esteem. Could be defined as: I’ll holdthe door if I’m not in a hurry (make your self esteem higher); someone elsecould have a different definition of helpfulness |
|
|
Self-Serving Attributional Bias (SSAB)? |
tendency to take credit for things you do well, and blameothers for the bad stuff (goes well, im awesome, goes bad, world is unfair) -Internal attributions for success (I’m the best) -External attributions for failures (it was unfair) |
|
|
Unrealistically positive self-views? (positive bias) |
Ex: self-ratings on subjective traits -You are short, cant change that -Unrealistically self-positive self-view; idea I am better than I canpossibly be |
|
|
Unrealistic Optimism |
-You don’t think bad things can happen to you; you are wonderful, andbad things don’t happen to good people -Ex: beliefs about likelihood of cancer, divorcing, doing well inschool |
|
|
Illusionary Control |
-I can control things -We think we have control over events that we don’t have controlover; interpreted as “we are so wonderful we have this mystical power to takeover the world” -Gambling: people bet more if they are rolling the dice than ifsomeone else is rolling the dice |
|
|
Langery lottery ticket Experiment (purpose, methods (IV, DV), Results, Conclusion) |
Purpose: Test Illusionary control Methods: Ss picked or were given lottery ticket, exp. needed to but them back -IV: choice (you were able to select vs. just given to you) -DV: Ss's Sell-back price (experimenter needs them back; asks to buy themback for whatever price) -Results: Those who did not choose the ticket asked for lower price, those whopicked their own asked for sig. higher price Conc: when choose ticket, feel like you are in control of situation; when you did not choose it you do not have control |
|
|
3. Doing whatever it takes to maintain SE -who do people associate with? why? |
-associate with winners, dissociate from losers -"basking in reflected glory" --> association with successful people boosts SE |
|
|
Does Association always boost SE? |
-no -Associate with people whose successes help our SE (Basking) -Dissociate from people whose failureshurt our SE |
|
|
Cialdini'as football study (purpose, methods (IV, DV)) |
-predict association vs. disassociation -given trivia test about their school IV: SE---> false feedback on trivia test(success, failure, no feedback control) DV: % Ss using “we” whendescribing football wins and losses (proportion that says we vs. they) |
|
|
Cialdini'as football study (results, conclusion) |
Results: success: % we same for wins/loss (already high SE, don't need to ass. or dis.) control: % we sig. higher for wins than loses -dissociation from school to protect SE failure: % we even more sig. higher for wins, sig lower for losses -associate w/ school to boost SE, dissociate to protect SE Conclusions: -associating with winning boosts SE -disassociating from losing protects SE -used team performance to boost SE in time of need -if team fails, be a jerk and push them away -over-association does not last but protects SE |
|
|
downwards vs. upwards social comparisons? what type of distinctiveness is associated with these comparisons? |
Downward social comparison: Joy outperforming afriend/sibling; = Positive distinctiveness Upward social comparison: comparing ourselves to others who are better than we are = negativedistinctiveness |
|
|
Tesser's Two Factor SE Maintenance Model -when do we bask? -when do we compare? |
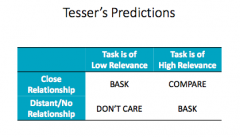
-do this to protect SE; can be jerks -ex: When you're forced into makingan upwards comparison, it is painful, deal with that pain by lashing out à where friendships are at risks |
|
|
whatever it takes con't -self handicapping? |
-sometimes we hurt ourselves to preserve our SE -you do something that willcause your likelihood of success in a task to go down --> prevents you from doing your best --> fear of failure -instead of trying your hardestthen failing, you have this handicap, can’t do your best and fail, protects your SE |
|
|
research supporting self-handicapping? |
-Ss take a test, take adrug -One boosts cognitiveperformance, one harms cognitive performance -IV: test difficulty (easy vs.hard) -DV: % choosing disruptive drug for next test -Everyone got false feedbackthey did well -Some wrote hard test, didreally well but wouldn’t do again, some wrote easy test, rdid really well,could do it again -Results: After writing the hard test,more likely to take disruptive drug the second test (when they thought theycouldn’t repeat their performance) -Difference pronounced more thanmen than women -conc: by choosing the disruptive drug for the second test, if they do poorly, they can blame it on the drug |
|
|
Textbook stuff - see notes for exp. what is autonomic thinking? |
nonconscious, unintentional,involuntary and effortless |
|
|
what are schemas? |
-mental structures that people use to organizetheir knowledge about the social world -they help us organize and make sense of the wordand fill in the gaps of our knowledge. Important when we encounter info that isconfusing/ambiguous |
|
|
priming? |
process by which recentexperiences increase the accessibility of a schema, trait or concept. Makes itmore likely that you will use this new info to interpret and event. This canhappen outside of conscious awareness |
|
|
Sult fulfilling prophecy? (making our schemas come true) |
people have a perception about what anotherperson is like which influences how they act towards the person which in turncauses the person to behave consistently with their expectations |
|
|
Judgemental, availability and representativeness heuristics? |
Judgmental heuristics = mentalshortcuts people use to make judgments quickly and efficiently Availability Heuristic: peoplebase a judgment on the ease which they can bring something to mind Representativeness Heuristic =people classify something according to how similar it is to a typical case |
|
|
Controlled social cognition |
Thinking that is conscious,intentional, voluntary and effortful |
|
|
Counterfactual Reasoning |
Mentally changing some aspectof the past as a way of imagining what might have been -Most likely to engage in this when we have justmissed avoiding a negative event -sympathy in near miss situations |
|
|
Thought Suppression |
attempt to avoid thinking about something aperson would prefer to forget |
|
|
monitering vs. operating process |
Monitoring process – searches forthe evidence that the unwanted thought is about to intrude the conscious Operating process = effortfulattempt to distract oneself by finding something else to think about |
|
|
self |
comprised of ones thoughts and beliefs aboutones self (known) and the active processor of information (knower). |
|
|
self concept vs self awareness |
-Self-Concept = the contents ofthe self, the knowledge of who we are -Self-Awareness = act of thinkingabout ourselves |
|
|
self-reference effect |
tendency for people to remember informationbetter if it relates to themselves |
|
|
introspection |
the process whereby people look inward andexamine their own feelings, thoughts and motives |
|
|
self-awareness theory |
· Idea that when people focustheir attention on themselves, they evaluate and compare their behavior withtheir internal standards and values |
|
|
Self-Perception Theory |
when our attitudes and feelingsare uncertain or ambiguous, we infer these states by observing our behavior andthe situation in which it occurs |
|
|
Social comparison theory |
we learn about our own attitudes and abilitiesby comparing ourselves with others. Especially when there is no objective standard revised: When we focus on our usualself, exposure to outstanding others inspires us to generate high hopes howeverwhen focusing on ideal self it is discouraging to see others surpass us |
|
|
self- verification |
People have a need to seekconfirmation that their self-concept (positive or negative) |

