![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
17 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Plague – Disease Presentations
Bubonic plague - tender swollen LN “bubo” 50% mortality (untreated) Septicemic plague - like GNR sepsis Pneumonic plague - 2-3 days with fever, cough with blood tinged sputum 100% mortality!!!!! Plague meningitis Pharyngeal plague Cutaneous plague - erythematous, eroded, crusting necrotic lesions |
Plague – Disease Presentations
Bubonic plague - tender swollen LN “bubo” 50% mortality (untreated) Septicemic plague - like GNR sepsis Pneumonic plague - 2-3 days with fever, cough with blood tinged sputum 100% mortality Plague meningitis Pharyngeal plague Cutaneous plague - erythematous, eroded, crusting necrotic lesions |
|
|
Y. pestis – Origins and Pathogenicity
Member of a 10-species genus 3 species pathogenic to mammals Yersinia common ancestor arose 42 to 187 million years ago. Y. pseudotuberculosis and Y. enterocolitica - 0.4 to 1.9 M years Clonal to Y. _______________ >90% chromosomal relatedness MLST – high degree of conserved sequence Y. pestis diverged between 1,500 and 20,000 years ago. Three biovars Antiqua; Mediavalis; Orientalis High level of pathogenicity >130 insertion sequences >145 pseudogenes Acquisition of virulence plasmids |
Y. pestis – Origins and Pathogenicity
Member of a 10-species genus 3 species pathogenic to mammals Yersinia common ancestor arose 42 to 187 million years ago. Y. pseudotuberculosis and Y. enterocolitica - 0.4 to 1.9 M years Clonal to Y. pseudotuberculosis >90% chromosomal relatedness MLST – high degree of conserved sequence Y. pestis diverged between 1,500 and 20,000 years ago. Three biovars Antiqua; Mediavalis; Orientalis High level of pathogenicity >130 insertion sequences >145 pseudogenes Acquisition of virulence plasmids |
|
|
Y. Pestis Virulence Factors
Plasmids: Chromosome: pFra - 100 kb pH 6.0 antigen __ capsular antigen Caf1A, Caf1M hms gene products Mouse toxin Others (?) Others (?) pLcr - 70 kb Yersinia Outer Proteins (Yops) Accessory gene products of the TTSS pPst - 9kb Plasminogen Activator (Pla) |
Y. Pestis Virulence Factors
Plasmids: Chromosome: pFra - 100 kb pH 6.0 antigen F1 capsular antigen Caf1A, Caf1M hms gene products Mouse toxin Others (?) Others (?) pLcr - 70 kb Yersinia Outer Proteins (Yops) Accessory gene products of the TTSS pPst - 9kb Plasminogen Activator (Pla) |
|
|
pFra
“Big” virulence plasmid unique to _____ (pMT1) Encodes ___________-regulated caf1 gene products __ capsular antigen subunit; chaperone; _____ protein Encodes the “murine toxin” Sequence characteristics: “mosaic” - multiple transpositions 56% homology with pHCM2 of Salmonella typhi >50 uncharacterized ORFs |
pFra
“Big” virulence plasmid unique to pestis (pMT1) Encodes temperature-regulated caf1 gene products F1 capsular antigen subunit; chaperone; anchor protein Encodes the “murine toxin” Sequence characteristics: “mosaic” - multiple transpositions 56% homology with pHCM2 of Salmonella typhi >50 uncharacterized ORFs |
|
|
Y. Pestis Capsule
Fraction 1 (F1) capsular antigen 15.5 kDa “sub-unit” protein from ____ gene Forms a large ___-like capsule on the cell surface Anti-phagocytic properties Encoded from a _________-regulated operon Cloned, expressed, and secreted in E. coli |
Y. Pestis Capsule
Fraction 1 (F1) capsular antigen 15.5 kDa “sub-unit” protein from caf1 gene Forms a large gel-like capsule on the cell surface Anti-phagocytic properties Encoded from a temperature-regulated operon Cloned, expressed, and secreted in E. coli |
|
|
Contribution of F1 to Protective Immunity
Expressed by almost all of Y. pestis isolates. Actively synthesized in vitro and in vivo. Burrows and Bacon, 1956; Lawton, et al., 1960; Meyer, et al., 1974 Crude preparations “immunogenic and protective”. Baker, et al., 1952; Burrows and Bacon, 1956 Early reports of a cell-free fraction in vitro. 30-50% of total F1 during stationary phase *****Dr. G’s study: Compare highly purified F1 from Y. pestis and E. coli in the outbred mouse model for protection ag. bubonic and pneumonic plague. Challenge strain: Y. pestis CO92 sc LD50 = 2 aerosol LD50 = 20,000 |
Contribution of F1 to Protective Immunity
Expressed by almost all of Y. pestis isolates. Actively synthesized in vitro and in vivo. Burrows and Bacon, 1956; Lawton, et al., 1960; Meyer, et al., 1974 Crude preparations “immunogenic and protective”. Baker, et al., 1952; Burrows and Bacon, 1956 Early reports of a cell-free fraction in vitro. 30-50% of total F1 during stationary phase Dr. G’s study: Compare highly purified F1 from Y. pestis and E. coli in the outbred mouse model for protection ag. bubonic and pneumonic plague. Challenge strain: Y. pestis CO92 sc LD50 = 2 aerosol LD50 = 20,000 |
|
|
Therapeutics for Plague
Treatment --------------- aggressive! : - Streptomycin 30mg/kg/day IM in 2 divided doses for 10 days - Doxycycline 200mg IV then 100mg IV BID for 10-14 days - Chloramphenicol 1gm IV QID x 10-14D Note: __________ is indicated for pneumonic plague. |
Therapeutics for Plague
Treatment --------------- aggressive! : - Streptomycin 30mg/kg/day IM in 2 divided doses for 10 days - Doxycycline 200mg IV then 100mg IV BID for 10-14 days - Chloramphenicol 1gm IV QID x 10-14D Note: Gentamicin is indicated for pneumonic plague. |
|
|
Plague Vaccines
“EV-type” Live-attenuated vaccine – Russia Highly reactogenic in humans Kills monkeys “Plague Vaccine USP” – Greer Laboratories Formalin-inactivated whole cell preparation 1.0 ml at time 0, 0.2 ml at 1-3 months 0.2 ml 3-6 months later Booster 0.2 ml q 6 months x 3 then q 1-2 years Not produced since 1999! “CSL” – Australia********** Heat-killed whole cell preparation In current use, but NOT licensed in U.S. |
Plague Vaccines
“EV-type” Live-attenuated vaccine – Russia Highly reactogenic in humans Kills monkeys “Plague Vaccine USP” – Greer Laboratories Formalin-inactivated whole cell preparation 1.0 ml at time 0, 0.2 ml at 1-3 months 0.2 ml 3-6 months later Booster 0.2 ml q 6 months x 3 then q 1-2 years Not produced since 1999! “CSL” – Australia Heat-killed whole cell preparation In current use, but NOT licensed in U.S. |
|
|
Bacillus spp.
Aerobic rods (may form filaments). > 20 species. Spore-forming. Most species saprophytic. Some motile Non- hemolytic to beta-hemolytic Exotoxin producers |
Bacillus spp.
Aerobic rods (may form filaments). > 20 species. Spore-forming. Most species saprophytic. Some motile Non- hemolytic to beta-hemolytic Exotoxin producers |
|
|
Disease Presentations
Cutaneous most common form - 95% of all cases 20% mortality, untreated Inhalation 100% mortality, untreated Gastrointestinal rare mortality ? |
Disease Presentations
Cutaneous most common form - 95% of all cases 20% mortality, untreated Inhalation 100% mortality, untreated Gastrointestinal rare mortality ? |
|
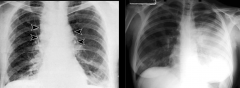
Pulmonary Anthrax vs Pneumonic Plague
|
Pulmonary Anthrax vs Pneumonic Plague
|
|
|
More on Inhalational Anthrax
Incubation period highly variable (up to 60 days). Early stages present as a “flu-like” non-specific illness. Mortality < 50% with treatment - lower than previously thought. Is this disease communicable or not? ** |
More on Inhalational Anthrax
Incubation period highly variable (up to 60 days). Early stages present as a “flu-like” non-specific illness. Mortality < 50% with treatment - lower than previously thought. Not a communicable disease. |
|
|
Bacillus anthracis
Gram: Spore forming? Two virulence plasmids: pXO1 encodes two toxins: _____ toxin (ET) and ____ toxin (LT) pXO2 encodes a ______ that has anti-phagocytic properties |
Bacillus anthracis
Gram-positive, spore-forming rod Two virulence plasmids: pXO1 encodes two toxins: Edema toxin (ET) and lethal toxin (LT) pXO2 encodes a capsule that has anti-phagocytic properties |
|
|
Edema Factor has what type of activity?
Lethal factor? |
EF= Adenylate Cyclase
LF = metalloprotease |
|
|
Virulence Determinants – cont.
Capsule Required for full virulence (Sterne strain is pXO2-) Poly-d-glutamic acid Not __________ by itself Other molecules Spore coat proteins Hemolysins Fimbriae (?) |
Virulence Determinants – cont.
Capsule Required for full virulence (Sterne strain is pXO2-) Poly-a-glutamic acid Not immunogenic by itself Other molecules Spore coat proteins Hemolysins Fimbriae (?) |
|
|
Protection Against Anthrax
Post-exposure Prophylaxsis Ciprofloxacin/Levofloxicin Doxycycline Vaccination AVA: “Anthrax Vaccine Adsorbed” Manufactured by Bioport, Lansing, MI B. anthracis, uses this strain ________ culture supernatant Alhydrogel “precipitate” Highly variable amounts of PA, low levels of LF (and EF?) Other secreted proteins? Six doses across 18 months |
Protection Against Anthrax
Post-exposure Prophylaxsis Ciprofloxacin/Levofloxicin Doxycycline Vaccination AVA: “Anthrax Vaccine Adsorbed” Manufactured by Bioport, Lansing, MI B. anthracis, Sterne, culture supernatant Alhydrogel “precipitate” Highly variable amounts of PA, low levels of LF (and EF?) Other secreted proteins? Six doses across 18 months |
|
|
Protection Against Anthrax – cont.
Recombinant Protective Antigen (rPA) Purified from culture supernatants B. anthracis and/or E. coli Formulated with Alhydrogel High level protection in immunized rabbits and non-human primates against inhalation anthrax. 2 vaccine doses used in animal models 3 doses proposed in humans |
Protection Against Anthrax – cont.
Recombinant Protective Antigen (rPA) Purified from culture supernatants B. anthracis and/or E. coli Formulated with Alhydrogel High level protection in immunized rabbits and non-human primates against inhalation anthrax. 2 vaccine doses used in animal models 3 doses proposed in humans |

