![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
127 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
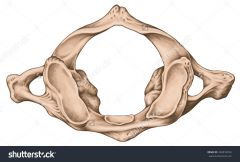
|
Cervical Vertebra - Atlas |
|
|
Synovial Joint |
Highly moveable, hinge, ball and socket joint |
|
|
Cartilaginous Joint |
Not as moveable, disc between bones like in the spinal column |
|
|
Fibrous Joint |
In cranium, more squiggly lines, least moveable of any joint |
|
|
Vertebral canal |
The space in the vertebral column where the spinal cord passes |
|
|
Spinous Process |
a bony projection off the posterior (back) of each vertebra |
|

|
Transverse process - a small bony projection off the right and left side of each vertebrae |
|
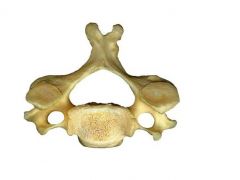
|
Cervical vertebra - Axis |
|
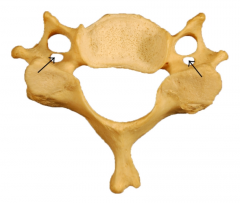
|
Transverse foramen - hole for the coratid artery |
|
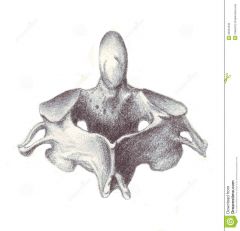
|
Cervical Vertebra - Axis - Dens |
|
|
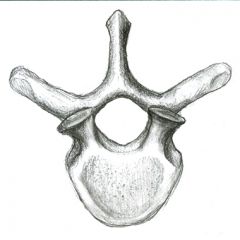
Thoracic Vertebra |
|
|
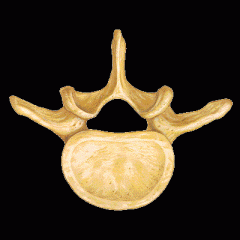
Lumbar Vertebra |
|
|
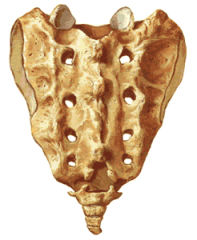
Sacral Vertebra |
|
|
Sacral Alae |
At the top of the sacrum there are wings from each side called the sacral ala. At theala , the sacrum fits between the two halves of the pelvis. |
|
|
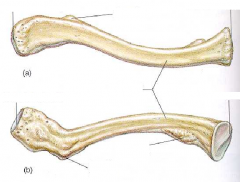
Right Clavicle |
|

|
Sternum (Costal Notches, Manubrium, Body, Xiphoid Process) |
|
|
True Rib |
a rib that is attached directly to the breastbone |
|
|
False Rib |
The 8th, 9th, and 10th pairs— false ribs—do not join the sternum directly but are connected to the 7th rib by cartilage. |
|
|
Floating Rib |
The phrase floating rib refers to the two lowermost, the eleventh and twelfth, rib pairs; so-called because they are attached only to the vertebrae–and not to the sternum or cartilage of the sternum. |
|
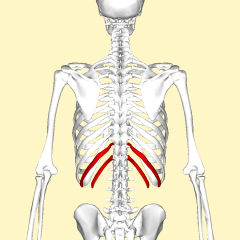
|
Floating Ribs |
|
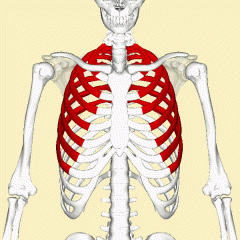
|
True Ribs |
|
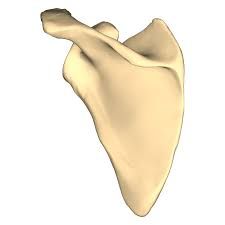
|
Left Scapula |
|
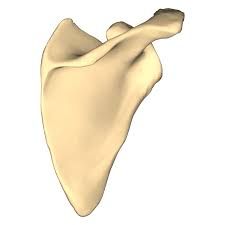
|
Right Scapula |
|
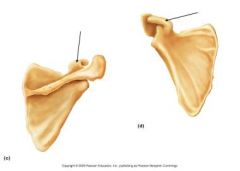
|
Corocoid Process |
|
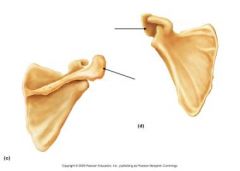
|
Acromion Process |
|

|
Right Humerus |
|

|
Left humerus |
|
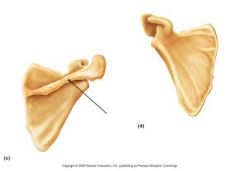
|
Scapular Spine |
|
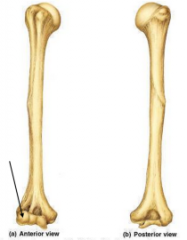
|
Capitulum |
|
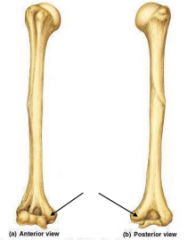
|
Medial Epicondyle |
|
|
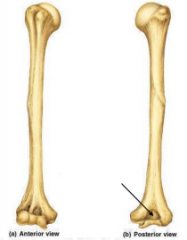
Olecranon Fossa |
|
|
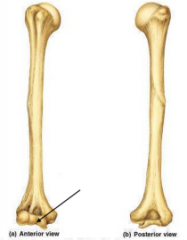
Trochlea |
|

|
Olecranon Process |
|
|
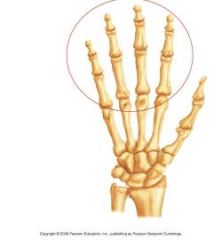
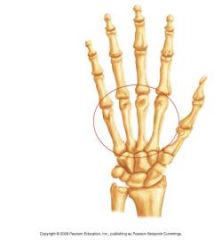
Phalanges |
|
|
Metacarpals |
|
|
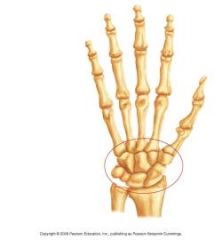
Carpals |
|
|
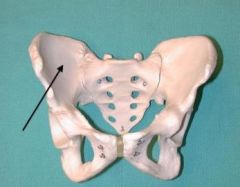
Illium |
|
|
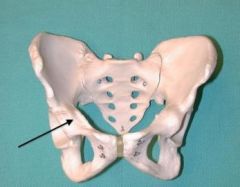
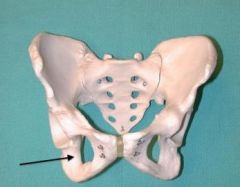
Pubic Bone |
|
|
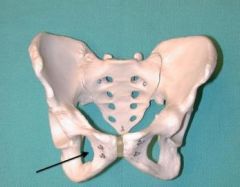
Ischium |
|
|
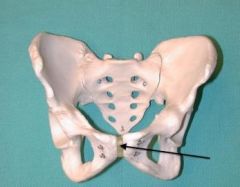
Obturator Foramen |
|
|
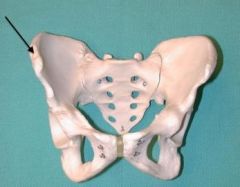
Pubic Symphasis |
|
|
Iliac Crest |
|
|
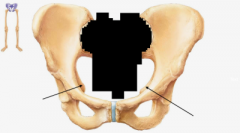
Acetabulum |
|
|
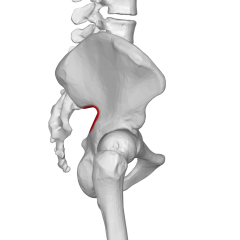
Greater Sciatic Notch |
|
|
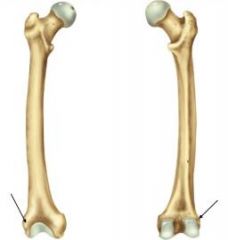
Lateral Epicondyle |
|
|
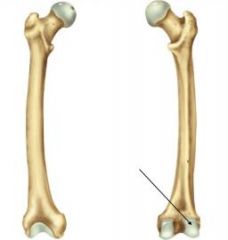
Lateral Condyle |
|

|
Styloid Process of Radius |
|
|
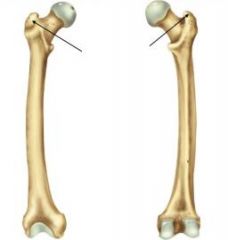
Greater Trochanter |
|

|
Lesser Trochanter |
|
|
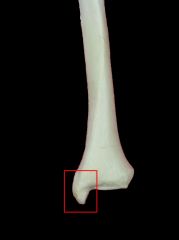
Medial Malleoulus Tibia |
|
|
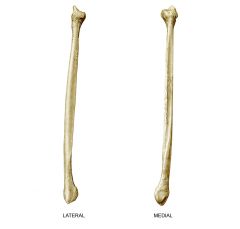
Styloid Process of Fibula |
|
|
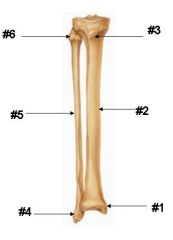
#4 - Lateral Malleolus Fibula |
|
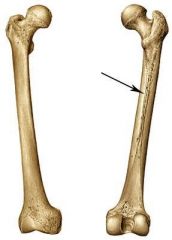
|
Linea Aspira |
|
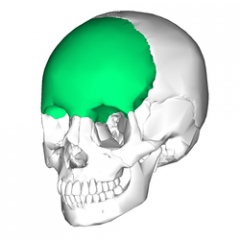
|
Frontal Bone |
|
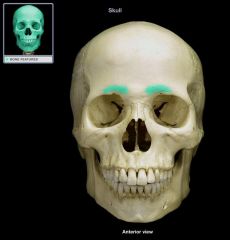
|
Supercilliary Arch |
|
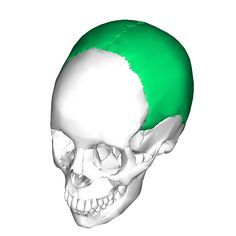
|
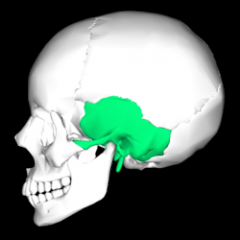
Parietal Bone |
|
|
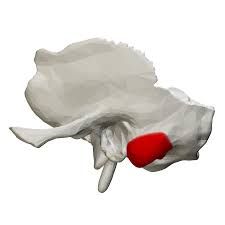
Temporal Bone |
|
|
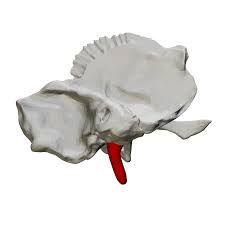
Mastoid Process Temporal Bone |
|
|
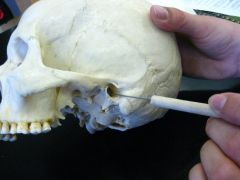
Styloid Process Temporal Bone |
|
|
External auditory meatus - Temporal Bone |
|
|
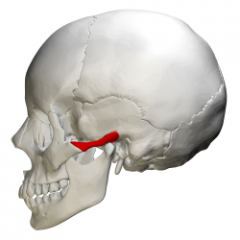
Zygomatic process - temporal bone |
|
|
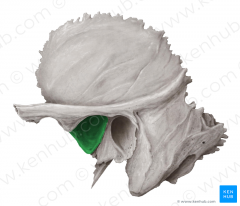
Medibular fossa - temporal bone |
|
|
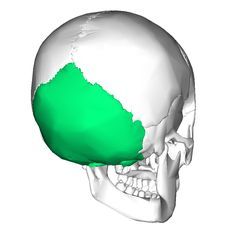
Occipital Bone |
|
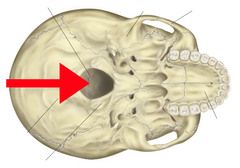
|
Foramen magnum - Occipital Bone |
|
|
External occipital protuberance |
|

|
Occipital Condyles |
|
|
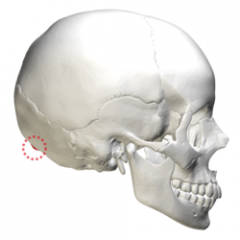
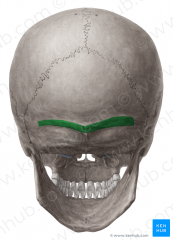
Superior Nuchal Line |
|
|
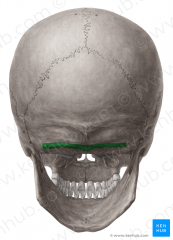
Inferior Nuchal Line |
|
|
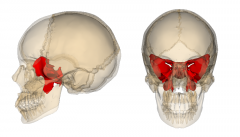
Sphenoid Bone |
|
|
Sphenoid Bone |
|
|
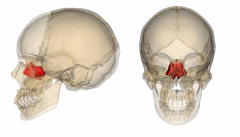
Ethmoid Bone |
|

|
Ethmoid Bone |
|
|
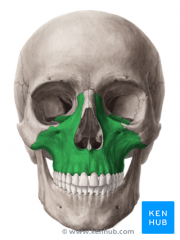
Maxilla |
|
|
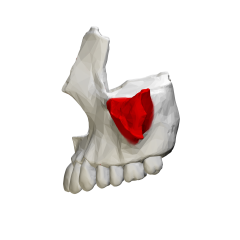
Zygomatic Process of the maxilla |
|
|
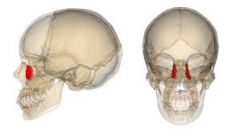
Lacrimal Bone |
|
|
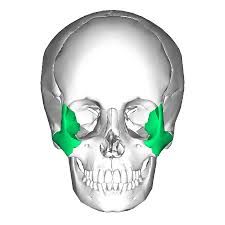
Zygomatic Bone |
|
|
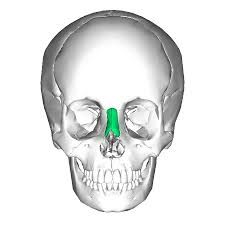
Nasal bone |
|
|
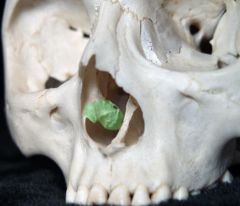
Inferior Nasal Concha |
|
|
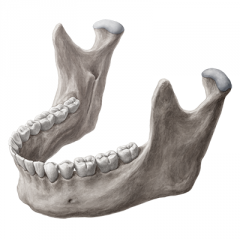
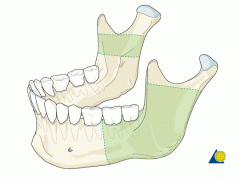
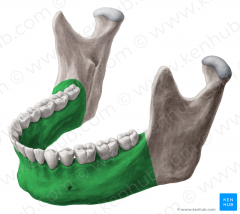
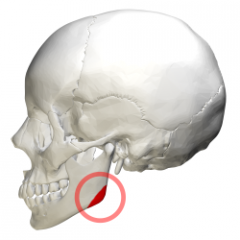
Mandible |
|
|
Ascending Ramus |
|
|
Body of Mandible |
|
|
Gonial angle |
|
|
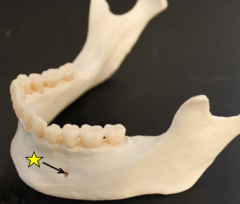
Mental Foramen Mandible |
|
|
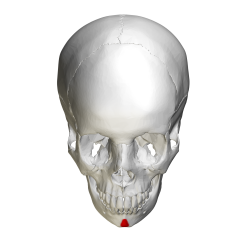
Mental Eminence Mandible |
|
|
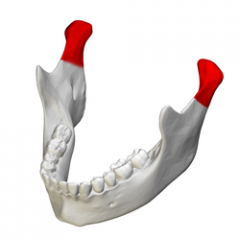
Mandibular Condyles |
|
|
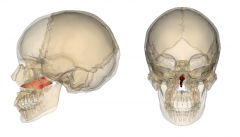
Vomer |
|
|
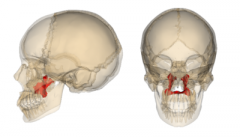
Palatine Bone |
|
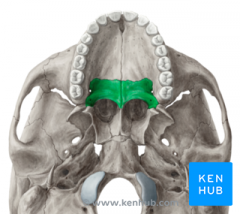
|
Palatine Bone |
|
|
What are the bones of the inner ear? |
Paired: - Malleus - Incus - Stapes |
|

|
Saggital Suture - between the two parietal bones |
|
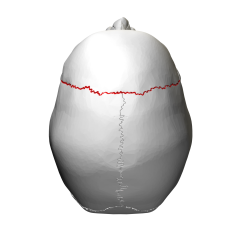
|
Coronal Suture - separating the frontal bone from the parietal bones |
|
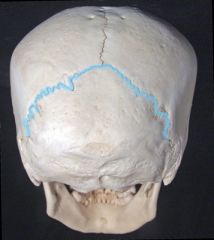
|
Lambdoidal suture - on the posterior aspect of the skull that connects the parietal bones with the occipital bone |
|
|
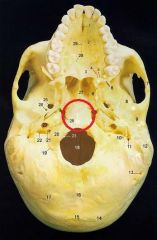
Basilar suture - The suture between the occipital bone and sphenoid bone |
|
|
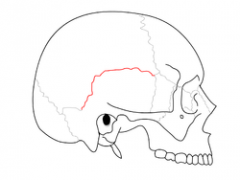
Squamosal suture - is a simple joint that unites the parietal and temporal bones of the skull |
|
|
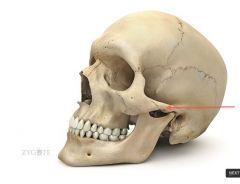
Zygomatic Arch |
|
|
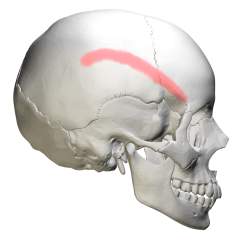
Temporal Line |
|
|
Hyoid Bone |
|

|
Sternal Manubrium |
|
|
Sternal Coastal Facets |
|
|
Humerus Medial Epicondyle |
|
|
What is the dental formula for adult humans? |
2:1:2:3 |
|
|
What is the dental formula for children 2-6? |
2:1:0:2 |
|
|
Occlusal Surface of a Tooth |
the surface of a tooth that occludes with or contacts an opposing surface of a tooth in the opposing jaw; |
|
|
The glenoid fossa of the scapula articulates with what bone? |
Humerus |
|
|
What is the medial bone of of the lower half of the leg? |
Tibia |
|
|
What is the process at the most proximal end of the ulna? |
Olecranon process |
|
|
What morphological features make a cervical vertebra unlike other vertebra |
Transverse foramen + spinous processes |
|
|
What morphological features make a thoracic vertebra unlike other vertebra |
They have facets for articulation of the ribs called coastal pits |
|
|
What is the name of the most inferior segment of the sternum |
xiphoid process |
|
|
What are the three bones of the os coxa? |
Illium, ischium, pubis |
|
|
What structure of the coxa articulates with the femur? |
Acetabelum |
|
|
What feature of the humerus articulates with the head of the radius |
Capitulum |
|
|
The proximal end of the clavicle articulates with what bone? |
sternum |
|
|
What is diapysis |
Shaft of a long bone |
|
|
What is epipyses |
End of the long bone. Growth center of the bone. |
|
|
How does pubic symphyseal face differ in an old or younger person? |
In a young person it's bumpier and rougher. As we age it gets smoother |
|
|
What is subpubic angle and how does it differ between males and females? |
Angle formed below pubic symphasis formed between inferior rami of the pubic bones. The angle is more than 90 degree in females and less than 90 degrees in males. |
|
|
How are pubic bones different in a male or a female? |
Bone is more triangular in a male and more rectangular than a female. Obturator foramen aare oval in male and more triangular in female. |
|
|
How is the cranium different in a male or a female? |
The supercilliary arches of the frontal bone are more pronounced in a male than a female. As is the mandibular fossa and other places muscle attaches (nuchal lines, etc.) |
|
|
How can you tell left from right radius? |
Ulnar notch is medial, styloid process is lateral when tuberosity is facing up |
|
|
How can you tell left from right ulna? |
The smooth notch articulates with the radius. It is located on the thumb side. |
|
|
What is the little dimple on the head of the femur called? |
Fovea Capitus |
|
|
How can you tell a left from right femur |
Linea aspire is posterior, see which direction the head is |
|
|
How can you tell a left from right Tibia |
Tuberosity should face up. Malleolus will be medial |
|
|
How can you tell left from right fibula? |
The teardrop points toward the heel - lateral malleolus. |
|
|
How do you tell a thoracic from a lumbar vertebra? |
The transverse processes on a lumbar form a 90 degree angle with the spine and the transverse processes on the thoracic form less than 90 degree angle. Lumbar looks like a moose. Thoracic looks like a giraffe. |
|
|
How to tell left from right rib |
Sharp side down. Flat end connects with sternum |

