![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
11 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Convulsions |
sudden transient brain dysfunction. It may occur with or without fever. |
|
|
Convulsions with fever |
1. febrile convulsions. 2.Acute meningitis (bacterial or viral) 3. cerebral malaria 4.viral encephalitis 5.Tubercular meningitis (TBM) 6. Brain abscess. |
|
|
Convulsions w/o fever |
1.Epilepsy 2.encephalopathy( hypertensive,hepatic,or uremic,hypoxic,ischemic), 3.trauma (head injury) 4.intracranial space occupying lesion 5. metabolic abnormalities (hypoglycemia,hypomagnesemia, hypocalcemia,hyponatremia and hypernatremia.) |
|
|
Febrile seizures occur at what age? and temp? |
6 mos to 6 yrs. temp is 100.4°F/38°C or higher. not related to CNS infection or metabolic disorders. |
|
|
Types of convulsions |
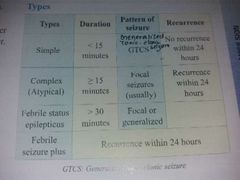
|
|
|
During investigation what do u rule out? |
Meningitis by CSF study. Also find out the fever cause. |
|
|
Leptomeninges means? |
inner meninges- arachnoid and the pia mater. |
|
|
what is pyogenic meningitis? |
inflammation of the leptomeninges due to invasion of pyogenic (pus causing) bacteria. |
|
|
Organisms which cause pyogenic meningitis. |
For neonates- E.coli, Grp B streptococci, listeria monocytogenes Beyond neonates- h. influenzae,S.pneumoniae, N.meningitides. |
|
|
Complication of pyogenic meningitis |
*Superficial cerebritis as it extends to the cerebrum. Can also affect deeper brain structures too. * vasculitis *vascular thrombosis *cerebral edema *cerebral infarction *Raised ICP *Impaired CSF flow |
|
|
Clinical manifestations in older children and neonates. |

|

