![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
28 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Ct findings in ABPA
|
Central bronchiectasis
|
|
|
Anterior mediastinum
|
Sternum to pericardium
Lymphomas Thymomas |
|
|
Middle mediastinum
|
Pericardium to 1 cm from vert bodies
Foregut duplication cysts: bronchogenic, esophageal duplication, neuroenteric |
|
|
Posterior mediastinum
|
1 cm from vert bodies to vert bodies
34% of mediastinal masses Includes esophagus Neurogenic Sympathetic chain ganglion: neuron lasting, ganglioneuroblastoma, ganglioneuroma |
|
|
Type 2 pneumocyte
|
Large size, micro villi on surface, lamellar bodies in cytoplasm
Secrete lamellar bodies into alveolar space and surfactant coats alveoli Also involved in lipid synthesis, clearance of alveolar fluid |
|
|
Type 1 pneumocyte
|
Flat cells that cover large area
Provide protective barrier and allow gas exchange |
|
|
Pores of kohn
|
Alveolar to alveolar connection
Dvp at 1-2 yrs |
|
|
Canals of lambert
|
Bronchioles to alveolus connection
Dvp at age 6 |
|
|
Why infants more likely to dvp pna, atelectasis or resp failure
|
Fewer alveoli
Less collateral ventilation Increased chest wall compliance to resist decreases in lung compliance Weaker cartilaginous support causing more dynamic collapse Increased airway resistance due to smaller airways |
|
|
Alveolar gas equation
|

|
|
|
What is zileuton
|
Leukotrien modifier
Inhibits 5-lipoxygenase path and prevents synthesis of cysteinyl leukotrienes and LTB4 Short duration of action Hepatotoxicity |
|
|
Cxr findings of PE
|
Wedge shaped pleural based opacification
|
|
|
Factors that increase fetal breathing mvts
|

|
|
|
Factors that decrease fetal breathing movements
|

|
|
|
Base excess
|
Amount of acid needed to correct 1l blood to ph 7.4 and pCO2 40
To estimate bicarbonate needed BE x ECF ECF= kg x 0.3 |
|

|

|
|
|
PHOX2b genotype/phenotyp
|
PARM- poly alanine repeat expansion genotypes ( 20/27 to 20/33) and non-pARM require mechanical vent 24 hrs/d
20/24, 20/25- less than 24 hours/d AD but most occur denovo |
|
|
Laplace's law
|

|
|
|
ASA toxicity
|
Tachypnea
Tachycardia Low pco2 but only slightly elevated pH Mixed resp alkalosis and metabolic acidosis |
|
|
Periodic breathing
|
3 or mor episodes of central episode >=3s sparTed by no more than 20 sec of nml rr
|
|
|
Relative risk
|

|
|
|
Compliance of respiratory system
|

|
|
|
Static compliance
|
sCL=compliance/lung volume
|
|
|
Who has not compliant lungs. Adults or children
|
Adults
Similar static compliance so use same pleural pressure but higher tidal volumes |
|
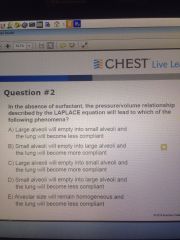
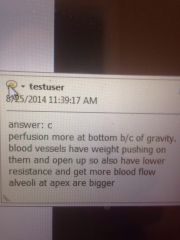
|
B
|
|

|
|
|
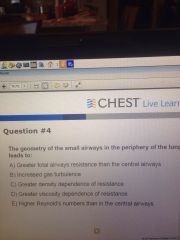
|
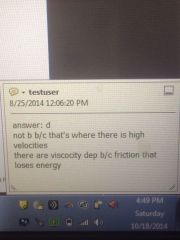
|
|
|
Resistance equation
|
r= change in p/flow
|

