![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
24 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back

Mudstones |
1. most abundant sedimentary rocks
2. pelites, lutites, argalliceous sed. rocks |
|
|
Siltstones
|
50% silt
|
|
|
Claytones
|
more than 50% clay
|
|
|
Mudstone
|
silt and clay
|
|
|
Shale
|
laminated or bedded mudstone
|
|
|
Texture
|
1. Silt generally more common than clay
2. Generally not rounded - Difficult to round quartz silt - Platy because of cleavage *Micas *Clay minerals |
|
|
Composition
|
1. Clay and mica minerals
2. Quartz 3. Feldspars 4. Identified by x-ray refraction (XRD) |
|
|
Clay minerals (Hydrous Aluminious silicates)
|
1. Kaolinite
2. Smectite 3. Chlorite 4. Illite |
|
|
Clay mineral building blocks: Tetrahedron
|
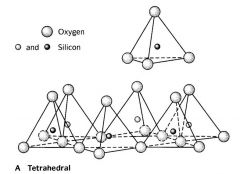
Silica tetrahedron in a layer structure
|
|
|
Clay mineral building blocks: Octahedron
|
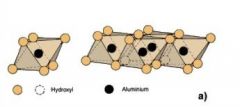
|
|
|
Kaolinite 1:1
|
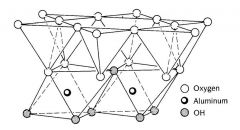
1. Non-expandable
2. No extra ions 3. Basal spacing 7 angstroms 4. No edge changes |
|
|
Smectite 2:1
|
1. Non-expandable
2. K 3. Basal spacing 10 angstroms |
|
|
Chlorite 2:1
|
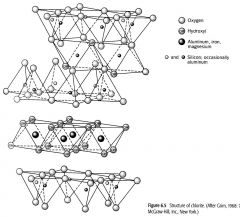
1. Non-expandable
2. Fe + Mg 3. Fe + Mg also in octahedral hydroxyl sheet 4. Basal spacing 14 angstroms |
|
|
Smectite
|
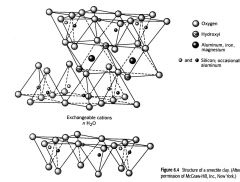
1. Very expanbable
2. lots of extra ions 3. Basal spacing basically 14 angstroms, but varies from 9-22. |
|
|
Provenance
|
Weathering of feldspars
|
|
|
Weathering of feldspars: Kaolinite
|
1. Expansive leaching of high alumina rocks
- Granite - Rhyolite - Gneiss 2. Low ph (not a lot of H) 3. Bauxite (from Cyanite/high aluminium rock |
|
|
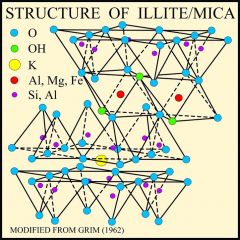
Weathering of Feldspars: Illite
|
intermediate leaching of K-rich rocks
|
|
|
Weathering of feldspars: Chlorite
|
1. Poor leaching of Fe- and Mg-rich rocks
2. High ph |
|
|
Weathering of feldspars: Smectite
|
1. Poor leaching of Ca-, Na-, Fe-, and Mg-rich rocks
2. High ph |
|
|
Diagenesis: Time
|
1. Paleozoic:
- Illite - Chlorite 2. Kaolinite - Mezosoic and Cenozoic 3. Smectite - Cenozoic (very important) |
|
|
Glauconite
|
1. Iron rich Chlorite (2:1)
2. Greensands |
|
|
Glauconite: Greensands
|
1. Shallow marine sandstones
- Agitated - Formed in a reducing environment - Deposited in oxidizing environment - 50-200 m in depth - Slow accumulation - Shallowing upward sequences and below uncomformities |
|
|
Bentonite
|
1. Smectite (2:1)
- "Weathered" glass shards from ash - Deposited in marine environment - Time lines - Not good for radiometric dating |
|
|
Black shales
|
1. Usually organic rick
2. Unoxidized - anaerobic 3. Euxenic 4. Pyrite common 5. Modern sample: Black Sea 6. No good modern analogue from Mesozoic and Paleozoic shales - Perhaps due to poor circulation and mixing due to more uniform temperature 7. Chattanooga (Devonian) and Fayetteville (Mississipian) shales |

