![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
28 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back

K-feldspar
|
Potassium feldspars are a group of polymorphs, polymorphs being minerals that have the same chemical composition but slightly different crystal structures
|
|

K-feldspar
|
When combined with water during hydrolysis it creates clay minerals (hydrous Al silicates)
|
|

Plagioclase feldspar
|
Plagioclase feldspars are a continuous mineral series in which calcium and sodium substitute for one another in the same crystal structure, dissociates with water in order to create acids in soils
|
|

Quartz
|
one of the most common minerals because it is chemically and physically stable at Earth’s surface conditions. It is a significant component of hydrothermal veins and felsic igneous rocks, and is often the dominant mineral in sandstones and siltstones,
|
|

Quartz
|
More resistant to weathering than the feldspar groups, also immobile.
|
|

Kaolinite
|
Al2Si2O5(OH)4
|
|

Pyrite
|
FeS2
|
|

Pyrite
|
Pyrite ---> Hematite
2Fe(+2)S2(-4) + O2 ---> Fe2(+3)O3(+2) + 2S(-4) |
|

Hematite
|
Fe2O3
|
|

Hematite
|
Branded Iron formations are proof of the difference between the reducing and oxidizing environments prior before and after The Great Oxidation Events
|
|
|
Magnetite
|

|
|

Calcite
|
Often found in limestone
|
|
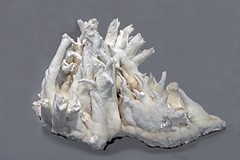
Aragonite
|
crystal lattice differs from that of calcite, resulting in a different crystal shape, an orthorhombic system with acicular crystals
|
|

Dolomite
|
The best way to tell one from the other is the acid test: a drop of 1 M HCl on calcite produces an instant, obvious fizz; a drop on dolomite produces slow or no obvious bubbling
|
|
|
Dolomite
|
CaMg(CO3)2, Magnesium makes it more resistant to HCl
|
|

Zircon
|
One of the most resistant minerals zircons can survive geologic processes like erosion, transport, even high-grade metamorphism, they contain a rich and varied record of geological processes. Radiometric dating of Uranium to Lead.
|
|

Plagioclase feldspar
|
will weather to form clay minerals, they are resistant enough that plagioclase grains forms a significant component of many detrital sediments and sedimentary rocks.
|
|
|
Halite
|

|
|
|
Barite
|

|
|
|
Orthoclase
|

|
|
|
Goethite
|

|
|
|
Limonite
|

|
|
|
Garnet
|

Garnet
|
|
|
Spharelite
|

|
|
|
Galena
|

|
|
|
Chlorite
|

|
|
|
Bauxite
|

|
|
|
Biotite
|

|

