![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
16 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
bone mass |
80% cortical, 20% cancellous cancellous has ten times the surface area. |
|
|
vertebral arches are composed of |
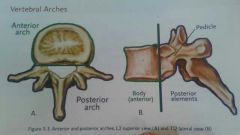
anterior and posterior arches |
|
|
anterior arch is composed of |
vertebral body and pedicles (anterior third) |
|
|
types of bone tissue |
1. cortical (hard, dense) 2. cancellous, trabecular (spongy, contains bone marrow, forms red blood and some white blood cells) |
|
|
posterior arches are composed of |
pedicles, laminar, processes |
|
|
vertebral foramen |
large enclosed space created by the anterior and posterior arches. forms the spinal canal and protects the spinal cord. |
|

|
|
|
|
cancellous bone is also referred to as |
trabecular bone or spongiosum |
|
|
para interarticularis |
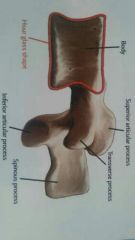
region of the lamina between the superior and inferior articular processes. |
|
|
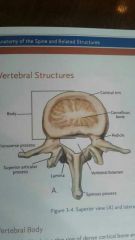
articular processes |
four processes extending from each vertebra. two superior, two inferior extending from junction of pedicles and laminae. |
|
|
zygapophyseal joints |
joint formed by the inferior and superior articular processes. Also called a facet joint. |
|
|
transverse processes |
two, one on each side of the pedicles. extend laterally, serve as connection points for ligaments and tendons |
|
|
spinous processes |
Extends posteriorly from the junction of the laminae. attachment point for ligaments and tendons. end of cervical spinous process may be bifid. |
|
|
end plate |
thin plate of vascularized tissue composed of an outer layer of cartilage and an inner layer of bone attached to the cortical rim of the vertebral body. serves as a growth ring for the vertebral body. |
|
|
apophyseal ring |
ring of cortical bone surrounding vertebral body beneath the end plate. excellent fixation point for interbody fusion devices. |
|
|
intervertebral foramen |
Foramen between vertebral body segments where spinal nerve roots leave the spinal cord |

