![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
9 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Name 3 common eye infections
|
* Conjunctivitis - a bacterial infection treated with antibiotic eye drops.
* Trachoma - tear production slows and the eyes become dry and sore. Rubbing leads to scarring. * Trichiasis - Ingrown eyelashes cause pain and lead to infection, ulceration and scarring. |
|
|
Define refraction
|
It is the process by which a light ray changes direction upon crossing an interface from one medium to another.
To an observer light appears to 'bend'. However, as light travels from an object to the eye in a straight line, it cannot bend. |
|
|
What is trichromacy?
|
thare are three cone types (found in the macula lutea) : S,M and L.
There 3 types detect 3 separate colours: red, green and blue. By varying the intensity of these colours the 3 cone types work together to produce ANY colour in the visible light spectrum. |
|
|
How does a Snellan chart work?
|
it is a measure of visual acuity. It consists of rows of letters, decreasing in size.
The person stands 6meters (20ft) away from the chart and reads the rows of letters. The vision of the person is compared to the vision of a person with normal eye sight so: The farthest distant the person can read / the furthest distance a person with normal sight can read. |
|
|
Name three eye care professionals.
|
* Opthalmologist - a Dr specialising in diagnosing and treating eye conditions.
* Optometrist - trained to perform eye tests and issue prescriptions. * Optician - makes the spectacles or contact lenses from the prescription. |
|
|
A diagram of the human eye
|
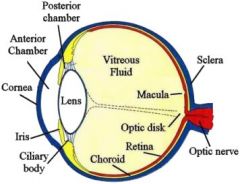
|
|
|
Name the most common refractive errors.
|
* Myopia - short sightedness, the image forms in front of the retina.
*Hyperopia- long sightedness, the image forms at the back of the retina. *Presbyopia - short and long sightedness meaning the person required bifocal lenses. *astigmatism-blurred vision in one direction, glasses are a solution. |
|
|
Four of the most common chronic eye conditions
|
* Cataract - The lens deteriorates causing 'clouding' (this accounts for 48% of world blindness).
* Glaucoma - Optic nerve damage. AMD - Age related macular degeneration is a disease of the retina and can be wet=new blood vessels grow over the retina, or dry=the pigments atrophy (die) *Retinopathy- damage to the retina or capillaries this can have a sudden or gradual onset. |
|
|
How do you calculate focal length?
|
Focal length (m) = 1 / optical power(d)
|

