![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
10 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Describe the placebo effect
|
Classic conditioning
If a person associates an action with a specific result they will expect that result everytime. For example, if a person believes swallowing a white pill will take away any pain they are feeling then any white pill, even a sugar pill, will work as the person believes strongly in the outcome. |
|
|
3 types of pain relief
|
*Asprin - blocks the release of the pain signalling hormone prostaglandin.
*Lignocaine-blocks the ion channels of the cell membrane causing cell 'numbness'. *Opiates - blocks the transmission of pain in the CNS and brain. |
|
|
What is the pain matrix
|
Pain signals travel from the body via the CNS to the part of the brain which recognises and interprets pain, the pain matrix. In response to the signals received the pain matrix sends signals to the site of the pain with instructions for action needed. The action signal is received and carried out so quickly it is almost instinctual. e.g when you quickly move your hand away from an open flame.
**this is known as a negative feedback loop.** |
|
|
Gate theory
|
A theory that pain signals must pass through a series of 'gates' before they react the brain.
These gates can be closed if the person is distracted from the pain and so the pain signals are prevented from reaching the brain. |
|
|
Pain scales
|
Pain is subjective for each individual. Pain scales allow the person to indicate how severe their pain is which allows healthcare professionals to offer adequate pain relief
|
|
|
What is the evolutionary trade-off?
|
the benefits of our evolution e.g being able to walk upright on two legs can bring about negative consequences such a back pain. In this way we evolve a disadvantage along with an advantage in an evolutionary compromise.
|
|
|
Describe the adaptive value of pain
|
The capacity to feel pain and adapt to it in order to avoid future harm.
The ability to experience pain have have existed in our early ancestors. This ability can be detrimental in terms of stress induced pain sensitivity. |
|
|
What are the two main pain classifications?
|
*Acute-this pain lasts until the injury causing the pain heals, it is useful in persuading people to act in order to minimise the pain and damage caused.
*Chronic- lasts long after the cause is healed and it becomes a medical problem in it's own right. |
|
|
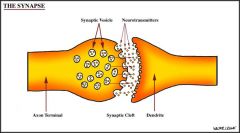
Describe neurotransmitter transferral
|
When an action potential reaches the terminal of the pre-synaptic neuron it triggers the release of the neurotransmitter that is stored at the axon terminal.
The neurotransmitter crosses the gap between this neuron and the post synaptic neuron and attaches to specific receptors on the surface of the post synaptic neuron. Neurotransmitter molecules bind with their receptor changing the electrical activity of the post synaptic neuron. |
|
|
A diagram of a synapse
|
|

