![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
101 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Positive Predictive Value |
Proportion of people who test positive who have the disorder. |
|
|
|
Prevalence |
Proportion of people in the population who had the disorder. |
|
|
|
Positive Likelihood Ratio |
Sensitivity/(1-specificity) |
|
|
|
Likelihood Ratio |
How likely a given test result is in people with the condition. |
|
|
|
null hypothesis |
there is no significant association between variables. |
|
|
|
Relative Risk (cohort study) |
= the incidence of disease in the exposed cohort divided by the incidence of disease in the nonexposed cohort. |
|
|
|
Odds Ratio (case-control) |
Odds of having the disease in the study group to the odds of having the disease in the control group. |
|
|
|
Splenic Injury Management |
Rest for 3 weeks is advocated. |
|
|
|
ANOVA |
3 or more independent variables. parametric data |
|
|
|
Kruskal - Wallis |
non-parametric version of ANOVA |
|
|
|
Moderate +LR |
5-10 |
|
|
|
Moderate +LR |
5-10 |
|
|
|
Moderate -LR |
0.1 - 0.2 |
|
|
|
Moderate +LR |
5-10 |
|
|
|
Moderate -LR |
0.1 - 0.2 |
|
|
|
Small +LR |
2-5 |
|
|
|
Small -LR |
0.2 - 0.5 |
|
|
|
Anabolic Andrenergic Steroids ( IOC standards ) |
ratio of testosterone to epitestoserone should be < 6:1.
Normal ratio rarely goes above 1.3.
1/1000 men has a ratio of 4. |
|
|
|
HGH |
Banned by the IOC but not officially tested. |
|
|

Front (Term) |
Papule |
A papule is a solid raised lesion that has distinct borders and is less than 1 cm in diameter. Papules may have a variety of shapes in profile (domed, flat-topped, umbilicated). |
|

Front (Term) |
Papule |
A papule is a solid raised lesion that has distinct borders and is less than 1 cm in diameter. Papules may have a variety of shapes in profile (domed, flat-topped, umbilicated). |
|

Front (Term) |
Macule |
A macule is a change in the color of the skin. It is flat, if you were to close your eyes and run your fingers over the surface of a purely macular lesion, you could not detect it. A macule greater than 1 cm. may be referred to as a patch.
|
|
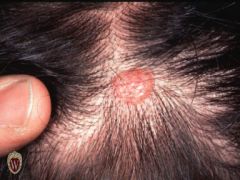
Front (Term) |
Papule |
A papule is a solid raised lesion that has distinct borders and is less than 1 cm in diameter. Papules may have a variety of shapes in profile (domed, flat-topped, umbilicated). |
|
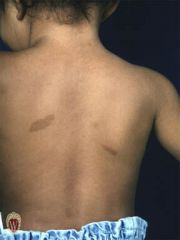
Front (Term) |
Macule |
A macule is a change in the color of the skin. It is flat, if you were to close your eyes and run your fingers over the surface of a purely macular lesion, you could not detect it. A macule greater than 1 cm. may be referred to as a patch.
|
|
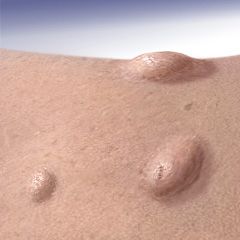
Front (Term) |
Nodule |
nodule is a raised solid lesion more than 1 cm. and may be in the epidermis, dermis, or subcutaneous tissue. |
|

Front (Term) |
Tumor |
A solid mass of skin or subcutaneous tissue that is typically larger than a nodule. |
|
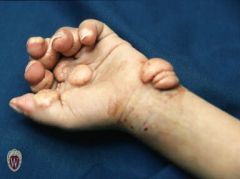
Front (Term) |
Tumor |
A solid mass of skin or subcutaneous tissue that is typically larger than a nodule. |
|

Front (Term) |
Plaque. |
A plaque is a solid, raised, flat-topped lesion greater than 1 cm. in diameter. |
|
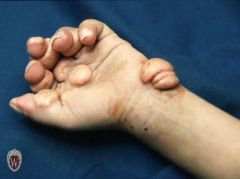
Front (Term) |
Tumor |
A solid mass of skin or subcutaneous tissue that is typically larger than a nodule. |
|
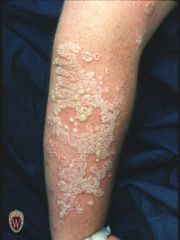
Front (Term) |
Plaque. |
A plaque is a solid, raised, flat-topped lesion greater than 1 cm. in diameter. |
|
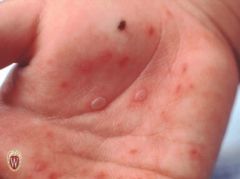
Front (Term) |
Vesicles |
Raised lesions of < 1 cm, filled with clear fluid. |
|
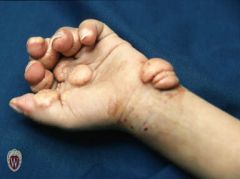
Front (Term) |
Tumor |
A solid mass of skin or subcutaneous tissue that is typically larger than a nodule. |
|
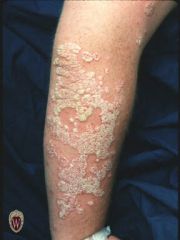
Front (Term) |
Plaque. |
A plaque is a solid, raised, flat-topped lesion greater than 1 cm. in diameter. |
|
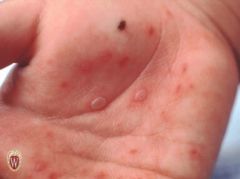
Front (Term) |
Vesicles |
Raised lesions of < 1 cm, filled with clear fluid. |
|

Front (Term) |
Bullae |
Circumscribed fluid filled lesions of > 1cm in diameter. |
|
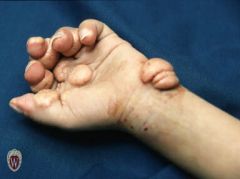
Front (Term) |
Tumor |
A solid mass of skin or subcutaneous tissue that is typically larger than a nodule. |
|
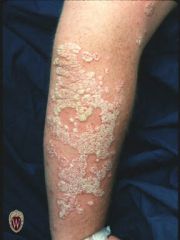
Front (Term) |
Plaque. |
A plaque is a solid, raised, flat-topped lesion greater than 1 cm. in diameter. |
|
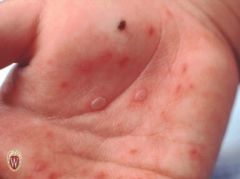
Front (Term) |
Vesicles |
Raised lesions of < 1 cm, filled with clear fluid. |
|

Front (Term) |
Bullae |
Circumscribed fluid filled lesions of > 1cm in diameter. |
|
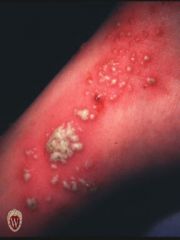
Front (Term) |
Pustules |
Pustules are circumscribed elevated lesions that contain pus. They are most commonly infected (as in folliculitis) but may be sterile (as in pustular psoriasis).
|
|
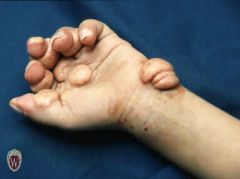
Front (Term) |
Tumor |
A solid mass of skin or subcutaneous tissue that is typically larger than a nodule. |
|

Front (Term) |
Plaque. |
A plaque is a solid, raised, flat-topped lesion greater than 1 cm. in diameter. |
|
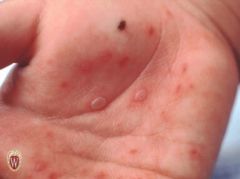
Front (Term) |
Vesicles |
Raised lesions of < 1 cm, filled with clear fluid. |
|
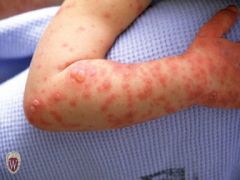
Front (Term) |
Bullae |
Circumscribed fluid filled lesions of > 1cm in diameter. |
|
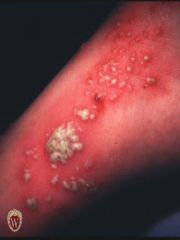
Front (Term) |
Pustules |
Pustules are circumscribed elevated lesions that contain pus. They are most commonly infected (as in folliculitis) but may be sterile (as in pustular psoriasis).
|
|
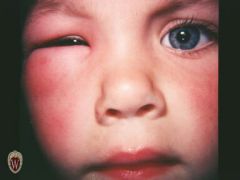
Front (Term) |
Wheal |
Edema in the upper extremity. |
|
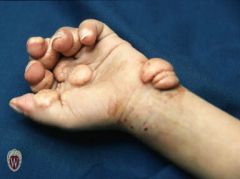
Front (Term) |
Tumor |
A solid mass of skin or subcutaneous tissue that is typically larger than a nodule. |
|
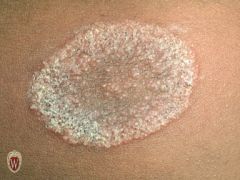
Front (Term) |
Scale |
Scale consists of flakes or plates that represent compacted desquamated layers of stratum corneum.
Tinea Corporis |
|
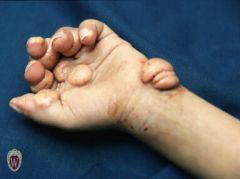
Front (Term) |
Tumor |
A solid mass of skin or subcutaneous tissue that is typically larger than a nodule. |
|

Front (Term) |
Plaque. |
A plaque is a solid, raised, flat-topped lesion greater than 1 cm. in diameter. |
|
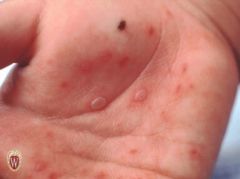
Front (Term) |
Vesicles |
Raised lesions of < 1 cm, filled with clear fluid. |
|

Front (Term) |
Bullae |
Circumscribed fluid filled lesions of > 1cm in diameter. |
|
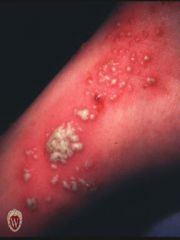
Front (Term) |
Pustules |
Pustules are circumscribed elevated lesions that contain pus. They are most commonly infected (as in folliculitis) but may be sterile (as in pustular psoriasis).
|
|
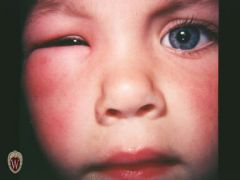
Front (Term) |
Wheal |
Edema in the upper extremity. |
|
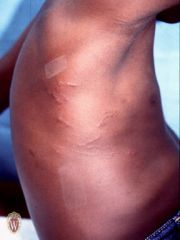
Front (Term) |
Burrows |
Linear lesions in skin caused by infestion and creates tunnels. |
|

Front (Term) |
Scale |
Scale consists of flakes or plates that represent compacted desquamated layers of stratum corneum.
Tinea Corporis |
|

Front (Term) |
Crusting |
Crusting is the result of the drying of plasma or exudate on the skin. Please remember that crusting is different from scaling.
Impetigo |
|

Front (Term) |
Fissures |
A fissure is linear cleavage of skin which extends into the dermis. |
|

Front (Term) |
Purpura |
Generally, the term "petechiae" refers to smaller lesions. "Purpura" and "ecchymoses" are terms that refer to larger lesions. In certain situations purpura may be palpable. In all situations, petechiae, ecchymoses, and purpura do not blanch when pressed. |
|
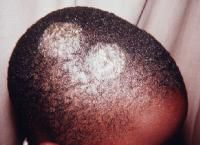
Front (Term) |
Tinea Capitis |
|
|
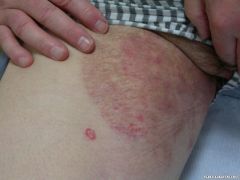
Front (Term) |
Tinea Cruris |
|
|
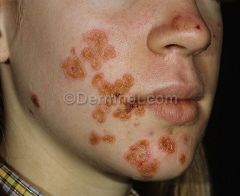
Front (Term) |
Impetigo |
|
|
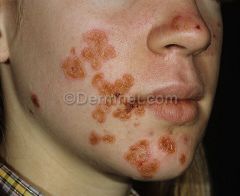
Front (Term) |
Impetigo |
|
|

Front (Term) |
Mulloscum Contagiosum |
Molluscum contagiosum is a viral skin infection that causes raised, pearl‑like papules or nodules on the skin. |
|

Cyclist comes to you c/o pain in the foot. How do you manage this condition? |
Dry feet, allow to dry. |
Trench Foot |
|
|
Kubler- Ross Reactions |
Denial Anger Bargaining Depression Acceptance |
|
|
|
Kubler- Ross Reactions |
Denial Anger Bargaining Depression Acceptance |
|
|
|
Psychogenic Shock |
Fainting, caused by vasodilation which is temporary. Causes decreased blood supply to the brain. |
|
|
|
Psychogenic Shock |
Fainting, caused by vasodilation which is temporary. Causes decreased blood supply to the brain. |
|
|
|
Neurogenic Shock |
General dilation of the blood vessels within the CV system. |
|
|
|
Cranial Nerve IX |
Glossopharyngeal
Swallowing, salivation, gag reflex, sensation of taste. |
|
|
|
Inability to flex the neck demonstrates diminished strength of what myotome? |
C2 |
|
|
|
Bladder and rectal continence is innervated by what dermatome? |
S4 |
|
|
|
During this stage, a host may be , infected but not infectious. |
Prodromal stage |
|
|
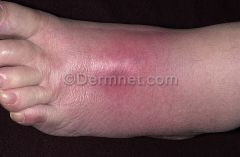
Front (Term) |
Cellulitus |
|
|
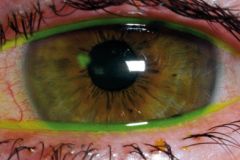
Basketball player suffers an eye injury during the first half. Cobalt Blue Light test demonstrates the above. Your athlete would like to finish the game. What do you do? |
Allow continued play if vision is not impaired. Antibiotic ointment should be applied and f/u with Opthamologist within 24 hours. |
Corneal Abrasion |
|

What are the appropriate steps to take for this patient? |
After approximating laceration with sterile skin closures. Rule out globe injury.
Immediate referral for full thickness lacerations, especially involving lid margin.
Do not reapproximate lid margins! |
|
|
|
Terry Thomas Sign |
Scapho-lunate space of 4mm or more on radiograph. |
|
|
|
Nose bleeds that are uncontrollable, should be managed how? |
48 HR referral for evaluation of possible septal hematoma.
May indicate possible ethmoid a. & nasoethmoid a. damage which are typically assoc. with cribiform fractures. |
|
|
|
A study look at students who study daily vs. students who study weekly and how well they perform on exams. Should use what statistical test if the data is parametric? |
Independent t-test |
IV: Studying - two levels [weekly vs daily] DV: Grade on exam |
|
|
Study comparing study habits and rate of success as measured by GPA. Comparing students who study, students who dont study and students who study cram before exam. What statistical technique should be used? |
One - way ANOVA |
3 levels to the IV |
|
|
A study look at students who study daily vs. students who study weekly and how well they perform on exams. Should use what statistical test if the data is parametric? |
Independent t-test |
IV: Studying - two levels [weekly vs daily] DV: Grade on exam |
|
|
Study comparing study habits and rate of success as measured by GPA. Comparing students who study, students who dont study and students who study cram before exam. What statistical technique should be used? |
One - way ANOVA |
3 levels to the IV |
|
|
When using McMurrays test on your patient with a possible meniscus tear, what would you expect if the specificity of McMurrays is 36%? |
36 % of the time you will correctly identify someone who DOES NOT have the condition.
If the test is positive, the clinician should not automatically Rule In because the specificity is so low. |
|
|
|
A study look at students who study daily vs. students who study weekly and how well they perform on exams. Should use what statistical test if the data is parametric? |
Independent t-test |
IV: Studying - two levels [weekly vs daily] DV: Grade on exam |
|
|
Study comparing study habits and rate of success as measured by GPA. Comparing students who study, students who dont study and students who study cram before exam. What statistical technique should be used? |
One - way ANOVA |
3 levels to the IV |
|
|
When using McMurrays test on your patient with a possible meniscus tear, what would you expect if the specificity of McMurrays is 36%? |
36 % of the time you will correctly identify someone who DOES NOT have the condition.
If the test is positive, the clinician should not automatically Rule In because the specificity is so low. |
|
|
|
Population t-test |
statistical test used to compare a sub population to a larger population. |
|
|
|
H0: Studying does not help improve exam grades
alpha = 0.05 t= 0.018
What can you infer from this data? |
It is ok to reject the null hypothesis.
studying does have an effect on grades.
we can accept the alternate hypothesis. |
|
|
|
Post - Hoc analysis |
Providing justification for why the researcher did not use random sampling. |
|
|
|
Probability of rejecting the null hypothesis when the null hypothesis is false.
or the probability of making the correct decision. |
Power |
Ranges from 0 - 1 |
|
|
R - O - T - O - T - O
Assuming all data was parametric and one variable with two levels was used.
What statistical test should be used ? |
Dependent t-test.
Subjects were randomized, and compared to themselves. |
|
|
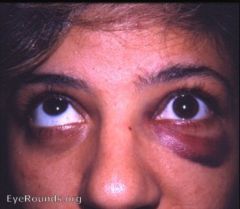
Athlete was struck in the eye by a wild pitch. How do you manage this injury? |
Urgent CT scan to rule out strangulation of extraocular muscles.
Refer out immediately! |
|
|

Athlete was struck in the eye by a wild pitch. How do you manage this injury? |
Urgent CT scan to rule out strangulation of extraocular muscles.
Refer out immediately! |
|
|
|
Athlete with a nose bleed presents with clear fluid draining from nose and mentions a sweet taste to his blood. What is he experiencing? |
High suspicion for cribiform plate fracture which is a predisposing condition for meningitis. The athlete must receive antibiotics and see an Otolaryngologist ASAP! |
|
|
|
Management of Scapula fractures. |
Typically Immobilization and progressive ROM for 6 weeks.
90% are stable body/spine fractures and do not require surgery. |
|
|
|
Sprengel Deformity |
Typically a cosmetic surgery if it impedes ROM, shoulder abduction that can not attain 100 degrees.
Occurs in kids younger than age 6.
Not ideal to perform surgery after age of 8. |
|
|
|
Throwing athletes with SLAP tears, managed surgically are allowed to throw at what time frame? |
4 months interval throwing.
6 months from the mound.
7 months full velocity. |
|
|
|
How do you treat and manage? |
Ice and elevate.
12-24 Hours aspirate with sterile tools. |
|
|
|
ACI |
Relatively young patients. Focal, shallow lesions. 2 - 10 cm^2 |
|
|
|
Microfracture |
Indicated in grade III/IV articular surface lesions surrounded by normal articular cartilage in young patients. |
|

