![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
66 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
List what would be included in Daily Intake.
|
Food
Drink IV Fluids Ice Popcicly NG Peg Tube |
|
|
List what would be included in daily Output.
|
BM
Urine Emesis Sputum Blood NG Drainage Ostomy Output Drains |
|
|
How Frequently is I & O Totaled?
|
At the end of every shift...Every 8 Hours.
|
|
|
What is the purpose of assessing the abdomen and bladder for distension?
|
Fluid Retention
Kidney Failure Neurogenic Bladder |
|
|
In which direction should the client be wiped after a bowel movement, and why?
|
Front to Back.
To avoid contamination of the urethra. |
|
|
Before and during a bath, what can/should be assessed?
|
Skin
Adema LOC Mental Acquity Activity Tollerence Pressure Ulcers Palor/Color ROM Ego Integrity Discomfort |
|
|
What are some principles to consider during a bath?
|
Client Comfort
Ambient Temperature Water Temperature Client Strength Mental State Culture Client ROM |
|
|
Describe the Preferred order of the bath.
|
Head to Toe except Peri Care.
Clean water. Peri Area. |
|
|
Describe the role of the RN with regard to foot care.
|
Provide Nail Care except where contra indicated from DM issues.
Assess for Pressure Ulcers Foot Drop Prevention Foot Rub Education |
|
|
What does the acronym PVR mean in bladder care?
|
Post Void Residual.
The amount of Urine left in the bladder when the client has finished voiding. It can be attributed to Neurogenic Bladder. |
|
|
Describe Standars of Care
|
Guidelines by which nurses should practice they are defined by:
Nursing Practice Acts American Nurses Association (ANA) Policies & Procedures |
|
|
Describe agency policies and procedures.
|
Established by agencies
Nurses working in any agency are obligated to know them and abide by them. |
|
|
If a student makes an error, who is responsible?
|
The Student // The Instructor // The Facility
|
|
|
Define Statutory Law
|
Created by elected and appointed officials
Nurse Practice Act is state statute (RCWs only) WACs are developed by Washington State Nursing Care Quality Assurance Commission |
|
|
Define Common Law
|
LECTURE
-Common Law -Case law -Created by judicial decisions Examples: Roe v. Wade (abortion), Informed Consent POTTER - 407 Created by judicial decisions made in courts when individual legal cases are decided. Examples are Informed Consent and Clients Right to Refuse Treatment. |
|
|
Define Criminal Law
|
Acts that threaten society and its order
Criminal acts are prosecuted Felony=serious crime Misdemeanor=less serious crime This is what State Patrol Background check is for (crimes against person) |
|
|
Define Civil Law
|
LECTURE
Protection of a PERSONS rights, not society as whole Example: OJ Simpson having to pay money to families POTTER - 407 Protects the rights of individual persons within our society and encourage fair and equitable treatment among people. |
|
|
Define Incident Report
|
Done at hospitals as part of quality assurance
Not a part of the legal record |
|
|
Define Battery
|
Intentional touching of anothers body or anything the person is touching or holding without consent. It can be harmful to the client and cause injury, or be merely offensive to the clients personal dignity.
Potter 413 |
|
|
Define Assult
|
Willful attempt or threat to harm another, along with the ability to harm
|
|
|
Define Use of Restraints
|
Only to ensure physical safety of resident or other residents
Written order of duration (usually 24 hrs) Circumstances under which restraints can be used |
|
|
Define a Felony
|
It is part of Criminal Law.
It is the most serious type of crime. |
|
|
Define a Misdemeanor
|
It is part of Criminal Law.
A lesser serious crime. |
|
|
Define a Tort
|
Civil wrong committed against person or property
It can be Unintentional or Intentional |
|
|
What is the Patient Self-Determination Act?
|
PSDA
Most hospitals, nursing homes, home health agencies, and HMO's routinely provide information on advance directives at the time of admission. They are required to do so under a federal law called the Patient Self-Determination Act (PSDA). The PSDA simply requires that most health care institutions (but not individual doctors) do the following: 1. Give you at the time of admission a written summary of: your health care decision-making rights (Each state has developed such a summary for hospitals, nursing homes, and home health agencies to use.) the facility's policies with respect to recognizing advance directives. 2. Ask you if you have an advance directive, and document that fact in your medical record if you do. (It is up to you to make sure they get a copy of it). 3. Educate their staff and community about advance directives. 4. Never discriminate against patients based on whether or not they have an advance directive. Thus, it is against the law for them to require either that you have or not have an advance directive. |
|
|
Define advance directive:
|
A written document in the form of a living will or durable power of attorney prepared by a competent individual that specifies what, if any, extraordinary procedures, surgeries, medications, or treatments the patient desires in the future, when he or she can no longer make such decisions about medical treatment.
|
|
|
Define Malpractice
|
Malpractice
One type of negligence Professional misconduct, unreasonable lack of skill, evil practice, illegal or immoral conduct See Uniform Disciplinary Code |
|
|
Define Tort
|
A wrongful act or injury, committed by an entity or person against another person or another person's property, that may be pursued in civil court by the injured party.
|
|
|
Define the Good Samaritan Law
|
Despite the rules of common law, a healthcare provider who voluntarily and without reasonable expectation of compensation or reward provides the services described in that subsection is not liable for damages that result from the person's negligence in acting or failing to act while providing the services, unless it is established that the damages were caused by the gross negligence of the person.
|
|
|
What are the reporting ramifications of gunshot wounds?
|
They are reportable to the State Department of Health Monthly.
|
|
|
Define the Reporting Ramifications of STD's.
|
They must be reported to the Local Health Department withing 3 working days.
|
|
|
Define confidentiality:
|
The maintenance of privacy, by not sharing or divulging to a third party privileged or entrusted information.
Especially prudent with regard to HIPAA |
|
|
Define Negligence
|
Conduct that falls below the standard of care Characterized by inadvertence, thoughtlessness or inattention, carelessness
|
|
|
Define Malpractice
|
Professional misconduct, unreasonable lack of skill, evil practice, illegal or immoral conduct
|
|
|
Define the Criteria for
|
Nurse owed duty to client
Nurse did not carry out that duty Client was injured (damage occurred) Clients injury was result of nurses failure to carry out the duty |
|
|
Define Responsibility
|
The characteristics of reliability and dependibility. The ability to distinguish between right and wrong.
Includes a duty to perform actions well and thoughtfully. Example...Giving a Drug. The nuse has a RESPONSIBILTIY to assess the clients need for the meds, give it correctly and safely, and evaluate the response to the drug. |
|
|
Define Accountability
|
The nurse being answerable for their actions. It involves follow up and a reflective analysis of ones decisions to evaluate their effectivenss.
|
|
|
Define Moral Dilemma
|
There is evidence that each choice has justifiable moral arguments and ethical principles to support it.
(Lecture from 141 Week 10) |
|
|
Define the The Patient's Bill of Rights
|
The Patient's Bill of Rights was first adopted by the American Hospital Association in 1973 and revised in October 1992. Patient rights were developed with the expectation that hospitals and health care institutions would support these rights in the interest of delivering effective patient care. The American Hospital Association encourages institutions to translate and/or simplify the bill of rights to meet the needs of their specific patient populations and to make patient rights and responsibilities understandable to patients and their families
|
|
|
How is a report made to the nursing commission for Unsafe Nursing.
|
(4) In providing reports to the nursing commission, a person may call the nursing commission office for technical assistance in submitting a report. Reports are to be submitted in writing and include the name of the nurse, licensure identification, if available, the name of the facility, the names of any patients involved, a brief summary of the specific concern which is the basis for the report, and the name, address and telephone number of the individual submitting the report.
|
|
|
Describe the Legal Reporting obligations of the nurse with Elder abuse.
|
866-ENDHARM
Mandatory reporters are professionals identified by law who MUST make a report if they have reason to believe that the abuse, abandonment, neglect, or financial exploitation of a vulnerable adult has occurred. Mandatory reporters are |
|
|
Define Protocol.
|
A protocol is a written plan specifying the procedures to be followed during care of clients with a select clinical condition or situation, such as carew of a postoperative client. It is a clinical guideline, which can still be customized for a client.
|
|
|
Define Standing Orders
|
Orders, rules, regulations, protocols, or procedures prepared by the professional staff of a hospital or clinic and used as guidelines in the preparation and carrying out of medical and surgical procedures.
Tabers An example would be in a a Cardic Care setting, the physician might have a standard set of orders, for certain conditions, which the nurse can administer without first contacting the physician. |
|
|
Define Standards of Care
|
Guidelines by which nurses should practice
Defined by: -Nursing Practice Acts -American Nurses Association (ANA) -Policies & Procedures |
|
|
Describe the components of ethical decision making.
|
It requires deliberate, systematic thinking.
-Determine it is an ethical problem -Gather all relevant information -Examine and determine self values and issues -Verbalize the problem -Consider possible courses of action -Negotiate an outcome -Evalute the process |
|
|
Define a cation
|
An ion with a positive electric charge; opposite of anion.
|
|
|
Define an Anion
|
An ion carrying a negative charge; the opposite of cation.
|
|
|
Define milliequivalent
|
ABBR: mEq. One thousandth of a chemical equivalent.
The concentration of electrolytes in a certain volume of solution is usually expressed as milliequivalent per liter (mEq/L). It is calculated by multiplying the milligrams per liter by the valence of the chemical and dividing by the molecular weight of the substance. |
|
|
What physiological processes can Acid-Base Balance alter?
|
Respiration
Metabolism Functions of the CNS |
|
|
Define and Describe Intracellular fluids.
|
ICF
Comprises all fluids WITHIN body calls. Accounts for about 40% of adult body weight. |
|
|
Define and Describe Extracellular fluids.
|
ECF
All the fluid outside of a cell. It is futher divided into three smaller compartments. |
|
|
Define the ECF Interstitial Fluid.
|
It contains Lymph and is the fluid between the cells and outside the blood vessels.
|
|
|
Define the ECF Intravascular fluid.
|
Blood Plasma
|
|
|
Define the ECF Transcellular fluid
|
CSF, Pleural Fluid, peritoneal and synovial fluids.
Together the ECF compose about 20% of body weight. |
|
|
Define an Electrolyte
|
An element or compound that when melted or disolved in water or another solvement separates into ions and is able to carry an electrical current.
|
|
|
Give some examples of Cation Electrolytes.
|
Na
K Ca |
|
|
Give some examples of Anion Electrolytes.
|
Cl-
HCO3- and SO4 |
|
|
Define and Describe Na+
|
Sodium. It is a Cation Electrolyte.
|
|
|
Define and Describe K+
|
It is Potassium. A Cation Electrolyte.
|
|
|
Define and describe Ca+
|
Calcium is a Cation Electrolyte.
|
|
|
What is Osmolarity used to measure in clinical practice?
|
Urine and Serum
|
|
|
Define Interstitial Fluid
|
The fluid between cells, in tissue spaces.
|
|
|
Define Diffusion.
|
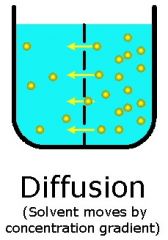
The Movement of a solute in a solution across a semipermeable membrane from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration.
|
|
|
Define Osmosis.
|
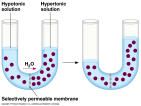
The movement of a pure solvent such as water, through a semipermeable membrane from an area of lesser solute concentration to an area of greater solute concentration in an attempt to equalize the concentrations on both sides of the membrane.
|
|
|
Define Filtration
|
The process by which water and diffusible substances move together in response to fluid pressure, moving from an area of higher pressure to lower pressure.
|
|
|
Define Active Transport.
|
It is the process of metabolic activity and expenditure of energy to move materials across cell membranes.
Allows cells to admit larger molecules than they would otherwise be able to admit or to move molecules from areas of lesser concentration to areas of greater concentration....Uphill. It is the mechanism by which cells absorb glucose and other substances to carry out metabolic activities. An example is the Na+ K+ Pump |

