![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
14 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Scoliosis
|
A lateral curvature of the spine >10° in the coronal plane.
Associated with rotation around vertical axis. Often associated with rib cage deformities, uneven shoulder height, scapular levels and iliac crest levels. |
|
|
Clinical Signs and Symptoms
|
Generalized back pain
Body asymmetry (ribs, hips, shoulders) Muscle hypertrophy/compensation Can have neurological impact. Cardiac and pulmonary compromise in severe cases |
|
|
Adams Forward Bending Test
|
pt bends forward,
look for: is one shoulder higher than other does a shoulder blade stick out more than the other does an arm stick out more than another IS THERE A BULGE IN THE BACK |
|
|
Curve is quantified using the ______.
|
Cobb angle
|
|
|
COBB ANGLE
|
Measured between two most angled vertebrae at top and bottom of curve
|
|
|
MRI is indicated
|
congenital presentation
atypical curves neuro signs |
|
|
Treatment – Basic Guideline
|
Observation up to 30°
Bracing 30 to 45° Surgical >45° |
|
|
most important risk factor for Respiratory Failure in scoliosis
|
degree of curve
|
|
|
Rib cage deformity ultimately leads to
|
decr PaO2
|
|
|
wedge vertebrae
|
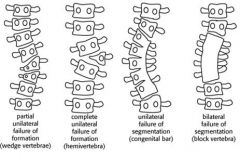
partial unilateral failure of formation
|
|
|
hemivertebrae
|
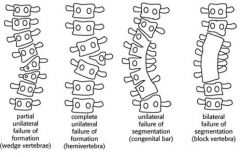
complete unilateral failure of formation
|
|
|
congenital bar
|
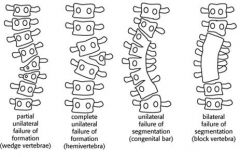
unilateral failure of segmentation
|
|
|
block vertebrae
|
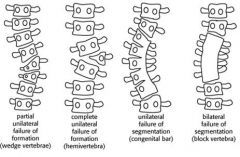
bilateral failure of segmentation
|
|
|
neuromuscular causes of kyphoscoliosis
|
muscular dystrophy
poliomylitis cerebral palsy |

