![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
16 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Stimulus |
a change in the environment that triggers a response |
|
|
Receptors |
Specialised cells that detect a change |
|
|
Stimulus response model |
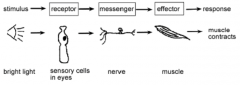
|
|
|
Voluntary Response |
- Neural message goes to the brain - conscious control of response |
|
|
Involuntary Response |
- Neural message only goes to the spinal cord - no conscious control of the response |
|
|
Central Nervous System |
The receptors send a message to |
|
|
Why are some parts of the body more sensitive than others? |
Some nerve's are more sensitive because they have greater amounts of recepter cells |
|
|
Reflex Response |
A reflex response is automatic ,rapid and it's function is protection |
|
|
Reflex Arc |
The reflex responses travel through the reflex arc Stimulus > receptor > sensory neuron > CNS > relay neuron > motor neuron > effector > response |
|
|
Synapses |
Between neurons are small gaps called synapsess |
|
|
neurotansmitters |
Electrical impulses are converted to chemicals called neurotransmitters |
|
|
Neurotransmitters types |
Adrenalin - associated with alertness Dopamine - associated with emotions Serotinin - mood, body temperature |
|
|
three main parts of nervous system |
the brain, the spinal cord, nerve fibres |
|
|
Systems |
Central Nervous System ( CNS ) : brain and spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System ( PNS ): All other neural paths |
|
|
Nerve Fibres |
Nerve Fibres are bundles of nerve cells (neurons) that pass signs ( impulses ) to the brain |
|
|
How do Nerve Fibres work? |
From the CNS, nerve fibres send impulses ( signs ) to the effectors ( muscle/ glands ) |

