![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
23 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Closed system |

A system which can lose or gain energy but cannot lose or gain Mass from its environment. |
|
|
|
Chemical Energy |
A form of energy produced through reactions that occur in chemical compounds |

Food Mmmmmmm |
|
|
Law of conservation of energy |
Energy can neither be created nor destroyed, energy just changes form |

|
|
|
Convection |
Transfer of thermal energy from one place to another by the movement of fluids |

|
|
|
Radiation |
The transfer of energy by electromagnetic Rays, may occur in empty space |

|
|
|
Conduction |
Transfer of thermal energy that occurs in solids liquids and gases when two different substances touch |

|
|
|
Heat |
Energy transferred between two objects of different temperatures moves from warm to cool |

|
|
|
Energy |
The ability of a system to do work. Energy is required for changes to happen |

|
|
|
Temperature |
Average kinetic energy of all the particles in a material. * measured by a thermometer |

|
|
|
System |
A group of interacting elements forming a complex whole |
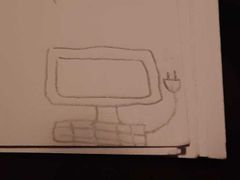
|
|
|
Electrical energy |
A form of energy made available by the flow of electric charge through a conductor |
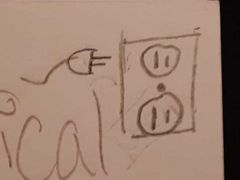
|
|
|
Kinetic energy |
Energy of motion |

|
|
|
Light energy |
A form of energy that exhibits wavelike Behavior as it travels through space. Part of the electromagnetic spect. |

|
|
|
Elastic energy |
A form of energy that gives an object the ability to bounce or stretch |

|
|
|
Potential energy |
Energy that is stored in a system or object |

|
|
|
Energy transformation |
The change of energy from one type to another |

|
|
|
Sound Energy |
A form of energy that is made up of vibrations and requires a medium to travel ( air, water, solids ) |
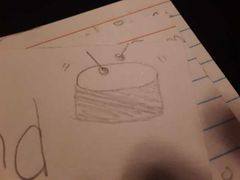
|
|
|
Thermal energy |
Thermal energy is the total KE (motion)of tiny particles that make up matter faster = more heat |

|
|
|
Mechanical energy |
The sum of the motion KE and position PE of an object or parts of a system |
Bike |
|
|
Convection current |
A cycle motion occurs because the density of a fluid is related to its temperature |

|
|
|
Nuclear Energy |
Energy as a result of atoms being forced together or atoms being separated |

|
|
|
Open system |
A system which can lose or gain mass or energy from its environment |

|
|
|
Closed system |
A system which can lose or gain energy but cannot lose or gain Mass from its environment |

|

