![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
179 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What are light and sound? |
Energy that can be transformed. |
|
|
|
how Does the transfer of energy involve conversion? |
No the energy remains in its original form but tracked to a new median or region. Wh |
|
|
|
Where does heat transfer by conduction generally occur? |
In solids |
|
|
|
Wheres does heat transfer by convection generally occur? |
in liquids and gasses |
|
|
|
Where can radiation occur? |
Vacuums and space |
|
|
|
How does heat travel through conduction? |
When fast moving particles collide with nearby particles, making them move faster |
|
|
|
What happens if you heat one end of a metal bar? |
The energy is transferred form the hot end to the cold end by atoms of that metal bumping into one anther. |
|
|
|
Why does heat travel faster in solids than liquids or gases? |
Because conduction occurs faster when particles in an object are closer together. |
|
|
|
Why are the gases the poorest conductors? |
Because the particles in gases are really far apart |
|
|
|
What solids don’t conduct heat well? |
Plastic and fabrics |
|
|
|
What are materials that don’t conduct heat well referred to as? |
insulators |
|
|
|
What happens when particles with warm air have greater kenetic energy? |
They take up more space making warm less dense cooler surrounding air |
|
|
|
What happens as warm air rises? |
It transfers some of its energy to surroundings causing the air to cool |
|
|
|
What happens when air cools and loses kenetic energy? |
The particles are brought closer together resulting in the density of the air increasing so it begins to fall |
|
|
|
the flow of Warm air up and cool air down crater as cuticular current called? |
The convection current. |
|
|
|
interpret this diagram |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
How do sound and light travel? |
As waves which transfer and propagate that energy. |
|
|
|
What are the circular ripples created when a stone is dropped in a still pool of water examples of? |
Waves propagating energy |
|
|
|
The stone falling through the water causes the water to bop up and down and |
the energy of the oscillating water moves outwards from the centre of the disturbance creating a circular pattern of waves. |
|
|
|
How does the medium or material carrying a transverse wave oscillate? |
At right angles to the direction of energy transfer. |
|
|
|
What do transverse waves consist of? |
A series of crests and troughs |
|
|
|
How long is a wavelength in a transverse wave? |
The distance between any two corresponding points on neighbouring waves. or the distance between two adjacent crests. |
|
|
|
What is the amplitude of the wave? |
The maximum distance that each particle moves away from its usual resting or equilibrium position. |
|
|
|
How does a transverse wave oscillate? |
up and down |
|
|
|
how do longitudinal waves oscillate? |
from side to side by compressing and refracting. |
|
|
|
What happens to the particles around the drum when you strive a drum? |
The particles are pushed together than spread apart |
|
|
|
What happens to the particles around the drum when you strive a drum? |
The particles are pushed together than spread apart |
|
|
|
What happens to the energy of the vibrating skin when you strike a drum? |
It’s transferred to nearby particles, making them vibrate as quickly as the drum skin. |
|
|
|
when you strike a drum skin what happens? |
A series of compression and refractions occur |
|
|
|
What is the wavelength of a longitudinal wave? |
The distance between the centre of two adjacent refractions. |
|
|
|
Can sound travel through empty space? |
no |
|
|
|
Why can sound only be transferred through a medium? |
Because vibrating particles carry the energy |
|
|
|
Why can’t sound travel through empty space? |
Because there are no particles to vibrate the energy through |
|
|
|
Why can sound only be transferred through a medium? |
Because vibrating particles carry the energy |
|
|
|
Why can’t sound travel through empty space? |
Because there are no particles to vibrate the energy through |
|
|
|
Why can light travel through a vacuum? |
Because it does not require a medium to vibrate though |
|
|
|
What is the frequency of vibrating of a wave? |
the number of complete waves generated per second |
|
|
|
What is frequency measured in? |
Hertz (Hz) |
|
|
|
What is one Hertz equal to? |
one oscillation |
|
|
|
What does the frequency of a sound determine? |
the pitch, high frequency vibration produce high pitch |
|
|
|
What determines a sound waves loudness? |
Amplitude |
|
|
|
What determines a sound waves loudness? |
Amplitude |
|
|
|
What does the higher amplitude equal |
a louder sound |
|
|
|
How do you calculate the wavelength, speed and frequency of a wave? |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
formula for frequency? |
wave speed(m/s)/wavelength (m) |
|
|
|
Formula for wave speed? |
frequency (Hz) *wavelength (m) |
|
|
|
Formula for wave speed? |
frequency (Hz) *wavelength (m) |
|
|
|
Wavelength formula? |
Wave speed (M/s) / frequency (Hz) |
|
|
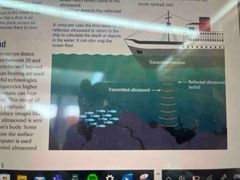
how ultra sound works |
Interpret this |
|
|
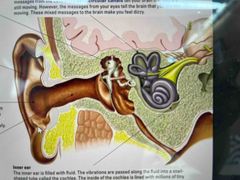
Where is the outer ear and outline it’s functions |
The outer ear collets the energy of the vibrating air and funnels it through the ear canal - the air along the ear canal vibrates making the eardrum - high pitched sounds make the eardrum vibrate quickly |
|
|
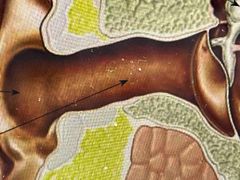
Elaborate? |
This is the ear canal - contains wax and tiny hairs to trap dust for the eardrum |
|
|
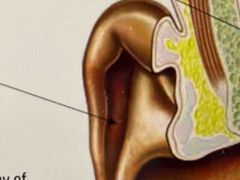
What is this part of the ear? |
The auricle - The outside part of the ear - contains a sponges tissue called cartilage |
|
|

Expand? |
This is the middle ear - contains the three smallest bones in the body, the ossicles - they send vibrations from the eardrum to the inner ear - The largest ossicle (stirrup) presses a thin layer of skin called the oval window at the entrance of the inner ear |
|
|
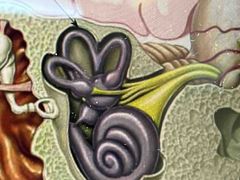
Elaborate? |
These are the semicircular canals - they control your sense of balance - if you move fluid in these tubes flow past cells that sense movement - these cells send signals to the brain that tell you if your moving and how you are moving |
|
|
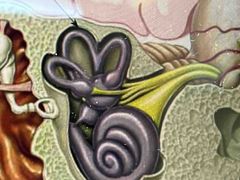
Elaborate? |
These are the semicircular canals - they control your sense of balance - if you move fluid in these tubes flow past cells that sense movement - these cells send signals to the brain that tell you if your moving and how you are moving |
|
|
|
Why dont sounds travel faster in liquids and solids? |
because mediums that are more tightly packed have less distance to travel to collide with neighbouring particles |
|
|
|
At what speed does sound travel through the air? |
340 m/s |
|
|
|
At what speed does sound travel through the air? |
340 m/s |
|
|
|
How fast do sound waves travel through the ocean? |
1533 m/s |
|
|
|
How fast do sound waves travel through the ocean? |
1533 m/s |
|
|
|
What is used in the ocean to communicate and track food? |
Echolocation |
|
|
|
What is Echolocation? |
Reflected sound |
|
|
|
What do ocean animals send out? |
high frequency pulses (ultrasound) that are reflected back when start strike a target |
|
|
|
What does the speed of sound in gases depend on? |
temperature |
|
|
|
why does sound travel faster in warm air? |
because there is more lentil energy in warm particles |
|
|
|
What is supersonic speed |
something travelling at the speed of sound eg. a plane |
|
|
|
What is a Mach number |
the ratio of and objects speed compared to the speed of the surrounding air |
|
|
|
What does it mean if an object is travelling at 2 Mach? |
it’s going twice the speed of sound |
|
|
|
What is happens when a plane produces a supersonic boom? |
the supersonic boom occurs because the pressure waves produced by the nose and tail of the plane collide and are pushed together |
|
|
|
What frequencies can a human ear detect? |
between 20 and 20000 hz |
|
|
|
What is ultra sound? |
frequencies higher than the human ear can detect. |
|
|
|
How is an ultra sound image produced? |
the ultra sound is sent through the mother body, some of its reflected through the surface of the baby. a computer is used for to change reflected ultrasound into an image. |
|
|
|
What is ultrasound used in? |
It is used in sonar to produce image of underwater objects or the ocean floor. |
|
|
|
How is ultrasound used in the water? |
1. sent down in the water 2. objects underwater reflect some of the ultrasound 3. A receiver detects the reflected ultrasound |
A computer uses time taken for the ultrasound to return to calculate depth |
|
|
Are sound waves invisible? |
yea |
|
|
|
How can sound be studied? |
Converting the sound energy into an electrical device using a device called a “cathode rat oscilloscope” ( CRO) |
|
|
|
what does a microphone connected to the CRO measure? |
the air pressure changes associated with the compression and refractions of sound waves and produces on the CRO screen called a waveform |
|
|
|
What does high frequency create on a CRO? |
bunched up waveforms |
|
|
|
What so loud sounds create on a CRO display? |
tall waveforms |
|
|
|
What is commonly used to measure the sound level of loudness of a sound? |
the decibel scale (dB) |
|
|
|
What is the quietest audible sound? |
0dB |
|
|
|
If each 10-fold increase in sound level is an extra 10dB higher, what is 1000 times more powerful than the quietest audible sound? |
30 dB |
|
|
|
Can any level above 85 decibel cause hearing loss? |
yes |
|
|
|
What is the main function of the ear? |
To detect sound |
|
|
|
What does the ear do? |
collects the energy of vibrating particles and changes it into electrical signals that’s are send to the brain |
|
|
|
What does the ear do? |
collects the energy of vibrating particles and changes it into electrical signals that’s are send to the brain |
|
|
|
What are the three main parts of the ear? |
the inner, middle and outer ear |
|
|
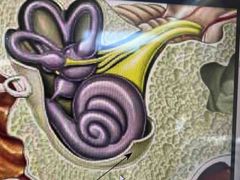
Interpret this |
this is the inner ear - it’s filled with fluid - vibrating passes along the fluid into a snail shaped tube called the cochlea - the inside of the cochlea is lined with millions of tiny hairs - each tiny hair is attached to a nerve receptor - when the fluids vibrate, the hairs move and the receptors changes the energy of the moving hairs into electrical signals that are sent to the brain. |
|
|
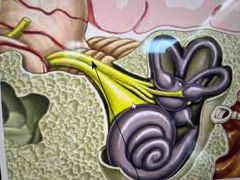
this is? |
it’s the auditory nerve - nerves from the receptors in the cochlea merge to form a large nerve that sends signals to the brain. |
|
|
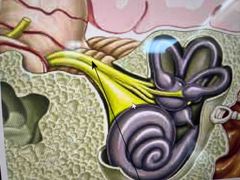
this is? |
it’s the auditory nerve - nerves from the receptors in the cochlea merge to form a large nerve that sends signals to the brain. |
|
|
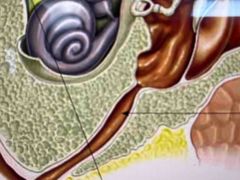
What is this? |
The eustachian tube - joins the middle ear to the nose and the throat - it’s usually closed - when pressure on the eardrum is not the same on both sides the tube opens - air moves either in or out of the middle ear until the pressure is balanced again |
|
|
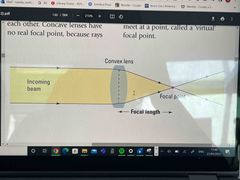
Explain why this is a convex (converging) lens |
Light rays that pass through them are refracted toward each other so they meet ( converge) at a point ( the focal point) |
Explain why this is a convex (converging) lens |
|
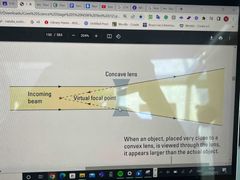
Explain why this is a concave (divergent) lens? |
when rays of light pass through these lenses they refract away (diverge) from each other |
|
|
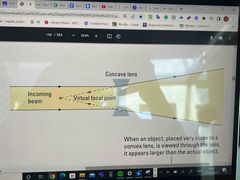
Explain why this is a concave (divergent) lens? |
when rays of light pass through these lenses they refract away (diverge) from each other |
|
|
|
Why do concave lenses have no real focal point? |
because rays of light do not meet after passing the lens however if you do trace down the rays back to where they came from they do meet at the virtual focal point. |
|
|
|
What is an example of an electromagnetic wave? |
Light |
|
|
|
What form is an electromagnetic wave? |
Transverse |
Compression or transverse? |
|
|
How fast do electromagnetic waves travel through the air? |
300,00 kilometres per second |
|
|
|
Can electromagnet waves travel through a vacuum? |
Yes |
|
|
|
What are the three properties of electromagnetic waves? |
1. They are transverse 2. They are able to travel through most substances including vacuums 3. Airspeed is 300,000 km/s |
|
|
|
What direction does light travel in? |
Straight lines |
|
|
|
How do our eyes construct and receive images? |
Because our eyes receive countless light rays from objects that we view and brain constructs an image of these objects using impulses from the eyes. |
|
|
|
Expand on the fact that individual light rays are not visible |
Streams of light rays or beams of light may be seen when the light is scattered or reflected from particles through which it travels and then redirected to the eyes. |
|
|
|
Give an example of how beams of light can be seen. |
Beams of light can be seen from car headlights on a foggy night as light is scattered from water vapour in the air. |
|
|
|
What happens when light strikes a shiny surface? |
The light is reflected from that surface. |
|
|
|
What does the angle of incidence equal |
the angle of reflection |
|
|
|
Represent how the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection |
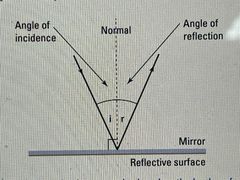
(add photo)
|
|
|
|
What are the two forms of curved mirrors? |
Concave (Curved inward) and Convex (curved outwards) |
|
|
|
How does a Concave mirror reflect light and why? |
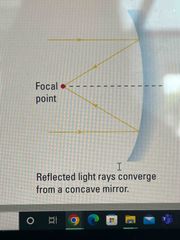
Because the light of reflected towards the same focal point and follow the law of reflection |
|
|
|
How does a Convex mirror reflect light and why? |
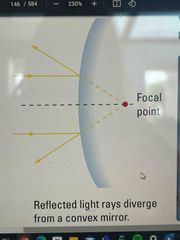
Light in a convex is reflected from the focal point which is behind the mirror creating a diverging image |
|
|
|
Where are parallel rays of light reflected to? |
the focal point |
|
|
|
What is a surface that absorbs light called? |
Opaque |
|
|
|
What does it mean if light travels through a surface? |
It's transparent |
|
|
|
What is a surface that allows objects to be detected but not seen called? |
translucent |
|
|
|
Example of refracting or bending light? |
A flower where half the stem is in the water and half is out of the water. Light from the stem above the water travels in a straight line through the air to your eyes. light reflected from the water appears ben because it's passing through a different transparent media. |
|
|
|
What is bending through different media called? |
refraction |
|
|
|
What happens when light travels from one transparent medium to another? |
It speeds up or slows down |
|
|
|
What is the bending of light rays passing from on medium to another caused by? |
lights change of speed |
|
|
|
When passed through light speeds up as it is passed through a different median its bends away from the normal |
when light slows down it bends toward the normal |
|
|
|
What does the amount of light bending depend on? |
which angle the light crosses at |
|
|
|
Why are lenses useful? |
they bend light in a predictable way |
|
|

What part of the eye is this? |
the iris - coloured ring of muscle - opens and closes to control the amount of light entering the pupil |
|
|
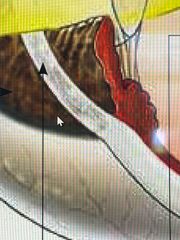
Expand? |
This is the cornea - refracts the incoming light so that is passed through the pupil towards the lens |
|
|
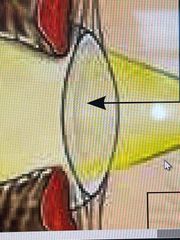
What is this? |
the lens - completes refracting so rays from each point are focused on a retina |
|
|

What is this? |
the suspensory ligament - attached the ciliary muscle to the lens |
|
|

expand on this? |
it’s the ciliary muscle - contract to thin lens when viewing distance objects |
|
|

what is this arrow pointing to? |
the retina - images form here - light sensitive cells detect brightness and colour of different parts of the image - this information is sent through the optic nerve - images are upside down in the retina and the brain flips it |
|
|
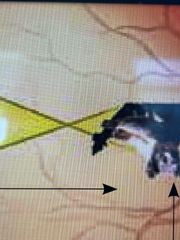
what is this arrow pointing to? |
the retina - images form here - light sensitive cells detect brightness and colour of different parts of the image - this information is sent through the optic nerve - images are upside down in the retina and the brain flips it |
|
|

interpret this |
- image is upside down - if the cornea and lens have worked together to refract the incoming light by the right amount the image is clear and sharp |
|
|

what is this? |
the optics nerve - connects the retina to the brain |
|
|
|
What is the shape of the lens controlled by? |
the ciliary muscles |
|
|
|
What happens in the eye when you look at nearby objects? |
the ciliary muscles contact the suspensory ligaments become slack causing lens to bulge |
|
|
|
What happens in the eye when you look at nearby objects? |
the ciliary muscles contact the suspensory ligaments become slack causing lens to bulge |
|
|
|
What is the action of obtaining a sharp image on the lens called? |
accommodation |
|
|
|
What happens if the cornea and lens bend too much? |
the light rays focus before the retina, lenses for these glasses diverge the light rays a little before entering the eye |
|
|
|
What happens if the cornea and lens bend too much? |
the light rays focus before the retina, lenses for these glasses diverge the light rays a little before entering the eye |
|
|
|
What happens if the cornea and lens don’t bend enough light? |
the light rays focused at a point past the retina causing long sightedness |
|
|
|
What colours does the visible spectrum consist of? |
red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo and violent |
|
|
|
What is dispersion? |
the separation of white light into its component colour as a result of refraction |
|
|
|
Why do colours split up in a glass triangle? |
because each colour of light has a slightly different speed in glass therefore refracted at a different angle |
|
|
|
How can coloured objects separate white light? |
by absorbing some colours and refracting others |
|
|
|
What does the colour of an object depend on? |
which parts of the spectrum are reflected towards you eyes |
|
|
|
What colours does a red surface absorb? |
all the colour on the spectrum expect for red |
|
|
|
How does transparent light split white light? |
by absorbing some colours and allowing others to pass though |
|
|
|
The human eye only has three kinds of colour sensitive cones ( cells in the retina) what colors do these cells detect? |
blue, green and red |
|
|
|
Does our brain re-create colours? |
Yes |
|
|
|
What colour causes red cones to fire? |
Red |
|
|
|
What colours activate multiple cones? |
activates secondary colour |
|
|
|
What is the speed that all electromagnetic waves travel through the air? |
300,000 km/per second |
|
|
|
What are fields generated by? |
Oscillating electric charges |
|
|
|
What do electromagnetic waves usually consist of? |
Pulsing electric and magnetic fields. |
|
|
|
Luminous objects eg. compact fluorescent lights caused charged particles (mainly electrons) to be accelerated generating the pulsing magnetic and electric fields which we call electromeagenctic fields |
memorise |
|
|
|
What is the frequency of electromagnetic waves a measure of? |
The number of pulses of electric and magnetic fields generated per second |
|
|
|
What is the wavelength of an electromagnetic wave? |
The distance between adjacent crests or troughs in the electric or magnetic field. |
|
|
|
Electric and magnetic fields pulse at right angles too? |
The direction of motion of the wave |
|
|
|
What is the entire range of electromagnetic radiation called? |
The electromagnetic spectrum |
|
|
|
What does a higher frequency of the electromagnetic scale mean? |
It carries higher energy intesitiy therefore and penetrate objects like body tissue. |
|
|
|
UV light has a higher frequency than visible light which means? |
It has a greater energy intensity This causes materials to glow because the energy of UV light excites the molecules in these materials to emit visible light. |
|
|
|
What are radio waves? |
Radio waves include low-intensity electromagnetic waves including - tv, Am and Fm - Frequency of these waves cause electrons in receiving antennas of these devices to vibrate at the same frequency. |
|
|
|
What does the receiving antenna detect? |
detects the modulated wave |
|
|
|
What does AM stand for? |
Amplitude modulation |
|
|
|
What does FM stand for? |
Frequency modulation |
|
|
|
What do digital signals consist of? |
On and off pulses each representing a particular signal or strength value. |
|
|
|
What do both analogue and digital signals do as they travel through the air? |
Fade away |
|
|
|
When and why was the Coaxial cable designed? |
During WW1 to improve the speed of communications |
|
|
|
What can coaxial cable do? |
Simultaneously transmit many more telephone calls and television signals than the copper cables |
|
|
|
What do Coaxial cables consist of? |
A conducting wire at the centre that can carry analogue digital signals, surrounded by insulating materials and an outer conductor, this acts as a shield to minimise electrical and radio frequency. |
|
|
|
What type of waves allows mobile phone calls to be transmitted over long distances? |
High-frequency waves (microwaves) |
|
|
|
What of the range of Ghz that can carry many signals at the same time, but repeaters are needed so that the signals do not fade away? |
0.3GHz - 300 Ghz |
|
|
|
Why does each repeater twoer need to be within sight of the next one? |
Because radio waves travel in straight lines. |
|
|
|
What do communication satellites allow? |
High-frequency radio waves to be transmitted at the speed of light from continent to continent. This is done by signals which are transmitted to a satellite that is in a geostationary orbit (Orbits the earth once every 24 hours) |
|
|
|
What are optic fibres? |
Long thing flexible stands of glass |
|
|
|
How do optic fibres work? |
Electric signals from sources (e.g. microphones) are converted into high pulses of light, generally near-infrared range, which carries digital signals through the optic fibres. Light pulses received at the other end are converted back into electrical signals that cab be fed into things like speakers. |
|
|
|
What can light signals that go through optic fibres be converted into? |
many forms including microwaves. |
|
|
|
When was the laser invented? |
1958 |
|
|
|
What happens as beams travel through the optic fibres? |
The glass absorbs some of the energy. |
|
|
|
How often are repeaters needed along the optic fibres to amplify the signal? |
35-55km |
|
|
|
How is the glass in the optic fibre made so light won't escape through it? |
By covering glass with a cladding of denser glass and plastic. |
|
|
|
What is the process of total internal reflection? |
As light travels from the inner glass cone to the denser cladding it bends so much that instead of leaving the glass it is refracted back into it. |
|

