![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
12 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Solid |
firm and stable in shape; not liquid or fluid |

|
|
|
Liquid |
having a consistency like that of water or oil, i.e., flowing freely but of constant volume |

|
|
|
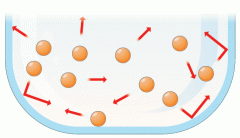
Gas |
an airlike fluid substance which expands freely to fill any space available, irrespective of its quantity
|
|
|
|
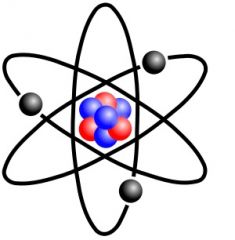
Atom |
the smallest component of an element having the chemical properties of the element, consisting of a nucleus containing combinations of neutrons and protons and one or more electrons bound to the nucleus by electrical attraction; the number of protons determines the identity of the element |
|
|
|
Property |
a description for the states of matter |

|
|
|
Mass |
In physics, the property of matter that measures its resistance to acceleration. Roughly, the mass of an object is a measure of the number of atoms in it. The basic unit of measurement for mass is the kilogram. |

|
|
|
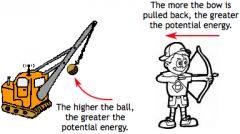
Potential Energy |
the energy possessed by a body by virtue of its position relative to others, stresses within itself, electric charge, and other factors
|
|
|
|
Kinetic Energy |
how fast or slow something moves |

|
|
|
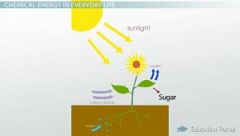
Chemical Energy |
___________ is stored in the bonds of chemical compounds (atoms and molecules). It is released in a chemical reaction, often producing heat as a by product (exothermic reaction). Batteries, biomass, petroleum, natural gas, and coal are examples of stored chemical energy.
|
|
|
|
Force |
In physics, something that causes a change in the motion of an object. The modern definition of force (an object's mass multiplied by its acceleration) was given by Isaac Newton in Newton's laws of motion.
|
|
|
|
Element |
An ___________ is a substance consisting of atoms which all have the same number of protons - i.e. the same atomic number. ___________ are chemically the simplest substances and hence cannot be broken down using chemical methods. __________ can only be changed into other _________ using nuclear methods.
|

|
|
|
Heat |
In physics, a form of energy associated with the movement of atoms and molecules in any material. The higher the temperature of a material, the faster the atoms are moving, and hence the greater the amount of energy present as ____.
|

|

