![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
49 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
define biodiversity
|
the diversity of life (how many individuals are present in a species, how many species in an ecosystem, how many ecosystems exist in an area etc.)
|
|
|
decribe the effects on biodiversity of alteration of a habitat
|
disrupts an ecosystems balance causing organisms to flee, adapt to new environment, or become extinct
|
|
|
the loss of only a few species of plants, animals, or microorganisms can disrupt the balance that drives important processes such as
|
gas exchange, soil fertilization, temperature regulation, etc
|
|
|
two human causes of ecosystems becoming disrupted are
|
increased pollution and decreased soil quality which can negatively affect human health
|
|
|
lack of biodiversity can also
|
induce the emergence and spread of infectious disease
|
|
|
explain how loss of biodiversity can negatively affect human health
|
potential medical treatments come from natural sources and the premature loss of different species elimates the possibility of new drug discovery
|
|
|
Trophic levels are based on
|
the feeding relationships that determine energy flow and chemical cycling
|
|
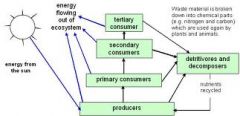
Explain the importance and function of each trophic level
|
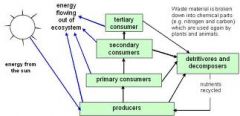
Producers: mainly consist of plants
Primary consumers: herbivores that eat plants or algae Secondary consumers: carnivores that eat the primary consumers Tertiary consumers: eat the secondary consumer Decomposers: consumers that feed of animal waste and dead organisms |
|
|
energy is ______ aas the trophic levels progess up the chain from producer to tertiary consumer
|
lost
|
|
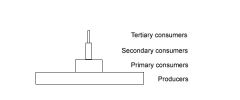
Explain the pyramid of numbers
|
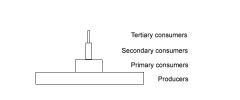
It is a representation of the population size of each trophic level. The producers, being the most populous, are on teh bottom of this period with the tertiary consumers on the top with the fewest numbers
|
|
|
Why is the stability of producers important
|
producers are vital for the carbon cycle
|
|
|
why is the stability of decomposers important
|
they recycle carbon, complete ammonification (essential in the nitrogen cycle), add phosphorous back to the soil
|
|
|
why is the stability of consumers important
|
regulate/balance the amount of food, water, shelter, and space for other organisms
|
|
|
predator/prey interactions
|
Also known as predation-results in benefit for one speices and a detriment for the other
Predation is when an animal (predator) eats another animal (its prey) |
|
|
What is another form of predation beside a carnivore consuming other animals
|
herbivorism is another form-animal (predator) eats a plant (prey)
does not always result in death of plant |
|
|
parasitism
|
a predator that lives on or in its host, causing detrimental effects to the host
|
|
|
example of parasitism
|
insects and virsuses living off and reproductin intheir hosts is an example of parasitism
|
|
|
competition
|
when 2 or more species in a community use the same resources
|
|
|
why is competition difficult to find in nature
|
because it is not continuous. Either the weaker population will die or one population will evolve to utilize other available resources
|
|
|
symbiosis
|
when two species live close together
|
|
|
example of symbiosis
|
parasitism
|
|
|
commensalism
|
occurs when 2 species occupy a similiar space and ONE species may benefit from the other, NO harmful effects to either
|
|
|
mutualism
|
when both species occupy a similiar space and BOTH benefit from each other
|
|
|
Species involved in mutualistic relationships must ______ to survive
|
coevolve
As one species evolves, the other must also evolve if it is to be successful in life |
|
|
the number of individuals per unit area or volume is
|
population density
|
|
|
population density changes to reflect the
|
rates of birth, immigration, emigration, and death
|
|
|
when birth rates are high,
|
population density INCREASES
|
|
|
when death rates are high,
|
population density DECREASES
|
|
|
when birth and death rates are even,
|
population density has reached equilibrium
|
|
|
immigration _____ population density, emigration _______ it and when the two are balanced the population is _____
|
swells
decreases level |
|
|
more consumers in any one area utilize resources so birth and immigration both ______ supply
|
drain
|
|
|
emigration and death decrease the population and its density, allowing natural resources to
|
replenish themselves
|
|
|
How can changes in climate alter the ecosystem-provide an example
|
Can alter the ability of organisms to grow
For instance, during drought conditions, plants that are less succulent are unable to maintain water regulation and perish. Organisms that fed on that particular plant must find a new food source or they will die off |
|
|
how can the introduction of nonnative species alter the ecosystem
|
can effectively wipe out an existing or indigenous species.
problematic because they reproduce rapidly, spread over large areas, and have few or no natural controls such as disease or predators to keep them in check |
|
|
who is responsible for the introduction of many nonnative species
|
humans
|
|
|
provide an example of the harmful result of the introduction of nonnative species
|
Introduction of the Zebra muscle.
these nonnative muscles are consuming the phytoplankton on which native species previously fed, and the nonnative speices are reproducing faster than the native species. Therefore the local food web is affected by a decrease in its lower level food supply |
|
|
how can changes in population size alter the ecosystem
|
as populations increase in size, they consume more resources and excrete more waste. these behaviors are a drain to the ecosystem
|
|
|
Living things in an ecosystem include plants, animals, bacteria, fungi, etc.
|
biotic factors
|
|
|
If one population in a community increases, it affects the ability of another population to succeed by
|
limiting the available amount of food, water, shelter, and space
|
|
|
non-living aspects of an ecosystem include soil quality, rainfall, and temperature
|
abiotic factors
|
|
|
changes in climate and soil can cause effects at the beginning of the food chain, thus
|
limiting or accelerating the growth of population
|
|
|
during times of decreased light, plants break down the products of photosynthesis through cellular _________
|
respiration
|
|
|
glucose, with the help of oxygen, breaks down and produces
|
carbon dioxide and water as wastes.
|
|
|
approximately ____% of the products of photosynthesis are used by the plant for energy
|
50%
|
|
|
_______ is the process by which plants make carbohydrates from the energy of the sun, carbon dioxide and water
|
photosynthesis
|
|
|
Photosynthesis occurs in the ________ where the pigment chlorophyll traps sun energy.
|
chloroplast
|
|
|
the two major steps of photosynthesis are
|
light and dark reactions
|
|
|
sunlight is trapped, water is split, and oxygen is given off. ATP is made and hydrogens reduce NADP to NADPH2. Which reaction is this
|
light reaction
the products of the light reactions enter into the dark reactions (calvin cycle) |
|
|
explain the dark reactions
|
carbon dioxide enters during the dark reactions which can occur with or without the presence of light. the energy is transferred from NADPH2 and ATP allow for the fixation of carbon into glucose.
|

