![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
45 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Atomic number |
number of protons in the nucleus of an atom |
|
|
Electrons |
negatively charged particles found in atoms |
|
|
Protons |
positively charged particle found in atoms |
|
|
Metalliods |
elements with properties between those of metals and non-metals |
|
|
History of the periodic table |
- Democritus 460-370BC - Antoine Lavoisier 1743-1799 - John Dalton 1766-1849 - Joseph John Thompson 1856-1940 - Ernest Rutherford 1871-1937 - Niels Bohr |
|
|
Metalloids |
elements with properties between those of metals and those of non-metals (e.g. silicon and arsenic) |
|
|
Optical fibres |
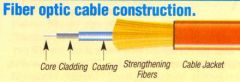
thin strand of glass of plastic that carries information as a light signal |
|
|
Frequency |
the number of waves that pass through a certain point in one second, measured in Hertz (Hz) |
|
|
Dimitri Mendeleev |
- 1834-1907 - Came up with 63 elements - wrote the names and properties of the element on cards and arranged them in order of atomic weight |
|
|
Convection |
transfer of thermal energy in a liquid or gas involving the movement of the material |
|
|
Nuclear radiation |
- 3 forms - Alpha, Beta, and gamma - neutrons in the nucleus |
|
|
Graphing |
5 marks - 1 for heading - 1 for scale - 1 for line of best fit - 1 for units of measurement |
|
|
Variables |
2 types - Independent - what you change - dependent - measurement Also: - controls anything that you keep to make it a fair test |
|
|
Radiation |
Emission of energy from the nucleus of an atom as either particles or waves |
|
|
Refraction |
process where light slows down in different materials |
|
|
lenses |
A curved piece of transparent material such as glass or plastic
|
|
|
Radioactive decay |
when the ratio of neutrons to protons becomes to high, the nucleus is unstable and it decays or changes into another isotope. it causes an emission of radiation
|
|
|
Atomic mass |
the weight of an atom
- mostly made up of neutrons and protons - electrons weight very little |
|
|
Molecules |
atoms joined together e.g. O + O = O2 |
|
|
Electron configuration |
arrangement of electrons in an atom in energy levels with a specific number of electrons |
|
|
Covalent Bonding |
bonding formed when two atoms share one or more pairs of electrons |
|
|
Ionic Bonding |
bonding formed between positively and negatively charged ions
|
|
|
Sound Waves |
- travels as a longitudinal wave
- travel as compression and rarefaction - needs a medium to travel through |
|
|
Light |
- transverse waves
- up and down - does not need a medium to travel through - moves like a slinky spring |
|
|
Electromagnetic Spectrum |
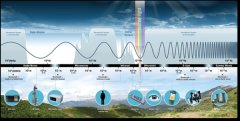
The electromagnetic (EM) spectrum is the range of all types of EM radiation. |
|
|
How is radiation used in medical? |
- X-rays - diagnosing conditions - Treating Cancer |
|
|
Alpha Particles |
- positively-charged particle emitted from the nucleus of a radioactive atom; identical to a helium nucleus - 2 protons, 2 neutrons
- paper can stop alpha particles |
|
|
Beta Particles |
- negatively-charged particles emitted from the nucleus of a radioactive atom; identical to an electron
- light metals stop beta particles |
|
|
Gamma Particles |
- high-frequency electromagnetic radiation similar to X-rays but of shorter wavelength - Lead stops gamma rays |
|
|
Microwave uses |
- cooking food
- Mobile phones, this that they don't have to be very big - speed cameras and radars |
|
|
Wave Formula |
v = f x y
V = speed of waves (m/s) F = frequency of the wave (Hz) Y = wavelength (m) |
|
|
Radioisotopes |
different form of the atoms of an element that have the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons. |
|
|
Atoms |
smallest particle of matter that cannot be created, destroyed or broken down (invisible)
|
|
|
Neutrons |
neutral particles found in the nucleus' of atoms |
|
|
Valence shell |
the outer most shell of an atom
|
|
|
Metals |
Class of chemical elements with similar properties:
- lustrous (shiny) - good conductors of heat and electricity - malleable - ductile |
|
|
Non-metals |
elements that do not show the properties common to all metals
|
|
|
Wavelength |
length between the same point on a repeating wave
|
|
|
Conduction |
transfer of thermal energy involving a direct contact with no movement of material
|
|
|
Heat energy |
energy produced by heat |
|
|
Types of waves
|
- Transverse - light - Longitudinal - sound |
|
|
reflection |
light bounced off a surface |
|
|
Concave Lens |
- lens that is thinner in the centre than at the edges
- cause light rays passing through to diverge (move apart) |
|
|
Convex Lens |
- lens that is thicker in the centre than at the edges - causes light rays passing through to converge (move together) |
|
|
Half-Life |
- time taken for half of the radioactive nuclei in a sample to decay
- time taken for the radioactivity of a sample to drop to half of what it was |

