![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
24 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Autotrophs |
Organism uses photosynthesis to get energy |
|
|
Heterotrophs |
Organism uses other organisms to get energy |
|
|
Herbivores |
Organism eats plants |
|
|
Secondary consumer |
Organism eats herbivores |
|
|
Tertiary consumer |
Organism eats secondary consumers |
|
|
Carnivore |
Organism eats organism |
|
|
Omnivore |
Organism eats both plants & organisms |
|
|
Main energy source on Earth |
Sun |
|
|
Scavenger |
Organism eats dead/decaying organisms that it did not kill itself |
|
|
Decomposer |
Organism eats dead organisms & plants & breaks them down into simpler molecules |
|
|
Energy pyramid |

- More organisms at bottom - More energy at bottom (100%) - More biomass at bottom - 10% energy transfer from trophic level to trophic level, rest lost through heat |
|
|
Biomass pyramid |

- More organisms at bottom - More energy at bottom (100%) - More biomass at bottom |
|
|
Number pyramid |
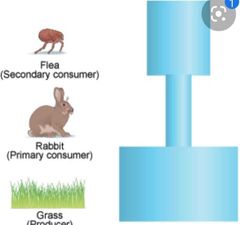
- Imperfect pyramid |
|
|
Trophic levels |

- Number of steps from sun - 10% of energy is passed from trophic level to trophic level |
|
|
Laws of thermodynamics |
- Energy cannot be created or destroyed - Some energy is lost as heat |
|
|
Food chain |
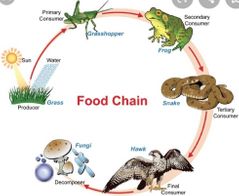
|
|
|
Food web |

|
|
|
Water cycle |
Evaporation: liquid from bodies of water to gas Transpiration: liquid from plants to gas Condensation: gas from clouds to liquid Precipitation: liquid to Earth Runoff: liquid from mountains to bodies of water Groundwater: water beneath the Earths surface |
|
|
Carbon cycle |

Carbon source releases Carbon Carbon sink stores Carbon Plants take in carbon dioxide and water and make oxygen and sugar through photosynthesis Animals breath and so do humans cellular respiration |
|
|
Nitrogen cycle |

the process of turning the nitrogen in the atmosphere into something that plants and animals can use |
|
|
Oxygen cycle |
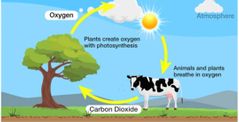
|
|
|
System of the earth |
Closed (only energy transferred) |
|
|
Human impacts |
- eutrophication - oilfields - pollution - climate change - deforestation - using ground water - fossil fuels |
|
|
Cellular respiration |
Cells convert chemical energy stored in sugars into energy for cells to use |

