![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
15 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Name 5 types of precipitation.
|
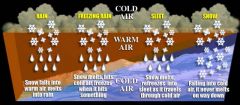
1. rain
2. sleet 3. freezing rain 4. hail 5. snow |
|
|
What is rain?
|

Rain is the most common kind of precipitation. Raindrops must be at least 0.5 millimeters in diameter.
|
|
|
How large must drops of rain be?
|

Drops of water must be atleast 0.5 millimeters in diameter. (Note for scale: 0.5 millimeter = 2/100 inch, do not need to know inches)
|
|
|
What is sleet?
|
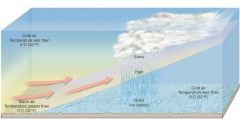
Ice particles smaller than 5 millimeters in diameter. (A form of precipitation.)
|
|
|
What is freezing rain?
|
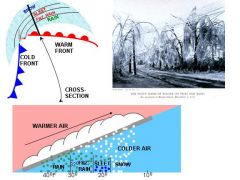
Rain that freezes when it touches the ground.
|
|
|
What is hail?
|

Round pellets of ice larger than 5 millimeters. (A form of precipitation.)
|
|

What is snow?
|
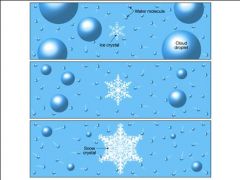
Water vapor (in a cloud) converted directly into ice crystals.
|
|
|
How many sides or branches does every snowflake have?
|

Every snowflake has six sides.
|
|
|
What is used to measure the amount of rain that falls?
|
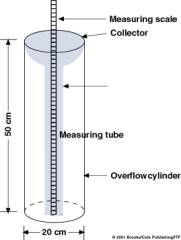
A rain guage
|
|
|
Name the 2 ways snowfall can be measured?
|

1. A ruler (pushed into the snow on the ground).
2. Melting the collected snow and measuring the depth of water it produces. |
|
|
What is a drought?
|

A long period of unusually low precipitation.
|
|
|
What is cloud seeding?
|
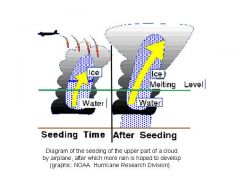
A method of producing rain from clouds by sprinkling dry ice or silver iodide from planes into the clouds.
|
|
|
What is precipitation?
|
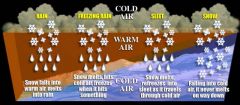
Any form of water that falls from clouds and reaches the Earth's surface.
|
|
|
What must hapen for water droplets or ice crystals to fall to Earth?
|
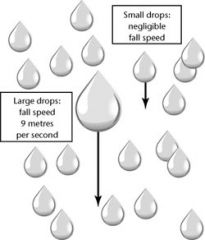
They must grow heavy enough to fall through the air.
|
|
|
What 3 factors are needed for precipitation to occur?
|
There must be:
1. water vapor 2. cold temperatures (dew point must be reached) 3. presence of particals |

