![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
10 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Hertzsprung Russel Diagram |
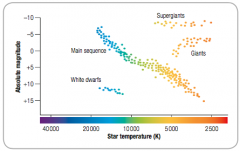
|
|
|
Size and brightness of star |
Two factors determine the brightness of a star: luminosity - how much energy it puts out in a given time distance - how far it is from us |
|
|
Life cycle of a star |
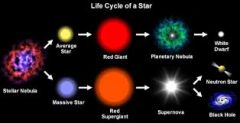
|
|
|
Main sequence star |
These are the most numerous true stars in the universe, and include the Earth's Sun. After a star has formed, it generates thermal energy in the dense core region through nuclear fusion of hydrogen atoms into helium |
|
|
What is inertia |
Inertia is the resistance of any physical object to any change in its state of motion; this includes changes to its speed, direction, or state of rest. It is the tendency of objects to keep moving in a straight line at constant velocity. |
|
|
What is energy |
Energy is the driving force for the universe. Energy is a quantitative property of a system which may be kinetic, potential, or other in form. There are many different forms of energy. One form of energy can be transferred to another form. |
|
|
Weight & mass |
The mass of an object is a measure of the object's inertial property, or the amount of matter it contains. The weight of an object is a measure of the force exerted on the object by gravity, or the force needed to support it. The pull of gravity on the earth gives an object a downward acceleration of about 9.8 m/s2. |
|
|
Velocity time graph |
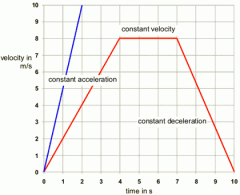
|
|
|
Acceleration |
Acceleration is a measure of the change in velocity over time. Zero acceleration means there is no change in velocity over time, namely constant velocity. Constant velocity can be any velocity (including zero velocity or "at rest"), so the object's velocity doesn't have to be zero to have zero acceleration. |
|
|
Balanced and unbalanced forces |
When balanced forces act on an object at rest, the object will not move. If you push against a wall, the wall pushes back with an equal but opposite force. Neither you nor the wall will move. Forces that cause a change in the motion of an object are unbalanced forces. |

