![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
25 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Microscopes |
- Provide inner view - Magnification up to x1000 |
|
|
Stereo Microscopes |
- Binocular microscopes - Can be any specimen - Use lenses in 2 directions - Magnification up to x100 - Shows a 3D image |
|
|
Electron Microscopes |
- 2 types of electron microscopes - SEM and TEM
|
|
|
TEM |
Transmission Electron Microscope Specimen needs to be thin Electrons pass through Looks like xxxxx |
|
|
SEM |
Scanning Electron Microscope Specimen can be anything Electrons reflect Looks like little blobs or tadpoles |
|
|
Binocular Microscope |
A light microscope that has two ocular lenses |
|
|
Monocular Microscope |
A light microscope that has only one ocular lens |
|
|
Light Microscope |
A microscope that uses light to reveal the image |
|
|
Parts Of A Light Microscope |
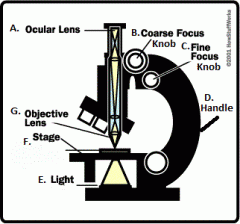
A. Ocular Lens B. Course Focus Knob C. Fine Focus Knob D. Handle E. Light F. Stage G. Objective Lens
|
|
|
Calculate The Magnification Of A Microscope |
Multiply the magnification of the ocular lens by the magnification of the objective lens |
|
|
Parts Of A Animal Cell |
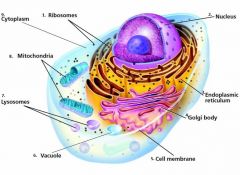
1. Ribosomes 2. Nucleus 3. Endoplasmic Reticulum 4. Golgi Bodies 5. Cell Membrane 6. Vacuole 7. Lysosomes 8. Mitochondria 9. Cytoplam |
|
|
Parts Of An Plant Cell |
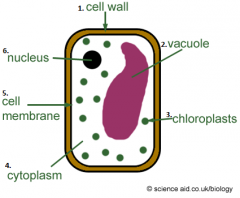
1. Cell Wall 2. Vacuole 3. Chloroplasts 4. Cytoplasm 5. Cell Membrane 6. Nucleus |
|
|
Parts Of A Fungal Cell |
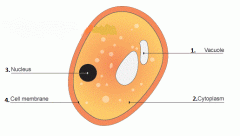
1. Vacuole 2. Cytoplasm 3. Nucleus 4. Cell Membrane |
|

Golgi Bodies |
Stacks of membrane covered sac's that package and move proteins to the outside of the cell |
|

Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) |
A folded membrane that moves materials around the cell |
|

Chloroplast |
Contains a green pigment called "chlorophyll" which is what makes the plant green |
|

Cell Wall |
Rigid structure outside the cell membrane that protects the cell It is the outside wall |
|

Cell Membrane |
Forms the outer boundry of the cell and only allows certain substances to move in and out of the cell like food and water and carbon dioxide out. Inside Wall |
|

Nucleus |
Largest organelle in the cell, directs all the activities of the cell around. |
|

Nuclear Membrane |
Outside of the nucleus |
|

Vacuole |
A temporary storage place for the cell, holds sap and water. |
|

Vacuole Membrane |
The thin layer that seperates the vacuole from the cytoplasm |
|

Cytoplam |
Jelly like substance inside the cell that the organelles all float in |
|

Chlorophyll |
Provides the green pigmentation present in all cells |
|
|
How Do Cells Form A Body? |
cell - tissue - organs - organ system - body |

