![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
68 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Question:
What is a LogBook used for |
A complete record of your investigation, thoughts and ideas.
|
|
|
Question:
What is the Variable |
An observation/measurement that can change during an experiment.
|
|
|
Question:
What is the Independent variable |
The variable that deliberately changes in an experiment.
|
|
|
Question:
What is the Dependant variable is |
The variable that depends on the independant variable. The variable is what we measure and what is affected during an experiment.
|
|
|
Question:
What is the control is |
The control is the one without the independant variable. The control is used to see what would happen if you didn't do anything to it but kept everything else constant.
|
|
|
Question:
What does a report contain |
Abstract, Introduction, Aim, Hypothesis, Materials, Method, Results, Discussion, Conclusion and Bibliography.
|
|
|
Question:
What is Cellular Respiration |
Cellular Respiration is the process of breaking down of glucose so that energy is released in a form for our cells then can use. Oxygen is essential for cellular respiration.
Glucose + Oxygen --> Carbon Dioxide + Water + Energy (ATP) |
|
|
Question:
What is the Respiratory System responsible for |
The Respiratory System is responsible for getting oxygen into the body and carbon dioxide out of the body.
|
|
|
Question:
What is the Circulatory System responsible for |
The Circulatory System is responsible for transporting Oxygen and nutrients to cells and wastes away from them.
Heart --> Artery --> Capillary --> Body cells --> Capillary --> Vein |
|
|
Question:
Oxygenated blood travels through the |
The oxygenated blood travels through the pulmonary vein to the left atrium of heart, then the left ventricle of heart, then the aorta, then the arterioles, then capillary and then body cell.
|
|
|
Question:
Deoxygenated blood travels through the |
The deoxygenated blood travels through the capillary to the venules, then the vena cava, then the right atrium of heart, then the right ventricle of heart, then the pulmonary artery and then to the lungs.
|
|
|
Question:
What is the digestive system is responsible for |
The Digestive system is responsible to supply our body with nutrients it requires from food.
|
|
|
Question:
a. Where is villi located b. What does the villi do c. Why is villi shaped like fingers |
a. Small intestine
b. The absorption of nutrients and molecules. c. To maximum surface area to increase the efficiency of nutrients being absorbed into the surrounding capillaries. |
|
|
Question:
What does the Pancreas makes |
The pancreas makes enzymes which are lipases, amylases and proteases that turn the food into molecules and are sent to the small intestine.
|
|
|
Question:
What does the Liver do |
Has 500 different functions (sorting, toring and changing digested foods.) It creates bile, where it is involved in mechanical digestion of lipids (fats and oils). It removes excess protein because it can form toxic compounds. The liver converts waste products to the kidneys. It changes dangerous substances so it doesn't harm the body.
|
|
|
Question:
What does the Kidney do |
Kidney is made up of approximately one million nephrons which filters blood, remove waste products and chemicals in excess which all of that keeps various chemicals and water within appropriate levels.
|
|
|
Question:
Define 'population' |
A group of organisms of the same species in the same area.
|
|
|
Question:
Define 'community' |
Populations of organisms living together in the same habitat.
|
|
|
Question:
What is an ecosystem? |
An ecosystem is a complex level of organisms made up by living and non-living (water, temperature, light and pH) parts. Dynamic system of organisms interacting with each other and the environment.
|
|
|
Question:
Define 'ecology' |
The study of ecosystems.
|
|
|
Question:
What are Producers |
also known as Autotrophs because they are self feeders and don't rely on other organisms. Producers are the base of the food chain and essential. Producers use photosynthesis to capture light energy and convert inorganic substances into organic substances. Plants create oxygen as a waste product.
|
|
|
Question:
What are Consumers |
also known as Heterotrophs because they are unable to make their own food and obtain their nutrition from consuming other organisms.
|
|
|
Question:
a. What are Herbivores b. What are Carnivores c. What are Omnivores d. What are Detritivores |
a. Herbivores eats plants and are primary consumers.
b. Carnivores eat other animals and are secondary consumers. c. Omnivores eat plants and animals to obtain their full nutrition. d. Release enzymes to break down organic matter and absorbs products that have been externally digested. |
|
|
Question:
What do the Decomposers do |
Decomposers convert organic matter into inorganic matter. The waste is returned to the environment to be recycled by producers.
Eg. Bacteria and Fungi. |
|
|
Question:
a. What is competition b. What is intraspecific competition c. What is Interspecific competition |
a. The competition happens when organisms within an ecosystem will compete where their needs overlap.
b. The competition of resources from the members of the same species. c. The competition of resources between members of different species. |
|
|
Question:
What is Predator-prey relationships |
One species kills and eats another, the predator is the killer and the prey is the food source.
|
|
|
Question:
What is Herbivore-plant relationships |
Plants can be eaten by herbivores but they may contain physical structures/chemicals to prevent them from eating it.
|
|
|
Question:
What is Symbiotic relationships |
Organisms living together depend on each other.
Eg. Parasitism, the parasite benefits but the host is harmed. Mutualism, both species benefit. Commensalism, one species benefits but the other does no harm. |
|
|
Question:
What is distribution |
The quantity of organisms of how far a species has travelled and/or spread out.
|
|
|
Question:
What is density |
Density is the quantity of organisms in a given area.
|
|
|
Question:
What is the tolerance range |
The range where a type of species can tolerate such temperatures.
|
|
|
Question:
What is the optimum range |
The ideal range where a type of species can function its best.
|
|
|
Question:
Name the three sampling methods used to estimate the density and distribution and state what is each one is used for. |
Transects are used to estimate the density and distribution when environmental conditions vary along the sample under investigation.
Quadrats are used to estimate the distribution and abundance of organisms that are stationary or don't move much. Mark, Release and Recapture is used to determine the abundance of mobile species. |
|
|
Question:
State the Estimated average density equation |
Estimated average density = total no. of individuals counted divided by no. of quadrats x area of each quadrat.
|
|
|
Question:
a. What do the roots do b. What do the roots hair do |
a. The roots help anchor the plant and obtain oxygen, water and mineral salts from the soil.
b. The root hairs increase the amount of surface area for more absorption. |
|
|
Question:
a. What is being transported in the phloem b. What is that process called c. Name some substances being transported in the phloem |
a. Organic substances are transported up and down the plant.
b. Translocation. c. Sugar (Glucose), Nitrogenous compounds (amino acids and soluble carbohydrates. |
|
|
Question:
a. What is being transported in the xylem b. What is that process called c. Why do xylem vessels have strong thick walls |
a. Water is transported from the roots and out through the stomata as water vapour.
b. Transpiration. c. To help hold up and support the plant. |
|
|
Question:
Vascular bundles are |
Vascular bundles are groups of phloem and xylem vessels located together.
|
|
|
Question:
Chloroplasts are |
Leaf cells that contain organelles called chloroplasts. Chloroplasts contain chlorophyll, a green pigment that is involved in capturing light energy. The synthesis of glucose also occurs in the chloroplasts.
|
|
|
Question:
Flaccid happens when |
Flaccid happens when the water has moved out of the cell vacuoles and the cells turn because water is in short supply.
|
|
|
Question:
Turgid happens when |
Turgid happens when the plant has plenty of water and opens the pore to take in carbon dioxide in and oxygen out.
|
|
|
Question:
a. Stomata is located b. What does the stomata do c. Why does the stomata in the leaves help pull the water up |
a. Located on the underside of the leaves.
b. The exchanges of gases take place. Oxygen and carbon dioxide. c. Evaporation of water |
|
|
Question:
What are Flowers is made up of |
Flowers are made up of reproductive structures. Within the flower there are structures that product gametes. Anthers produce pollen grains and ovaries produce ova.
|
|
|
Question:
a. What is fertilisation b. What is pollination c. What are the three other types of pollination |
a. The penetration of the ovum by a sperm.
b. When pollen grains lands on the stigma. c. Cross-pollination is when pollination with other plants or from other species. WInd-pollination is when pollen is transferred between plants by the wind. Insect/animals as vectors that carry their pollen between plants and reward the animal with food. |
|
|
Question:
a. What is photosynthesis b. Name the reactants of photosynthesis c. Name the products of photosynthesis d. State the chemical equation of photosynthesis |
a. Photosynthesis is the process of capturing light energy and its conversion into chemical energy, it involves using light energy to synthesis glucose.
b. Carbon dioxide + Water c. Glucose + Oxygen + Water d. |
|
|
Question:
What is Metabolism is |
The chemical reactions occuring within an organism that enable the organism to use energy and grow and repair cells.
|
|
|
Question:
a. What is Aerobic Respiration b. State the word equation for aerobic respiration.. c. State the chemical equation for aerobic respiration |
a. The chemical process of glucose breaking down so that energy is released in a form for cells to use.
b. Glucose + Oxygen ---> Carbon dioxide + Water + Energy c. |
|
|
Question:
What are the three stages of Aerobic Respiration |
Glycolysis occurs in the cytosol of the cell and doesn't require oxygen. The next two stages, the Krebs cycle and electron transport chain reactions that occur in the mitochondria.
|
|
|
Question:
a. What is Anaerobic respiration b. State the word equation of Anaerobic Respiration for animals and humans c. State the word equation of Anaerobic Respiration for plants |
a. The chemical process of food breaking down without needing oxygen.
b. Glucose ---> Lactic Acid + Energy c. Glucose --> Ethanol + Carbon dioxide + Energy |
|
|
Question:
a. What are protons b. What are electrons c. Why are atoms electrically equal |
a. Protons have a positive electric charge.
b. Orbit the nucleus and have an electric charge and equal in size to a proton but has 1/1800 of the mass of a proton. c. There's equal amount of electrons and the number of protons in its nucleus. |
|
|
Question:
State the Law of Conservation of Mass |
That matter cannot be created or destroyed during a chemical reaction.
|
|
|
Question:
State the Law of Constant Proportions |
A compound, no matter how it is formed, always contain the same relative amounts of each element.
|
|
|
Question:
What are exothermic reactions? |
Exothermic reactions is when there's less energy stored in the chemical bonds in the products than there was in the reactants.
|
|
|
Question:
What are endothermic reactions? |
Endothermic reactions is when energy is absorbed from the surroundings where the chemical bonds of the products contain more energy 'stored' than in the reactants.
|
|
|
Question:
What is chemical energy? |
Chemical energy is when energy of the substances is transformed by breaking the chemical bonds but do not make a new substance. Eg. Hand warmers (Iron + Oxygen --> Iron oxide)
|
|
|
Question:
What is the chemical process |
The chemical process is when chemical bonds are broken and form a new substance.
|
|
|
Question:
a. State the properties of acids. b. State the properties of bases. |
a. Acids are corrosive, sour and many acids in fruits are safe to eat.
b. Bases have a bitter taste, slippery or soapy to touch and corrosive. |
|
|
Question:
a. What are alkalis b. What is a pH scale used for c. What happens when you mix an acid and a base together |
a. Alkalis is when bases that can be dissolved in water.
b. To see how acidic or basic a substance is, ranging from 0-14. c. They neutralise and form products including water and a salt. |
|
|
Question:
What is pickling |
Pickling is the process of preserving food by putting in vinegar.
|
|
|
Question:
What is combustion |
The chemical process when a substance reacts with oxygen and heat is released.
Respiration is a slow combustion reaction. Oxidation reactions are combustion reactions where the transfer of electrons from a reactant and doesn't require oxygen. |
|
|
Question:
a. What are fossil fuels b. The products of combustion always include |
a. Fossil fuels can be natural gas, petrol and coal are formed from the remains of living things.
b. Carbon dioxide and water |
|
|
Question:
a. Where is Natural gas is used in b. What liquid do most cars use c. What fuel does a jet aircraft use |
a. Gas stoves and ovens.
b. Liquid octane from crude oil. c. Kerosene from crude oil. |
|
|
Question:
What is our Earth made up of? |
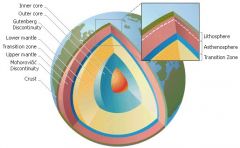
The atmosphere, a blanket of gases on the Earth.
Hydrosphere, the water on the surface of the Earth. Crust, solid rock and rigid. Mantle is partially molten rock from temperatures of 500°C to 2000°C. Outer core is made up of molten iron and nickel where the temperatures between 4000°C to 6000°C. The inner core is mostly iron, solid owing to extreme pressure and temperatures can be 7000°C |
|
|
Question:
What is the 'supercontinent' called when all the continents were joined together. |
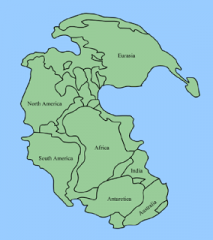
The land was called Pangaea, and the sea was called Panthalassa.
|
|
|
Question:
a. Why do the plates move? b. What is the convection current? |
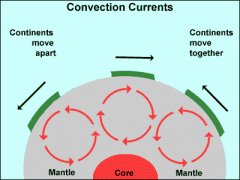
a. It is because of the heat causes the partially molten rock in the mantle to expand and rise towards the surface.
b. It spreads out, cools and falls back called the convection current where keeps the plates moving slowly. |
|
|
Question:
What is subduction? |
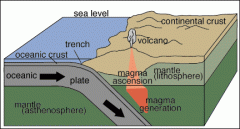
Subduction happens when two plates push against each other, the oceanic crust pushes against continental crusts and the oceanic crust sinks below the continental crust.
|
|
|
Question:
a. What is an anticline? b. What is a syncline? |
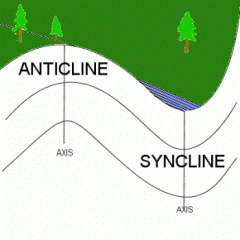
a. ______--------_______
b. -------_______-------- |
|
|
Question:
a. What is a fault? b. What is a slip fault? |
a. When there's movement along a crack where the crack was formed from huge forces acting on them.
b. Blocks of the crust slip horizontally past each other. |

