![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
66 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What does DNA stand for |
deoxyribonucleic acid |
|
|
|
Where is DNA found |
In the nucleus |
|
|
|
What are the four nitrogenous bases that are found on a DNA molecule |
Adenine Guanine Cytosine Thymine |
|
|
|
Label a DNA molecule |
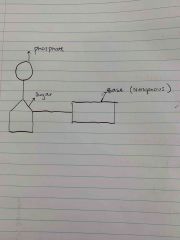
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
What is the complementary base paring TIL for DNA |
Adenine (A) pairs with Thymine(T) Guanine (G) pairs with Cytosine (C) |
|
|
|
What is the difference between Mitosis and Meiosis |
Mitosis is a asexual reproduction method, occurs in all organism, produces identical cells, it does not cross over and produces 2 daughter diploid cells Meioisis is a sexual cellular reproduction method only occurs in the reproduction cells of organisms, it mixes chromosomes and produces 4 haploid daughter cells |
|
|
|
What is the difference between a diploid and a haploid number of cells |
Diploid have 2 complete sets of chromosomes Haploid has one complete chromosomes |
|
|
|
How many chromosomes does a normal somatic cell have |
46 chromosomes |
|
|
|
How many chromosomes does a sex cell have |
23 chromosomes |
|
|
|
What are the sex chromosomes of a male |
X,y |
|
|
|
What are the sex chromosomes of a female |
Xx |
|
|
|
What does a gamete mean |
A mature haploid male or female germ cell |
Ovum/sperm |
|
|
Is is male or female sex cells that contain the Y chromosomes that determines sex |
Male |
|
|
|
What is meant by a homologous pair of chromosomes |
A set of one maternal and one paternal chromosomes that pair up with each other |
|
|
|
What is karyotyping |
Karyotyping is the process of pairing and ordering all of the chromosomes of an organism. |
|
|
|
What is the definition of a genotype |
A genotype is a set of alleles that determines the expression of a particular characteristic or trait |
|
|
|
What is a phenotype |
The set of observable characteristics of an individual resulting from the interaction of its genotype with the environment |
|
|
|
What is an allele |
The variation within a gene |
|
|
|
What is a punnet square |
A square diagram that is used to predict the genotype of a particular cross or breeding experiment |
|
|
|
What is complete dominance |
A form of dominance in heterozygous condition where the Allee that is dominant completely masks the effect of the recessive allele |
|
|
|
What is incomplete dominance |
It is a form of intermediate inheritance in which one allele is not completely expressed over it paired allele |
|
|
|
What is codominance |
A form of dominance where the allele of a gene pair in a heterozygote are fully expressed |
|
|
|
What is natural selection |
Natural selection is the process where organisms better adapted to their environment tend to survive and produce offspring |
|
|
|
What is artificial selection |
A form of selection in which humans actively choose which traits should be passed into offspring |
|
|
|
What is evolution |
The change in heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations |
|
|
|
What is evolution |
The change in heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations |
|
|
|
What is adaption |
The process of change by which an organism or species become better suited to its environment |
|
|
|
What is evolution |
The change in heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations |
|
|
|
What is adaption |
The process of change by which an organism or species become better suited to its environment |
|
|
|
What is a mutation |
When DNA gene is damaged or changed in a way as to alter the genetic message carried by that gene |
|
|
|
What is evolution |
The change in heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations |
|
|
|
What is adaption |
The process of change by which an organism or species become better suited to its environment |
|
|
|
What is a mutation |
When DNA gene is damaged or changed in a way as to alter the genetic message carried by that gene |
|
|
|
What is genetic isolation |
A population of organisms that has little genetic mixing with other organisms within the same species and prohibits much genetic variation |
|
|
|
What is evolution |
The change in heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations |
|
|
|
What is adaption |
The process of change by which an organism or species become better suited to its environment |
|
|
|
What is a mutation |
When DNA gene is damaged or changed in a way as to alter the genetic message carried by that gene |
|
|
|
What is genetic isolation |
A population of organisms that has little genetic mixing with other organisms within the same species and prohibits much genetic variation |
|
|
|
What is Selective agent |
The environment based factor which has huge impact on the mortality rate of a select organism |
|
|
|
What is evolution |
The change in heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations |
|
|
|
What is adaption |
The process of change by which an organism or species become better suited to its environment |
|
|
|
What is a mutation |
When DNA gene is damaged or changed in a way as to alter the genetic message carried by that gene |
|
|
|
What is genetic isolation |
A population of organisms that has little genetic mixing with other organisms within the same species and prohibits much genetic variation |
|
|
|
What is Selective agent |
The environment based factor which has huge impact on the mortality rate of a select organism |
|
|
|
What isvariation |
Any difference between cells and organisms caused by genetics difference or by the effect of environmental factors |
|
|
|
What is evolution |
The change in heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations |
|
|
|
What is adaption |
The process of change by which an organism or species become better suited to its environment |
|
|
|
What is a mutation |
When DNA gene is damaged or changed in a way as to alter the genetic message carried by that gene |
|
|
|
What is genetic isolation |
A population of organisms that has little genetic mixing with other organisms within the same species and prohibits much genetic variation |
|
|
|
What is Selective agent |
The environment based factor which has huge impact on the mortality rate of a select organism |
|
|
|
What isvariation |
Any difference between cells and organisms caused by genetics difference or by the effect of environmental factors |
|
|
|
The 3 ways fossil record supports evolution |
Older fossil are less complex than newer ones The number of species in existence seems to be increasing and more species spilt into several Fossil show the transition between species |
|
|
|
What are homologous structures how do they support evolution |
They are characteristics of a organism that have the same basic structure across many species Eg: mammal, birds and reptile all have they same bones and bone structure In their forearm |
|
|
|
What are homologous structures how do they support evolution |
They are characteristics of a organism that have the same basic structure across many species Eg: mammal, birds and reptile all have they same bones and bone structure In their forearm |
|
|
|
What is autotroph |
Autotrophs are organisms that are able to make energy-containing organic molecules from inorganic raw material using energy from things like the sun |
|
|
|
What are homologous structures how do they support evolution |
They are characteristics of a organism that have the same basic structure across many species Eg: mammal, birds and reptile all have they same bones and bone structure In their forearm |
|
|
|
What is autotroph |
Autotrophs are organisms that can produce their own food from substance in their surroundings using sunlight |
|
|
|
What are Heterotrophs |
Organisms that rely on other organisms for nutrition and energy |
|
|
|
What is a detritivore |
Organisms that eat **** ( decomposing plant or animal parts as well as feces) |
|
|
|
Different ways we can sample a ecosystem |
Quadrats, by counting the number of different organisms in a set square There is also pitfall traps, and sweep nets |
|
|
|
Different ways we can sample a ecosystem |
Quadrats, by counting the number of different organisms in a set square There is also pitfall traps, and sweep nets |
|
|
|
What is a trophic level |
The number of steps a organism is from the start of the chain. Producer are at level 1 |
|
|
|
Different ways we can sample a ecosystem |
Quadrats, by counting the number of different organisms in a set square There is also pitfall traps, and sweep nets |
|
|
|
What is a trophic level |
The number of steps a organism is from the start of the chain. Producer are at level 1 |
|
|
|
How much energy is passed on at each level of a energy pyramid |
A 10th of energy is passed down by each level |
|
|
|
Order of complexity |
Organism->population->community->ecosystem |
|

