![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
30 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is DNA? |
- a self replicating which is present in nearly all living organisms as the main component of chromosomes - the carrier of genetic information |
|
|
Describe the basic structure of DNA. |
DNA is made up of six smaller molecules, a five carbon sugar called deoxyribose, a phosphate molecule and four different nitrogenous bases (adenine, thymine, cytosine and guanine). |
|
|
Draw the basic structure of DNA. |
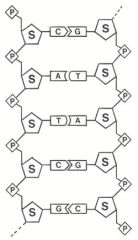
|
|
|
What base can Adenine bind to? |
Adenine can only bind to Thymine. |
|
|
What base can Guanine bind to? |
Guanine can only bind to Cytosine. |
|
|
Where is our DNA found? |
DNA is found in the nucleus of a cell. |
|
|
What structure is our DNA found as? |
Each base pair (A, T, C, G) is attached to a sugar molecule and a phosphate molecule, a base, sugar, and phosphate are called a nucleotide. Nucleotides are arranged in two long strands that form a spiral called a double helix. |
|
|
What is a karyotype and why are they useful to study? |
A karyotype is a visual diagram of a persons chromosomes. It can be used to if a baby will have a genetic disorder and if so, which one they will have. |
|
|
What are sex cells and what is another word for them? |
Sperm and egg, also known as gametes. |
|
|
Describe the difference between somatic cells and sex cells. |
Sex cells are difference in males and females (sperm and egg), somatic cells are any cells in a living organism other than the reproductive (sex) cells |
|
|
How many chromosomes are there in human somatic cells? What about human sex cells? |
46 chromosomes, organised into 23 pairs. There is only one chromosome in hu |
|
|
What combination of sex chromosomes do females have? What about males? |
Females have two sets of X chromosomes (X, X) while males have one X and one Y. |
|
|
Explain how the sex of a child is determined. |
The father determines the sex a child. A mother only has two X chromosomes, so she can only give an X which is a girl. A father has boy an X and a Y, so he can give either and that determines the gender. |
|
|
What does diploid mean? |
(of a cell or nucleus) containing two complete sets of chromosomes, one from each parent. |
|
|
What does haploid mean? Why are sex cells haploid? |
(of a cell or nucleus) having a single set of unpaired chromosomes. Sex cells also only have on set chromosomes, body cells have two. |
|
|
If a diploid cell has 62 chromosomes how many will its corresponding haploid cell have? |
31 |
|
|
What is mitosis? What sort of cells are involved? |
There are four stages of mitosis. Prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase. It is where somatic cells (body cells, hair, skin, muscles) grow, repair and replace. |
|
|
Describe the process of DNA replication. |
Also known as transcription. The genetic information is converted from a DNA sequence into mRNA. The mRNA carries the genetic information from the chromosome to the site of protein synthesis. Translation- during translation, the information carried by an mRNA is used to a polypeptide chain. Transcription, the double stranded DNA is too large and important to leave the nucleus so a copy of the gene is transcribed onto an mRNA molecule. |
|
|
What is meiosis? |
Meiosis is cell division involved in the formation of gametes (sex cells). It takes place in the men's testicles or women's ovaries. Meiosis has two key outcomes, reduction division, produces daughter cells with fewer chromosomes than the parent cells and recombination, products of meiosis have different combinations of genes. |
|
|
Homozygous |
having identical genes (e.g; for eyes, either BB or bb) |
|
|
Allele |
each of two or more alternative forms of a gene that arise by mutation and are found at the same place on a chromosome |
|
|
Genotype |
the combination of two genes (pair of alleles) inherited for a particular characteristic |
|
|
Incomplete dominance |
the pattern of inheritance in which a gene does not override another for the same characteristic and is not overridden by it; both are expressed |
|
|
Heterozygus |
two forms of a gene (e.g; for eyes Bb) |
|
|
Phenotype |
the set of observable characteristics of an individual resulting from the interaction of its genotype with the environment |
|
|
Name all the blood groups |
Type A blood- IaIa OR Iai Type B blood- IbIb OR Ibi Type O blood- ii Type AB blood- IaIb |
|
|
What is meant by the term 'carrier' in genetics? |
someone in whom a genetic disorder is not expressed but who passes it on to their children |
|
|
What does the term 'pure breeding' mean? |
A true breeding organism, sometimes also called a pure-bred, is an organism that always passes down a certain phenotypic trait to its offspring. An organism is referred to as true breeding for each trait to which this applies, and the term "true breeding" is also used to describe individual genetic traits. |
|
|
What is the difference between maternal and paternal chromosomes? |
Maternal is inherited from our mother, paternal is inherited from our father. |
|
|
Karyotype |
the number of general appearance (size, shape, banding) of a set of chromosomes |

