![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
14 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Matter |
Anything that has mass and occupies space |
|
|
The particle theory of matter |
1. All matter is made up of tiny particles.
2. Each pure substance has its own particles 3. Particles attract each other 4. Particle are always moving 5. Particles at a higher temp move faster on ave than particles at lower temp |
|
|
Classification of matter |
1. Mixtures 1.1. Mechanical mixtures 1.2. Solutions 2. Pure substances 2.1. Elements 2.2. Compounds |
|
|
1.Pure Substance 2. Mixture |
1. Matter that contains only one kind of particle (water and Helium) 2. Matter that contains more than one kind of particle. (e.g. air contains different gases: nitrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide and other) |
|
|
1. Elements 2. Compounds |
1. An element is a pure substance that cannot be broken down into simpler parts by physical or chemical methods 2. A compound is a pure substance that is made of two or more different elements which are chemically combined. It can be broken down in elements by chemical means (e.g. electrolysis to break down water into H2 and O) |
|
|
Physical property |
A characteristic of a substance that you can observe and and measure without changing identity of the subtance |
|
|
Qualitative physical properties |
* Can be observed and described without detailed measurement. 1. colour 2. odour 3. state 4. texure 5. lustre 6. malleability |
|
|
Quantitative physical properties |
* Properties that can be measured and assigned a particular measure. 1. Viscosity 2. Melting point 3. Boiling point 4. Solubility 5. Hardness 6. Conductivity 7. Density |
|
|
States of Matter |
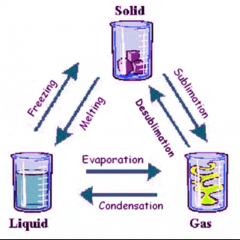
|
|
|
Solubility |
* A measure of the ability of a substance (solute) to dissolve in another substance (solvent). A solution with water as a solvent: "aqueous solution". e.g. blood Insoluble: substance that does not/has very low solubility. |
|
|
Hardness |
* The ability of a substance to be scratched. (useful to determine practical use) * Measured with Mohs Scale |
|
|
Conductivity |
* The ability to conduct electricity (electrical wires made of Copper). |
|
|
Density |
* The ratio of the mass of a substance to the volume it occupies. For a particular mass of a substance a certain volume is required. It is a property of solids but also gases and liquids. Liquids with different densities will separate in layers (e.g. oil & water) |
|
|
Water |
1. The only natural substance that exists in all three phases 2. Universal solvent (dissolves more substances than any other liquid) 3. Can absorb a lot of heat before beginning to become hot 4. Its solid form, ice is less dense than the liquid. |

