![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
52 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
History of the periodic table |
During the 19 century chemist began categorized elements according to similarities, in physical, chemical properties. The end result , studies was our modern periodic table. |
|
|
|
Johann Dobereiner |
Classified elements into groups of three called triads |
|
|
|
John Newlands |
Suggested, element arranged in octaves |
|
|
|
Dmitri Mendeleev |
Published increasing atomic mass |
|
|
|
Lothar Meyer |
Published element in increasing atomic mass
Father of the modern periodic table |
|
|
|
Henry Moseley |
He rearranged the elements in order of increasing atomic number |
|
|
|
Glen T.Seaborg |
Co-Discovering 10 new elements he moved 14 elements out of the main body of the periodic table |
|
|
|
Periodic table geography |
Broken down it to horizontal rows called periods And Vertical called groups |
|
|
|
Groups have 2 methods |
Old method New method
|
|
|
|
Old method is Old method also tells givesyou |
1A,2A,2A, 4B-8B,8B,8B,1B,2B 3A-8A The number of Valence electrons |
|
|
|
Valence electron |
The number of electrons found in the outer most shell. |
|
|
|
New method is |
1A-18A |
|
|
|
Periods go Groups go Period also tells you |
Across Up and down How many energy shells there are |
|
|
|
Atomic number = # of protons = Mass number is How do you find the # of neutrons |
= # of protons = # of electrons - is the atomic mass rounded up or down - is the atomic number - the mass number. |
|
|
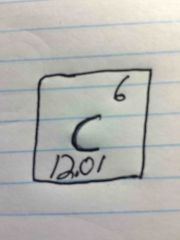
Find the Atomic # Atomic mass Mass # # of protons # of electrons # of neutrons |
6 12.01 12 6 6 6 |
|
|
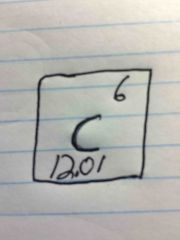
Find the Atomic # Atomic mass Mass # # of protons # of electrons # of neutrons |
6 12.01 12 6 6 6 |
|
|

Find element Symbol |
H Cu Ni Si N W He Be Mg Na Li I Ar F Al P
|
|
|

Find the name |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
What the Bohr model expression What does the n represent |
2n2 Number of levels |
|
|
|
What the Bohr model expression What does the n represent |
2n2 Number of levels |
|
|
|
What a Bohr model for hydrogen |
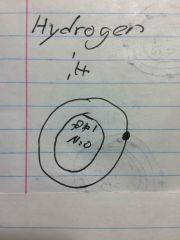
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
What the Bohr model expression What does the n represent |
2n2 Number of levels |
|
|
|
What's a Bohr model for hydrogen |
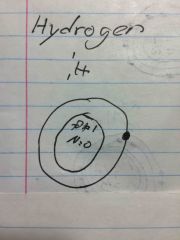
|
|
|
|
When is a Bohr model statable |
When the outer most shell is full |
|
|
|
Families virus pond to |
Groups |
|
|
|
Families correspond to |
Groups |
|
|
|
What's the name for group IA 4 points |
Alkali metals family -all metals -fairly soft an silver white in colour -good conductors - extremely chemical reactive |
Conductor ? Colour? Chemical re |
|
|
Groups IIA 4 points
|
Alkaline earth metals -solid at room temperature -harder than group IA - good electrical conductor -silvery white metals |
Temperature Electrical Colour |
|
|
Group VIA Point of this family |
Chalcogens Oxygen family -elements are more metallic as you move down the group - elements are less reactive as you move down the group |
|
|
|
Group VIA Point of this family |
Chalcogens Oxygen family -elements are more metallic as you move down the group - elements are less reactive as you move down the group |
|
|
|
Group VIIA 4 points of that family |
Halogens -form the largest number of compounds - extremely reactive - non metallic - range from solid to liquid to gas at room temperature |
|
|
|
Group VIA (Oxygen) 2 points |
Chalcogens Oxygen family -elements are more metallic as you move down the group - elements are less reactive as you move down the group |
Metallic Reactive |
|
|
Group VIIA 4 points |
Halogens -form the largest number of compounds - extremely reactive - non metallic - range from solid to liquid to gas at room temperature |
Compounds Reactive Non Room Tempature |
|
|
Group VIIIA 4 points |
Noble gases - AKA inert gases - stable and un reactive - colour less odourless -gases at room temperature |
St Reactive Less x2 Temperature |
|
|
Group IB 4 points |
Transition metals -posses properties of metal -very hard , with high melting and boiling points -very good electrical conductors -very malleable |
Properties High points Electrical Very m |
|
|
Metalloids 3 points |
-are found along the staircase -semiconductors of electricity -their ability to conduct electricity increases with the temperature |
Found along Semiconductor Conduct temperature |
|
|
Non metals 4 points |
-Solid non metals are generally very brittle -poor conductors of heat and electricity -have little or no metallic lustre -located in groups IIIA-VIIA
|
Brittle Conductors Metallic lustre |
|
|
Rare earth 2 series Located where |
Lanthanide series - top Actinide series -bottom Located at the very bottom of the periodic table |
|
|
|
Isotopes |
Elements with differing number of neutrons |
|
|
|
Ion |
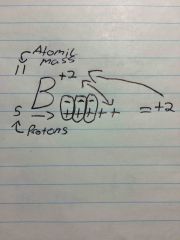
When there is a positive or negative charge to the element - protons can not Change |
|
|

|
Exploding bomb - for explosion |
|
|

|
Gas cylinder -for gassed under pressure |
|
|

|
Health hazard - may cause or suspected of causing serious health effects |
|
|

Front (Term) |
Flame - for fire hazards |
|
|

|
Health hazard - may cause serious health effects |
|
|

|
Flame - for fire hazards |
|
|
|
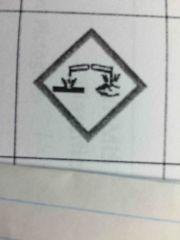
Corrosion - for corrosive damage to metals as well as skin and eyes |
|
|

|
Exclamation mark - may cause less serious health effects or damage |
|
|

|
Flame over circle - for oxidizing hazards |
|
|

|
Skull and crossbones - can cause death with short exposure to small amounts |
|
|
|
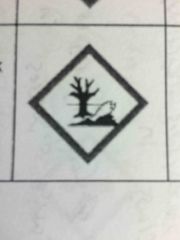
Environment -may cause damage to the environment |
|
|

|
Bio Hazardous infectious materials - can cause diseases in people or animals |
|

