![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
21 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
how can a force change motion ?
|
by changing an objects direction
speed or both (change the velocity) |
|
|
only what kind of what forces can change an objects velocity?
|
only unbalaned forces
|
|
|
examples of unbalanced forces changing an objects velocity
|

|
|
|
what happens if an unbalanced force is applied to an object at rest ?
|
the object will move in the direction of the net force
|
|
|
example of an unbalanced force acting on an object at rest
|

|
|
|
what happens when the net force acts in the same direction of a moving object ?
|
the object will speed up
|
|
|
what happens when the net force acting on a moving object is in the opposite direction that the object is moving ?
|
the object will slow down
|
|
|
example of when an object speeds up because net force acts in the same direction of the object
|

|
|
|
example of when the net force acting on an object is in the opposite direction of the object causes it to slow down
|

|
|
|
example of how can unbalnaced forces change the direction of an object ?
|

rail applies applies an unbalanced force on the ball therefore the ball changes direction
|
|
|
what do unblanced forces change and cause ?
|
change velocity
cause acceleration |
|
|
what is another term for a change in velocity?
|
acceleration
|
|
|
what is Newton's second law of motion
|
the acceleration (change in velocity) is equal to the net force acting on the object divided by the objects mass
|
|
|
Newton's second law equation
|

|
|
|
examples of newtons second law equation
|

|
|
|
what is circular motion
|
any motion in which an object is moving along a curved circlular path
(moving in a circle) |
|
|
what is centripedal force?
|
a force, in circular motion, that acts perpendicular to the direction of motion, toward the center of the curve
|
|
|
example of centripedal force
|
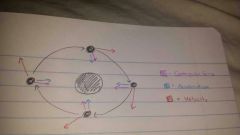
|
|
|
what is a satellite
|
any object that orbits a larger object
|
|
|
why do satellites exhibit centripadel force?
|
because they have circular motion
|
|
|
what does gravity act as when the moon is a satellite?
|
as a centripedal force
|

