![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
51 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
3 Properties of a solid ( state of matter) |
Possible answers : Vibrating particles , Low energy , Fixed shapes , Strong bonds, Can not be compressed. |
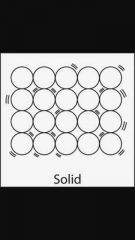
Diagram of a solid |
|
|
3 Properties of a Liquid (States of matter) |
Possible answers : 50% particles touch, Flow , More energy than a solid , Take shape of container , Move around each other , Weaker bonds , Can not be compressed |

Diagram of a Liquid |
|
|
3 Properties of a gas (States of matter) |
Possible answers : No bonds, Most energy , Do not touch , Lots of movement , Can be compressed, Fill container , Move in any direction |
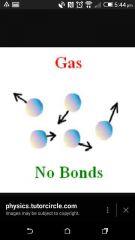
Diagram of gas |
|
|
What process changes a solid to a gas? |
Sublimination |
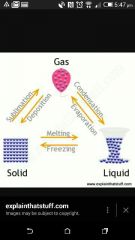
|
|
|
What is the process changing Gas to a solid ? |
Deposition |
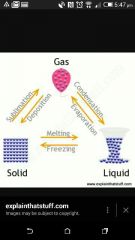
|
|
|
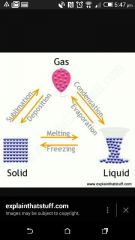
What is the process changing Gas to a liquid ? |
Condensation |
|
|
|
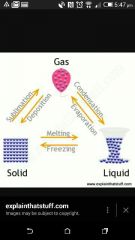
What is the process changing liquid to a gas? |
Boiling/ Evaporation |
|
|
|
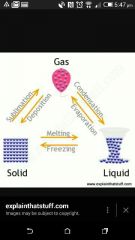
What is the process changing liquid to a solid ? |
Freezing |
|
|
|
If the forces are stronger is the Melting/boiling point Higer or lower ? |
Higher |
The harder the bond to break to more energy needed . |
|
|
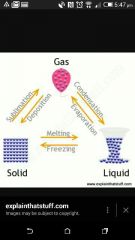
What is the process changing a solid to a liquid ? |
Melting |
|
|
|
Why is the simple model limited ? ( States of matter) |
No forces are represented , all particles are spheres , spheres represented as solid and inelastic |
|
|
|
What is an alloy ( Bonding) |
A mixture of 2 elements , 1 metal element. |
Think about Metallic Bonding. |
|
|
Are alloys harder or softer than the metal they contain ? |
Harder |
|
|
|
What do different atom sizes do to the regular arrangement ? (Bonding) |
Distorts it. |
|
|
|
What happens if nitinol ( alloy of nickel and aluminium ) is bent out of shape and heated or when an electrical current is passed through ? ( Bonding) |
It returns to its original shape because it is a shape memory alloy. |
Nitinol is a shape memory alloy |
|
|
If substance X has a melting point of -18 and a boling point of 42 what state is it at room temperature(20°) |
Liquid -18° ~ Gas 20° ~ Liquid 42° ~ Liquid |
Gas comes first , then liquid , then solid |
|
|
The particles in a metal is held together by ......( Bonds ) |
Strong metallic bonds |
The answer is in the name of the type of bonding. |
|
|
Metals have a ..... Boiling/melting point ( Bonds ) |
High |
Do they need a lot or little energy ? |
|
|
What kind of electrons do metals have in their outer shell? |
Loose electrons which form a sea of delocilozed negatively charged electrons around closely packed postive ions. |
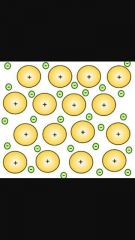
Diagram |
|
|
What Strong forces hold the particles in a metal together ? (bonds) |
Electrostatic Forces |
|
|
|
What allows the body panels in a metal to conduct electricity ? (Bonding) |
Free negative electrons which can move. |
What can the electrons do ? |
|
|
What allows the body panels to bend into shape ? ( bonding ) |
Layers which can slide and the fact that metal is malleable. |
Think of properties of metals. |
|
|
What 3 types of bonding is there ? |
Metallic , ionic , covelant |
|
|
|
What do non metals do in ionic bonding ? |
Gain electrons |

|
|
|
When can ions move on ionic compounds ? |
When dissolved in soloution or moulten . |
|
|
|
What do metals do in ionic Bonding ? |
Give away electrons |
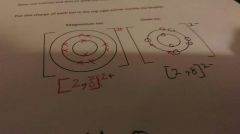
|
|
|
What is different about a solid ionic compounds arrangement ? |
Particles go postive , negative , postive , negative. |

|
|
|
Why do metals lose electrons ? |
To become postive ions |
Positive or negative ? |
|
|
In a dot and cross diagram how can you tell the particles in a compound are held together by ionic bonds ? |
Postive and negative charges . |
|
|
|
What moves in an ionic compound ? |
Ions |
|
|
|
What structure is an ionic compound ? |
Lattice |
Sounds like lettuce |
|
|
How do non- metals form bonds? |
Share electrons/ covlatant bonding. |
|
|
|
Which shells are involved in covalent bonding ? |
Outershells |
|
|
|
What diagrams are used in covalent bonding ? |
Dot and cross or solid line diagrams |
|
|
|
What is a polymer |
Large molecules made from lots of monomers joined by covalent bonds. |
|
|
|
What is another word for Strong covalent bonds ? |
Intramolecular bonds |
|
|
|
What are the chains of monomers held together by ? |
Weak forces or attraction / intermolecular forces |
|
|
|
What are two types of polymers ? |
Thermosoftening and thermosetting |
|
|
|
What are the rules of a polymer repeating unit? |
Break double bond, add bonds to side , brackets through bonds , add n at bottom right. |
|
|
|
What is a small molecule ? |
Made up of non-metals involving covalent bonds |
|
|
|
What kind of melting and boiling points do simple molecules have? |
Low because intermolecular bonds are easily broken . |
|
|
|
What state do simple molecules tend to be ? |
Liquid and gas |
|
|
|
What are 3 giant covalent structures? |
Diamond , Graphite and silicon dioxide |
|
|
|
What are 2 giant covalent structures ? |
Allotropes of carbon |
|
|
|
Give 3 Properties of diamond |
Each carbon linked to 4 other carbon , high melting point, strong bonds , shiny , hard, lattice , not a conductor. |
|
|
|
Give 3 Properties of Graphite |
Linked to 3 other carbon, conducts electricity , lattice , weak forces of attraction , softer , high melting point , layers slide . |
|
|
|
3 Properties of silicon dioxide |
Each silicon joined to 4 oxygen, Each oxygen joined to 2 silicon , Ridgid / hard , high melting point, not a conductor , lattice , white cyrstaline solid, Strong bonds. |
|
|
|
What is graphine ? |
Allotrope of carbon , planer sheets ( one atom thick) discovers through scotch tape method . |
|
|
|
What are the limitations of graphene ? |
Can't be produced in a large scale. |
|
|
|
What are fullerenes ? |
Molecules of carbon with hollow shape. |
|
|
|
3 uses of fullerenes ? |
Catalyst, lubricant, drug delivery in the body. |
|

