![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
57 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Arteries
|
blood vessels carrying blood away from the heart
|
|
|
Veins
|
blood vessels carrying blood towards the heart
|
|
|
Capillaries
|
tiny narrow vessels.
|
|
|
What is the pericardium? Think about your heart dissection.
|
It’s the thin membrane on the outside of the heart
|
|
|
What makes the pulmonary vein different from the other veins in your body?
|
It’s the only vein with oxygen rich blood
|
|
|
What side of the heart will you find the red blood and the blue blood?
|
Left side – red blood, right side – blue blood
|
|
|
Not all arteries carry oxygen rich blood away from your heart. Explain this.
|
The pulmonary artery carries oxygen poor blood away from your heart to your lungs.
|
|
|
Where is the pulmonary valve located – meaning what two parts of your heart is it between?
|
It’s found between the pulmonary artery and the right ventricle
|
|
|
What two chambers is the mitral valve in between? How about the tricuspid valve?
|
Mitral - left atrium and left ventricle
Tricuspid – right atrium and right ventricle |
|
|
Why are the “superior” vena cava and the “inferior” vena cava given their names?
|
Superior means above and sends blood to the heart from the upper part of the body. Inferior means below and sends blood from the lower part of the body
|
|
|
Use the words below to describe the flow of blood through your heart as it’s coming back from your brain.
Aorta, lungs, rest of the body, right ventricle, left ventricle, right atrium, left atrium, superior vena cava, pulmonary veins, pulmonary artery |
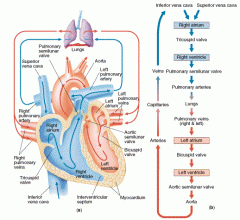
superior and inferior vena cava
right atrium right ventricle pulmonary artery lungs pulmonary veins left atrium left ventricle aorta body |
|
|
Hemoglobin
|
an iron-contained protein that binds chemically to oxygen molecules.
|
|
|
Atherosclerosis
|
a condition in which a artery wall thickens as a result of a build up of fatty materials.
|
|
|
Septum
|
The septum prevents oxygen-rich and oxygen poor blood from mixing in the heart.
|
|
|
4 parts of blood with functions and facts about them.
|
Red Blood Cells, White Blood Cells, Platelets, and Plasma
|
|
|
which parts of the body are high in oxygen and high in carbon dioxide?
|
(highest to lowest)
Oxygen: It is high in oxygen when it gets out of the lungs Carbon Dioxide: It is high in carbon dioxide right before it goes into the lungs. |
|
|
Where are valves loccated?
|
Valves are located in the between the ventricles and the large blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart.
|
|
|
What is the surface and anti-clumping proteins antigens and antibodies
|
anti-clumping proteins: ???
antigens: A, B, and O antigens. antibodies: Anti-A and Anti-B antibodies. |
|
|
Lymph
|
Any fluid that flows into the Lymphetic System.
|
|
|
Lymph nodes
|
Small knobs of tissue in the Lymphatic System.
|
|
|
Lymphetic System
|
The lymphatic system is a network ovf veinlike vessels that returns the fluid to the bloodstream.
|
|
|
Plasma
|
the liquid part of blood, mostly water, has dissolved nutrients in it
|
|
|
Hemoglobin
|
a chemical in RBC that carries oxygen and carbon dioxide
|
|
|
Antigens
|
a chemical identification tag on red blood cells
|
|
|
Antibodies
|
proteins in the blood plasma that destroy foreign substances
|
|
|
What are the 4 functions of blood?
|
transport oxygen and carbon dioxide to and from the body’s cells
help to clot blood when there are wounds, transport nutrients from the digestive system to the body’s cells, help fight infection and heal wounds |
|
|
Explain why there is both red and blue blood in your body?
|
Blue blood is blood without oxygen and red blood is blood with oxygen. The blood on the right side of the heart or in most of your veins has not been oxygenated. It is in these blood vessels before going to the lungs.
|
|
|
If you get sick what is your blood's reaction?
|
Create more white blood cells.
|
|
|
What is the function of red blood cells?
|
Red blood cells carries oxygen to other cells in the body.
|
|
|
How long do red blood cells live?
|
about 120 days.
|
|
|
What is the function of white blood cells?
|
To fight off infections.
|
|
|
How does the # of white blood compare to the # of red blood cells?
|
There are more red blood cells than white blood cells in your body.
|
|
|
How long do white blood cells live?
|
months to years.
|
|
|
In general, what is the job of the heart's atria?
|
The job of the heart’s atria is to receive blood from the body.
|
|
|
What is the function of platelets?
|
The function is to help clot blood when you are wounded.
|
|
|
44. If you are in a terrible accident where you find yourself in need of a blood transfusion, what blood type would you rather be and why? Talk about antibodies in your answer.
|
You would want to be Type AB. Type AB is the universal receiver. This blood type doesn’t have any antibodies to react with the antigens from other blood types
|
|
|
The left and right _____ are the two upper chambers of the heart.
|
atria.
|
|
|
What is the function of white blood cells?
|
To fight off infections.
|
|
|
How does the # of white blood compare to the # of red blood cells?
|
There are more red blood cells than white blood cells in your body.
|
|
|
How long do white blood cells live?
|
months to years.
|
|
|
In general, what is the job of the heart's atria?
|
The job of the heart’s atria is to receive blood from the body.
|
|
|
What is the function of platelets?
|
The function is to help clot blood when you are wounded.
|
|
|
44. If you are in a terrible accident where you find yourself in need of a blood transfusion, what blood type would you rather be and why? Talk about antibodies in your answer.
|
You would want to be Type AB. Type AB is the universal receiver. This blood type doesn’t have any antibodies to react with the antigens from other blood types
|
|
|
Type O blood can not receive blood from type AB. Why? (You need to have the words antigens and antibodies in your answer.)
|
because type O blood has antibodies A and antibodies B.
|
|
|
Describe what would happen to the blood in a blood transfusion if two blood types were NOT compatible.
|
The dominant blood would kill off all of the transfusion blood.
|
|
|
Which blood type is the “universal donor” and what does that mean? Use antigens and antibodies in your answer.
|
Type O is the universal donor. It can give to any blood type because it doesn’t have any antigens to react with other blood type’s antibodies.
|
|
|
Which blood type is the “universal receiver” and what does that mean? Use antigens and antibodies in your answer.
|
Type AB is the universal receiver. It doesn’t have any antibodies to react with other blood types antigens.
|
|
|
What are the four different blood types?
|
A, B, AB, and O
|
|
|
What type of blood can type B receive?
|
Type B and type O.
|
|
|
What does type B blood have antibodies against?
|
Type B has an Anti-A antibody.
|
|
|
The left and right _____ are the two upper chambers of the heart.
|
atria.
|
|
|
The blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart are
|
arteries.
|
|
|
Red blood cells contain _______, a chemical that carries oxygen and carbon dioxide.
|
hemoglobin
|
|
|
What prevents the backflow of blood in your heart?
|
valves
|
|
|
Who is Karl Landsteiner?
|
She discovered the ABO System of Blood Typing.
|
|
|
Where are antibodies found?
|
Plasma
|
|
|
Where are antigens found?
|
Red Blood Cell
|

