![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
42 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the word equation for photosynthesis? |
Water + Carbon Dioxide (light + chlorophyll) > Glucose + Oxygen |
|
|
What is light energy changed into and what is it stored in? |
Light energy is changed into chemical energy which is stored in the glucose that is made. |
|
|
What are the roots for? |
They absorb water from the soil, absorb nutrients and provide anchorage. |
|
|
Why are roots branched and spread out? |
To help them absorb water from a large volume of soil. |
|
|
What are the root hair cells for? |
They have a large surface area to help them absorb water quickly. |
|
|
What does water flow up through? |
The xylem cells which are made from hollow cells into the leaf. |
|
|
Why else is water needed? |
Mineral salts are dissolved in it, which are needed to keep the plants healthy. |
|
|
Why is water needed? |
It stops plants from wilting and can keep their leaves cool. |
|
|
What does carbon dioxide travel through? |
The stomata. |
|
|
Why are leaves thin? |
So that carbon dioxide does not have to go very far before reaching the cells that need it. |
|
|
How can photosynthesis be sped up? |
By increasing the amount of carbon dioxide around a plant, or by increasing the amount of light around a plant. |
|
|
Why are many leaves wide? |
So that they have a large surface area to trap as much sunlight as possible. |
|
|
Where does the most photosynthesis happen and why? |
In palisade cells, which are found near the upper surface of leaves. This is because palisade cells are packed with chloroplasts which contain chlorophyll which absorb light energy. |
|
|
What type of respiration do plants calls use to release the energy stored in glucose, and what's the word equation for it? |
Aerobic respiration. Glucose + Oxygen > Carbon Dioxide + Water + Energy |
|
|
Glucose is a type of sugar. What is it used for? |
Respiration, making other substances that aft as stores of energy (e.g : starch) and make new materials for growth. |
|
|
What is glucose turned into and what goes it do? |
It is turned into cellulose (for cell walls), fats and proteins. To make proteins, mineral salts called nitrates are needed. |
|
|
What are new substances that are made by a plant carried around in? |
Phloem tubes. |
|
|
What do new substances allow the plant to do? |
To help build up a plant's biomass (the mass of all the materials in the plant apart from water). |
|
|
What type of feeders are plants? |
Autotrophic, as they make their own food via photosynthesis. |
|
|
Only what part of the plant can photosynthesise and why? |
Green parts, as they contain a photosensitive pigment called chlorophyll, which absorbs the sun's energy. |
|
|
What does the flower do? |
Pollinate. |
|
|
What does the stem do? |
Support and transport of materialm |
|
|
What do the leaves do? |
Provide food. |
|
|
What does a plant cell look like? |
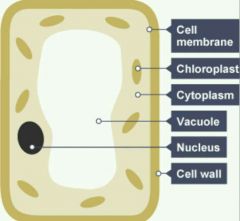
|
|
|
What features do both the plant and animal cell have? |
They both have a cell wall, cell membrane and nucleus. |
|
|
What does the nucleus do? |
It contains the genetic material which controls the activities of the cell. It also stores DNA of the plant and acts as a cell's command centre. |
|
|
What does the cytoplasm do? |
It contains most chemical processes that take place here, and it is controlled by enzymes. |
|
|
What does the cell membrane do? |
It controls the movement of substances in and out of the cell. |
|
|
What does the mitochondria do? |
Most energy is released by respiration here. |
|
|
What does the cell wall do? |
Strengthens the cell. |
|
|
What do the chloroplasts do? |
They contain chlorophyll, which absorbs light energy for photosynthesis. |
|
|
What does the vacuole do? |
Vacuoles are storage bubbles which store nutrients, food and wast products. |
|
|
What does a leaf cell look like? |
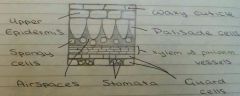
|
|
|
What are the palisade cells? |
They are regular shaped cells that have a lot of chloroplast, therefore most photosynthesis occurs in this layer. |
|
|
What are the xylem cells and phloem cells? |
Veins include xylem cells that allow water to be transported around the plant. Phloem cells transport sugar. |
|
|
What are the spongy cells? |
They are irregular shaped and have fewer chloroplasts. They have air spaces between them so that gases can move out. |
|
|
What are the stomata? |
They are tiny holes that open and close to allow Co2 in and O2 out of the leaf. |
|
|
What are the adaptations of a leaf? |
They have a large surface area to absorb light, they are thin so gases don't have far to diffuse, they have a network of veins to transport water (xylem) and sugar (phloem), they have stomata which allows gases to diffuse in and out, and they contain chlorophyll. |
|
|
What are the stomata controlled by? |
The gaurd cells, which help them open and close. |
|
|
What are the three essential minerals plants need to stay healthy, and what are they for? |
Nitrates - For protein manufacture. Pophates - For photosynthesis and respiration. Potassium - For photosynthesis and respiration. |
|
|
What is the glucose like in plants? |
Some glucose is used straight away in respiration, however, some is converted into starch and other substances for storage. Some glucose is used to make new chemicals such as proteins, sugars and fats that the plant also need to function properly. |
|
|
What are a few differences between photosynthesis and respiration? |
Photosynthesis happens during day, respiration at night. Food (glucose) is produced during photosynthesis. Also, respiration does not require light or chlorophyll. |

