![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
18 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
ASTRONOMY
|
Study of the stars.
astro - meaning stars onomy - study of |
|
|
COSMOLOGY
|
Study of the universe.
|
|
|
GALAXY
|
a system of millions or billions of stars, together with interstellar medium of gas and dust, and dark matter, held together by gravitational attraction.
|
|
|
DOPPLER EFFECT
|
increase or decrease in the frequency of sound, light or other waves as the source and observer move towards or away from each other
|
|
|
STEADY STATE THEORY
|
Theory that the galaxies are evenly spaced and the universe mantains a constant density.
|
|
|
BIG BANG THEORY
|
Theory that the universe originated from a cataclysmic explosion 14 billion years ago.
|
|
|
APPARENT MAGNITUDE
|
Measure of how bright a star will appear to observers on earth.
Brighter star have a low magnitude. Dimmer stars have higher magnitude. |
|
|
ABSOLUTE MAGNITUDE
|
Measure of how bright a star would appear if it was 10 parsecs away from earth.
|
|
|
DARK MATTER
|
Non - luminous material which exists in space.
Can exist in two forms: - Cold dark matter (weakly interacting) - Hot dark matter (high-energy random created soon after Big bang. |
|
|
LIGHT YEAR
|
Used to measure interstellar distances.
The distance that light will travel in a year. Approximately 9.5 trillion kilometres. |
|
|
PARSEC
|
Another unit of measurement Astronomers use.
1 parsec (pc.) is equivalent to 3.26 light years. |
|
|
COSMIC MICROWAVE BACKGROUND RADIATION
|
The 'afterglow' left by the Big Bang.
|
|
|
HUBBLE'S LAW
|
A law stating that the red shifts in the spectra of distant galaxies and their speeds of recession are proportional to their distance.
|
|
|
CARBON CYCLE
|

|
|
|
RED SHIFT & BLUE SHIFT
|
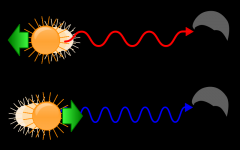
The displacement of spectral lines towards longer wavelengths, the red end of the spectrum in radiation from galaxies and celestial objects
Blue shift is opposite. |
|
|
LARGE HADRON COLLIDER
|
The highest energy particle collider ever made
|
|
|
HERTZSPRUNG - RUSSELL DIAGRAM
|
Scatter graph of stars showing relationship between luminosity and spectral types or temperatures
|
|
|
PLANETS
|
Mars, Venus, Earth, Mercury, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune
My Very Energetic Mother Just Served Us Nachos |

