![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
27 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
precipitation
|
When cloud particles become too heavy to remain suspended in the air, they fall to the earth as precipitation.
|
|
|
saturation
|
"thoroughly full"
|
|
|
density
|
is a measure of how tightly the matter within a body is packed together. It is a ratio of mass/volume.
|
|
|
cohesion
|
the intermolecular attraction between like-molecules.
|
|
|
water structure
|
2 hydrogen 1 oxygen molecule (H2O)
|
|
|
phase change diagram
|
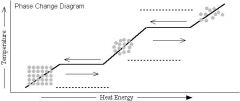
|
|
|
Coriolis Effect
|
The Earth's rotation imparts an acceleration known as the Coriolis effect. This acceleration causes cyclonic systems to turn towards the poles in the absence of strong steering currents.
|
|
|
longitude
|
east-west geographic coordinate
|
|
|
latitude
|
north-south geographic coordinate
|
|
|
Temperature
|
The temperature is measure related to the average kinetic energy of a mass's atoms as they move
|
|
|
condensation nuclei
|
Condensation nuclei are small particles or aerosol upon which water vapor attaches to break surface tension
|
|
|
heat
|
the amount of energy an atom has. Heat is energy transferred from one body or system to another due to a difference in temperature.
|
|
|
latent heat
|
latent heat is the amount of energy in the form of heat released or absorbed by a substance during a change of phase
|
|
|
runoff
|
a term used to describe the flow of water, from rain, snowmelt, or other sources, over the land
|
|
|
specific heat
|
is the measure of the heat energy required to increase the temperature of a unit quantity of a substance by a certain temperature interval.
|
|
|
hurricane
|
Tropical cyclone is a storm system characterized by a low pressure center and numerous thunderstorms that produce strong winds and flooding rain. Hurricanes are systems with sustained winds of 74 miles per hour.
|
|
|
kinetic energy
|
Kinetic energy is the energy of motion.
|
|
|
dew point
|
The dew point is the temperature to which a given parcel of air must be cooled, at constant barometric pressure, for water vapor to condense into water.
|
|
|
eye
|
The eye is the center of a hurricane. It is the calmest part of a hurricane.
|
|
|
convection
|
Convection refers to the movement of molecules within fluids. I.e. heating causing fluid motion.
|
|
|
adiabatic cooling
|
Adiabatic cooling happens as air mass expands with increasing elevation (because density of gases decreases farther into the atmosphere). As elevation increases, the air gets cooler because energy is drawn from the surroundings.
|
|
|
storm surge
|
Storm surge is simply water that is pushed toward the shore by the force of the winds swirling around the storm
|
|
|
conduction
|
Heat conduction or thermal conduction is the spontaneous transfer of thermal energy through matter, from a region of higher temperature to a region of lower temperature, and acts to equalize temperature differences
|
|
|
tropical storm
|
the the stage before a hurricane, maximum sustained winds are 39-73 mph
|
|
|
evaporation
|
Evaporation is the process by which water is converted from its liquid form to a gas
|
|
|
surface tension
|
Surface tension is a property of the surface of a liquid that causes it to behave as an elastic sheet
|
|
|
Tropical depression
|
Once a group of thunderstorms has come together under the right atmospheric conditions for a long enough time, they may organize into a tropical depression.
A tropical depression is an organized system of clouds and thunderstorms with a defined, closed surface circulation and maximum sustained winds of less than 39 miles per hour (63 km/h) |

