![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
37 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What is the body hierarchy? (Smallest to largest) |
Cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, organism |
|
|
|
What are cells? |
They are basic units of all living things |
|
|
|
What is a tissue? |
It is a group of cells that are similar in shape and function |
Ex. Many muscle cells make muscle tissue |
|
|
What is an organ? |
An organ is a structure that is made of 1 or more different types of tissues |
Ex. Heart |
|
|
What is an organ system? |
It is a group of organs that have related functions |
Ex. Circulatory system |
|
|
What is a unicellular organism? |
They are only visible under microscope. Only one celled organisms. |
Also referred to at microbes or micro-organsims |
|
|
What is bacteria? |
They are unicellular cells and are the most plentiful organism on Earth. |
Ex. Parasites and anaerobes |
|
|
What are protists? |
They are eukaryotic cells and are found in all water systems. Categorized as animal like and plant like |
|
|
|
What are plant like protists? |
Can produce their own food by photosynthesis. |
Ex. Euglena and diatoms |
|
|
What can animal like protists do? |
That must feed on living things or things that were living |
Ex. Amoebas and paramecia |
|
|
What is fungi? |
Can be uni or multi cellular |
Ex. Mold, athletes foot, mushrooms |
|
|
Microorganisms (microbes) |
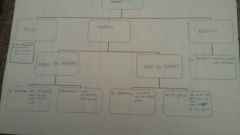
|
|
|
|
Cells growth |
Each cell can only grow to a certain size. |
|
|
|
Why do cells divide? |
Once reached limit must divide |
|
|
|
Why is it important for cells to be small? |
So that they can send messages from membrane to nucleus quickly. So that the surface area of the membrane is greater and nutrients and waste can properly entire and leave |
|
|
|
Are smaller or lager cells better |
Bigger is slower and small is faster. So smaller is better |
|
|
|
Does surface area and volume change when cells divide? |
Volume stays the same but surface area changes |
|
|
|
When do plant cells have a thin or thick cell wall |
Some cells in plants have a thin cell wall, such as the cells in leaves or petals, allow the structure to be flexible and used as storage. Stems have a thick wall and used for structure and protection |
|
|
|
What are specialized animal cells? |
Nerve cells, lung cells, red blood cells, white blood cells, stomach lining cells, fat cells and small intestine lining cells |
|
|
|
What is a nerve cell? |
Long and thin and conduct electrical signals from one location to another in the body |
|
|
|
Lung cells |
Are very thin and allow gases to exchange between the site and blood |
|
|
|
Red blood cells |
Are round with a special protein called hemoglobin to carry oxygen. |
|
|
|
White blood cells? |
Are able to move to find and destroyed invaders (pseudopod) |
|
|
|
Stomach lining cells |
Have many ribosomes to produce proteins and many golgi apparatus's to store and package these proteins that break down food. |
|
|
|
Fat cells |
Have many vacuoles to store extra nutrients that the body does not need |
|
|
|
Small intestine lining cells |
Have many villi (finger like projections) that increase the surface area of three cell to increase the absorption of nutrients. |
|
|
|
Invaders |
Organisms that cause some infection. Can produce waste that is toxic or poisonous to the body or destroy cells |
|
|
|
4 invaders |
Bacteria, fungi, protists and viruses |
|
|
|
Ex. Of Bacteria |
Step throat, pneumonia, food spoilage and water contamination |
|
|
|
Ex. Of Fungi |
Athletes foot |
|
|
|
Ex. Of Protists |
Malaria (mosquitoes) and beaver fever (drinking untreated stream/pond water) |
|
|
|
Viruses |
Are not living. Composed of a stand of genetic info covered in protein. 1. Invade a living cell (aka. host cell) 2. Inject it's own generic information into the cell and nucleus 3. Host cell then begins to create more viruses 4. The cell bursts and new viruses are released to invade other cells |
Ex. Cold, influenza, and HIV/AIDS |
|
|
Defenders |
The immune system protects organisms by desalting invaders |
|
|
|
2 defenders |
1. White blood cells (WBC) are present in the human body to attack invaders directly 2. Antibodies: made by specialized WBC which "lock" onto invading organisms to stop them from working |
|
|
|
White blood cells |
Engulf the invader and it's lysosomes release chemicals to destroy the invader, the WBC and the affected cells |
|
|
|
Antibodies |
A) each invading cell have distinctive molecules called markers on their cell membranes or protein coats B) markers have specific shape that antibodies are designed to fit C) each type of antibodies works on only one type of invest |
|
|
|
Antibodies |
A) each invading cell have distinctive molecules called markers on their cell membranes or protein coats B) markers have specific shape that antibodies are designed to fit C) each type of antibodies works on only one type of invest |
|

