![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
45 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Environment
11-1 |
Everything that surrounds an organism and acts upon it
*organisms get all that they need from the environment |
|
|
Ecology
11-1 |
study or relationships between living things and their environment
|
|
|
Interact
11-1 |
process of organisms acting upon one another or on the nonliving parts of their environment
|
|
|
Animals
11-1 |
* get nutrients and energy from eating plants or other animals
*oxygen from air |
|
|
Fish
11-1 |
get oxygen from dissolved oxygen in water
|
|
|
Plants
11-1 |
Green plants get nutrients and water from soil
Sunlight + water+minerals+ CO2= growth and make food for energy Oxygen from air= cellular respiration |
|
|
Ecologist
11-1 |
Scientists who study ecology
|
|
|
Population
11-2 |
group of the same kind of organisms living in a certain place
Ex: Zebras>grassland Ex: Eskimos>Alaska |
|
|
Community
11-1 |
all the populations that live in a certain place and can interact with one another
Ex: Zebras, Wildebeest, ants, bees, grassland= community |
|
|
Ecosystem
11-1 |
a group of COMMUNITIES interacting with each other and the nonliving parts of the environment(water, air, soil)
Ex: Grassland is the ecosystem Zebras, Wildebeest, ants, bees, |
|
|
Ecosystem: Self Supporting
11-2 |
Production of Energy>sun
transfer of energy> plants to animals Breakdown of material>organisms die and decompose Recycling>material in ecosystem used over and over |
|
|
Habitat
11-3 |
place where an organism lives
EX: Person's habitat is their house Polar bear and seal>Arctic Ocean provides food, water, shelter and a place to reproduce |
|
|
Niche
11-3 |
organisms role or job in its habitat
Students niche is to study Polar bears>hunt seals Seals> feed on fish |
|
|
Limiting Factor
11-4 |
condition in the environment that puts limits on the size a population can grow to
destroy habitat limits the size of the population EX: few mice=owls starve |
|
|
Carrying Capacity
11-4 |
Largest population size that can be supported by the available resources of an area
Deer population grows so move from forests into the town of Elba |
|
|
Range
11-4 |
area where a type of animal or plant population is found
Determined by the limiting factor EX: Black Bears eat fruit, nuts, berries so have large range Panda Bears eat Bamboo so range is small(China) |
|
|
Climate
11-5 |
average weather of an area over a long period of time
determines what plants and animals can live in an area |
|
|
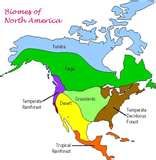
Biome
11-5 |
a large region that has similar types of plants and animals
|
|
|
How many Biomes are there on Earth?
11-5 |
7
tundra, taiga, temperate deciduous forest, temperate grassland, tropical rain forest, deserts |
|
|
Tundra
11-5 |
located FAR NORTH
ground(soil) always frozen moss, lichens grasses and small flowers, shrubs grow here Animals: birds, wolves, foxes and reindeer |
|
|
BIOME:
Taiga 11-5 |
South of the tundra
coniferous forests(evergreens) Animals: moose, squirrels, rabbits and beavers |
|
|
BIOME:
Temperate Deciduous forest 11-5 |
South of the taiga
moderate Climate long growing season with cold winter Deciduous trees: maple, oak, birch, leaves fall in the AUTUMN (New York State part of this Biome) |
|
|
BIOME:
Temperate grasslands/ Savannas 11-5 |
moderate Climate
not enough rain for all trees to grow Temperate Grassland: interior of continents rich soil for farming SAVANNAS: close to the equator scattered trees and shrubs |
|
|
BIOME:
Tropical Rainforests 11-5 |
Near the equator
large amounts of rainfall hot all year Tall trees |
|
|
BIOME:
Deserts 11-5 |
Temperature moderate or HOT
very LITTLE rain few plants grow Can find Cacti, Animals,: birds lizards scorpions |
|
|
Polar Ice BIOME
11-5 |
North and South Poles
very very cold temperature thick sheets of ice and almost lifeless Animals: penguins |
|
|
Succession
11-6 |
changes in the environment
gradual change in populations of organisms that occurs when the environment changes |
|
|
Climax Community
11-6 |
last community in succession
|
|
|
Succession to Climax Community
11-6 page 268 EXample: Fire Destroys the Forest to the Ground What Happens? |
1)Open field: burnt area=grasses and weeds(pioneer plants) first to grow
2) Shrub Land: shade then get grasses and shrub 3) Pine Forest: pine trees 4) Hardwood Forest: trees like maple and oak |
|
|
Natural Resources
11-7 |
material found in nature that is used by living things
Example: fish, trees, oil, coal, gas, water |
|
|
Renewable Resources
11-7 |
Natural Resource that can be reused or replaced
Example: water, soil, lumber cut the trees in the forest and then replant |
|
|
Nonrenewable Resource
11-7 |
natural resource that cannot be reused or replaced
Example: coal, oil, natural gas, minerals |
|
|
Conservation
11-7 |
wise use of natural resources
Example: buy and use energy efficient light bulbs solar and wind power |
|
|
Succession:
1 Open Field |

|
|
|
Succession:
3. Pine Forest |

|
|
|
Succession:
4: Hardwood Forest |

|
|
|
Succession:
2. Shrub or Scrub Land |

|
|
|
TUNDRA BIOME
|

|
|
|
TAIGA BIOME
|

|
|
|
Grassland BIOME
|

|
|
|
BIOME Deciduous Forest
|

|
|
|
BIOME Savanna
|

|
|
|
BIOME: Tropical Rainforest
|

|
|
|
BIOME: Deserts
|

|
|
|
BIOMES in the United States
|
|

