![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
57 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Monera
6-1 |
single celled organism
NO true NUCLEUS |
|
|
Bacteria
6-1 |
Simple one celled organisms
visible under a microscope |
|
|
Characteristics of Bacteria
6-1 |
has cytoplasm,
cell membrane cell wall NO NUCLEUS genetic material is in a ring in the cytoplasm reproduce asexually>binary fission |
|
|
KINGDOM MONERA
6-1 |
includes all bacteria
|
|
|
How are bacteria grouped?
6-1 |
grouped according to shape
round>cocci curved or spiral>spirilla rods>bacilli |
|
|
Coccus(s) cocci(p)
6-1 |
Spherical shaped bacterium
grow in pairs, chains or clusters |
|
|
Spirillum (s) spirilla(p)
6-1 |
spiral shaped bacterium
curved shaped some move with a flagellum |
|
|
Bacillus (s) bacillus (pl)
6-1 |
rod-shaped bacterium
grow in pairs or clusters some move with a flagellum |
|
|
Flagellum (s) flagella (p)
6-1 |
whiplike structure on a cell
help to move through liquid |
|
|
Bacteria Needs
6-1 |
*many need water and proper temperature
* thrive in darkness *some need Oxygen *get food by living inside plants or animals *most feed on dead plants or animals *some use sunlight for food |
|
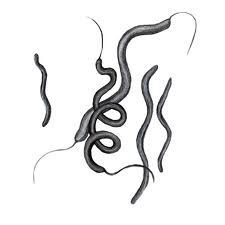
What am I?
|
I am a spirilla bacteria
|
|
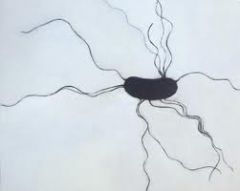
What am I?
|
I am flagella.
|
|
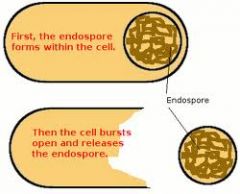
What am I?
|
I am an endospore.
|
|
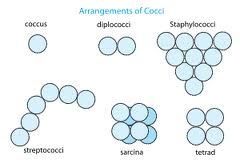
What am I?
|
I am a coccus bacteria
|
|
What am I?
|
I am a blue green bacteria?
|
|
What am I?
|
I am a bacillus bacteria.
|
|

Who am I?
|
I am the Father of Bacteriology.
I am Louis Pasteur. |
|
|
Bacteriology
6-2 |
The study of bacteria/
|
|
|
What food products are made from bacteria?
6-2 |
flavoring in butter
buttermilk yogurt cheese sauerkraut |
|
|
Bacteria in the digestive tract can help digest_________.
6-2 |
nutrients
some help form important vitamins |
|
|
What are nitrogen-fixing bacteria?
6-2 |
bacteria found in the soil and in the roots of some plants.
change nitrogen from the air into compounds plants can use |
|
|
Decomposition
6-2 |
breakdown of dead material(leaves and animal waste) by simple organisms
** puts important nutrients back into the soil** |
|
|
What is blight?
6-2 |
Blight is a plant disease sometimes caused by bacteria.
kills the flowers, young leaves, and stems of plants |
|
|
What diseases does bacteria cause in humans?
6-2 |
>strep throat
>pneumonia > Lyme disease |
|
|
What is rot?
6-2 |
a plant disease caused by bacteria
destroys cell walls of plant tissue |
|
|
What does bacteria do to food?
6-2 |
>foods spoil
>create poison > |
|
|
What is pasteurization?
6-2 |
a process used to slow down the spoiling of milk and other diary products.
|
|
|
Protozoan
6-3 |
one celled
animal like protist> cannot make their own food eat other organisms move own own |
|
|
Kingdom Protista
6-3 |
made up of very simple organisms
most unicellular has nucleus surrounded by a membrane |
|
|
Kingdom Protista continued
What are the 3 groups of Protista? 6-3 |
1. Protozoans
2. algae 3. slime molds |
|
|
What are some examples of animal like protists?
6-3 |
Amoebas
Paramecia trypanosomes |
|
|
What are the 3 structures that protisits use for moving?
6-3 |
flagella
cillia pseudopods |
|
|
Pseudopod
6-3 |
finger like extention of cytoplasm
|
|
|
cilium/cillia
6-3 |
tiny, hairlike structures
|
|
|
flagella/flagellum
6-3 |
whip like tail
|
|
|
AMOEBA
6-3 |
a protozoan
most live in fresh water fingerlike projections>pseudopods cell membrane is flexible moves with pseudopods |
|
|
PARAMECIUM
6-3 |
slipper shaped protozoan
lives in fresh water use cilia for movement and to get food |
|
|
TRYPANOSOMES
6-3 |
disease causing protozoan
in humans causes African Sleeping sickness have a flagella |
|
|
Plankton
6-4 |
microscopic organisms that float on or near the water's surface
unicellular |
|
|
Algae
6-4 |
part of protists kingdom
some unicellular some multicellular all contain chlorophyll make their own food through photosynthesis PLANTLIKE PROTIST |
|
|
Euglena
6-4 |
Unicellular algae
plantlike and animal like contains chlorophyll has an eyespot to detect light uses a flagellum to move changes shape with flexible outer coverin |
|
|
chlorophyll
6-4 |
green pigment found in plants and algae
|
|
|
Kingdom Fungi
6-5 |
cells have cell walls
many are multicellular grow well in soil no chloroplasts or chlorophyll do not make their own food |
|
|
Fungi continued
6-5 |
get food from dead or decaying matter
grow well in dark, warm, and wet places |
|
|
What is included in the Kingdom Fungi?
6-5 |
Yeasts
Molds Mushrooms YMM |
|
|
Mushrooms
6-5 |
Kingdom Fungi
Parts: Stalk, cap, hyphae, gills, |
|
|
Mushroom CAP
6-5 |
umbrella shaped top
|
|
|
Mushroom GILLS
6-5 |
underside of the cap is lined with these
produce spores |
|
|
Mushroom HYPHAE(A)
6-5 |
threadlike structures that makes up the body of molds and mushrooms
|
|
|
Mushroom SPORE
6-5 |
produced by the gills
the reproductive structures of fungi |
|
|
Mushroom SPORULATION
|
kind of asexual reproduction in which a new organisms forms from spores released from a parent
|
|
|
Mushroom STALK
6-5 |
stemlike part of a mushroom
|
|
|
Mushroom SPORE CASES
6-5/6-6 |
a case like structure in the mushroom or molds that contain thousands of spores
|
|
|
Molds
6-5 |
common fungi
grow on bread, fruit, vegetables look like treads>hyphae |
|
|
Yeasts
6-5 |
colorless
unicellular fungi have a cell membrane and cell wall contains cytoplasm and a nucleus reproduces by budding |
|
|
Budding
6-5/6-6 |
kind of asexual reproduction in which a new organism forms from a bud on a parent
yeast reproduces this way |
|
|
Fermentation
6-5 |
process by which a cell releases energy from food without using oxygen
|

