![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
12 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
CUMULUS |
a cloud forming rounded masses heaped on each other above a flat base at fairly low altitude. |

|
|
|
CIRRUS |
thin, wispy clouds that usually form above 18,000 feet. These clouds are blown by strong westerly winds aloft into streamers known as "mares' tails" |

|
|
|
CUMULONIMBUS |
a cloud forming a towering mass with a flat base at fairly low altitude and often a flat top, as in thunderstorms. |

|
|
|
STRATUS |
cloud forming a continuous horizontal gray sheet, often with rain or snow. |

|
|
|
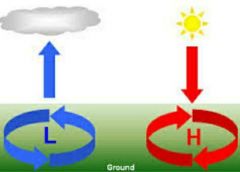
AIR PRESSURE |
the force exerted by air on any surface in contact with it. Changes in the air pressure or barometric pressure mean a change in weather |
|
|
|
TRANSPIRATION |
the process by which moisture is carried through plants from roots to small pores on the underside of leaves, where it changes to vapor and is released to the atmosphere. |

|
|
|
CONDENSATION |
the change of water from water vapor into liquid. |

|
|
|
EVAPORATION |
when a liquid for example water turn in to gas for example steam when heated. |

|
|
|
PRECIPITATION |
is any form of water - liquid or solid - falling from the sky. It includes rain, sleet, snow, hail and drizzle plus a few less common occurrences such as ice pellets, diamond dust and freezing rain. |

|
|
|
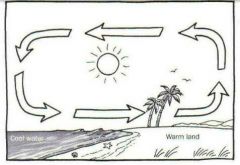
SEA BREEZE |
a breeze blowing toward the land from the sea, especially during the day owing to the relative warmth of the land. |
|
|
|
LAND BREEZE |
a breeze blowing toward the sea from the land, especially at night, owing to the relative warmth of the sea. |

|
|
|
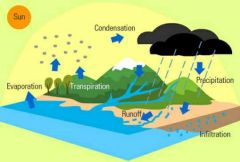
WATER CYCLE |
the cycle of processes by which water circulates between the earth's oceans, atmosphere, and land, involving precipitation as rain and snow, drainage in streams and rivers, and return to the atmosphere by evaporation and transpiration. |
|

