![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
34 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What does WHMIS stand for? |
Workplace Hazardous Materials Information Safety |
|
|
|
What are the names and symbols of all the classes of WHMIS A B C D D D E F |
A) Compressed gas B) Flammable and combustible Material C) Oxidizing Material D) Poisonous and Infectious Material Division 1- immediate and serious toxic effects D) Poisonous and Infectious Material Division 2- other toxic effects D) Bio hazardous Infectious Material E) Corrosive Material F) Dangerously Reactive Material |
|
|
|
What is Matter made of? What are all 7? |
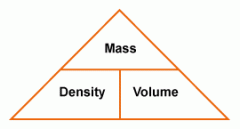
-Mass= the AMOUNT of substance (grams, kg) (M=D x V) -Volume= the amount of SPACE a substance takes up (liters, m3) (V=M/D) Density - the amount of mass in a certain volume of a substance of object (D=M/V) State - Solid, liquid, gas Conductivity - how easily something lets electricity or heat move through it Boiling point - The temperature when a substance changes state from a liquid to a solid Melting point - The temperature when a substance changes state from a solid to a liquid |
|
|
|
What are the Physical properties of Matter? |
Qualitative = Properties that can be DESCRIBED but not MEASURED Quantitative = Properties that can be MEASUERED numerically |
2 properties |
|
|
What is the Kinetic Molecular Theory |
All matter is made up of very small particles There is empty space between particles Particles are always moving Energy makes particles move |
More energy Particles are faster and farther apart |
|
|
Who was credited with developing a new way of explaining matter |
John Dalton (1766-1844) |
The first guy |
|
|
What was Dalton's Theory? |
All matter is made up of small particles called Atoms Atoms cannot be destroyed, created, or divided into smaller particles All atoms of the same element are identical in mass and size but are different from atoms of other elements Compounds are created when atoms of different elements link together in definite proportions |
|
|
|
J.J Thomson discovered that all atoms contain particles that later became known as electrons. What did this discovery make it possible to conclude about atoms? |
All atoms are composed of a combination of subatomic particles |
a) All atoms conduct electricity b) All atoms are composed of a combination of subatomic particles c) All atoms are identical to all other atoms d) All atoms are negatively charged |
|
|
What did Ernest Rutherford do? |
Experimented with charged particles and found that some particles were deflected in directions not originally predicted Suggested that deflection was because of the atom had a tiny dense center called a nucleus, and electrons move around the nucleus |
2 things (experimented and suggested) |
|
|
What did Niels Bohr propose? |
proposed that electrons surround the nucleus in specific "energy levels" or "shells" |
|
|
|
What is inside an Atom? |
Atom is the smallest particle of an element that retains the properties of the element All atoms are made up of three kinds of particles called SUBATOMIC PARTICLES Electrons Protons Neutrons (0) |
3 Things |
|
|
What do metals typically have the following physical properties? |
Are hard solids at room temp (except mercury which is a liquid) Shiny Ductile Malleable Good conductors of heat and electricity |
5 Things |
|
|
What do non-metals typically have the following physical properties? |
Are gases or brittle solids at room temp (except for bromine, which is a liquid) Not shiny Not ductile Not malleable Not good conductors of heat and electricity |
5 Things |
|
|
What is the periodic table? |
The name of the element The chemical symbol of the element the atomic number of the element - the number of protons in the nucleus of each one of its atoms The average atomic mass of the element - the weighted average of the masses of the atoms of an element The ion charge (or charges) of the element - the electric charge of its atoms when they gain or lose electrons. If the atoms can gain or lose electrons in more than one way, they will have a multiple ion charge |
5 Things |
|
|
On the Periodic table what group belongs to which name? Alkali Metals, Alkaline Earth Metals, Halogens, Noble gases |
Group 1, Group 2, Group 17, Group 18 |
First 2, Last 2 |
|
|
What is the Periodic table divided into? |
7 horizontal row=Periods 18 Vertical columns=Families |
More families then periods |
|
|
Where do metals and non-metals on the P Table and are they good heat conductors? |
-Metals appear on the left side of the periodic table. These elements are good conductors of heat and electricity. -Non-metals appear on the right side of the periodic table. These elements are poor conductors of heat and electricity.
|
Are there more metals or non-metals? |
|
|
What does the Atomic number mean? What does the Average Atomic Weight mean? |
The atomic number refers to the number of protons that an atom has in the nucleus. The average atomic mass is the weighted average of the masses of the atoms of an element. |
|
|
|
What is a multiple ion charge? |
If the atoms can gain or lose electrons in more than one way, they will have a multiple ion charge. |
2+ 3+ 4+ |
|
|
How many electrons can be on a Bohr model? |
First shell=max of 2 electrons Second shell=max of 8 electrons Third shell=max of 8 electrons The Valence shell is the electrons that are farthest away from the nucleus. Electrons in the valence shell are called valence electrons. |
|
|
|
How do atoms form Ions? |
An Ion is an atom with an electric charge because it has gained or lost electrons. An ion has a negative charge when it has more electrons than protons. An ion has a positive charge when it has more protons than electrons. |
3 Points |
|
|
Do metals tend to gain or loose electrons? Do non-metals tend to gain or loose electrons? |
Metals=tend to lose electrons and form positive ions Non-metals=(except for noble gases) tend to gain electrons and form negative ions |
|
|
|
What is a Compound? How is a compound related to a chemical bond? |
A Compound is a pure substance that is made up of 2 or more types of atoms that are joined together due to a chemical change. Atoms are held together in compounds by CHEMICAL BONDS Chemical Bonds are formed when atoms gain of lose electrons or when they share electrons |
|
|
|
What are Ionic Compounds? |
If atoms gain electrons from other atoms or lose electrons to other atoms When atoms of a metal come near atoms of a non-metal, they can join together to form and ionic compound Ionic Compounds are made up of charged particles (ions) but the positive charges and the negative charges balance, so ions compounds are neutral |
3 Points |
|
|
What is a repeating pattern of positive and negative ions in a compound is called... |
Ionic Lattice |
Think of the Cube |
|
|
What are Covalent Compounds? |
-Atoms share electrons instead of losing and gaining them. Covalent compounds form when non-metal atoms bond together by sharing their electrons Covalent Compounds are neutral (no charge) Neutral particles are made up of atoms that are joined together by covalent bonds called a molecule |
EG. Water molecules are a covalent compound Its molecules are made of hydrogen and oxygen |
|
|
What is a Polyatomic ion? |
An ion that is made up of two or more atoms that are held together with covalent bonds |
Poly=5 |
|
|
What do the Chemical names of some ionic compounds include? |
Roman Numerals |
IV |
|
|
What do Ionic compounds include?
|
Ionic compounds include multivalent metals - Metals that can form two or more different positive ions with different charges |
|
|
|
What is a Physical change? Examples? |
A substance changes in form but not in its chemical composition (changes shape but not the chemical part) All changes of state are physical changes Others include cutting, grinding, and tearing substances |
Changes of state |
|
|
What is a Chemical change? Examples? |
Chemical change cause one or more new substances to be formed Burning paper is an example of Chemical Change, it will be different from the original after it is burnt In any chemical change, the starting substance that reacts are called reactants The substances that result are called products |
Opposite of Physical change |
|
|
What does Exothermic mean? Example? What does Endothermic mean? Example? |
Exothermic = Energy and light is released (fireworks) Endothermic = Energy is absorbed (baking cookies) |
|
|
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 In Roman Numerals |
I II III IV V VI VII VIII IX X |
|
|
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Add Prefixes P2O5 |
Mono Di Tri Tetra Penta Hexa Hepta Octa Nona Deca Diphosphorus pentoxide |
Phosphorus Oxide |

