![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
27 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
A disturbance that transfers energy from place to place.
|

Wave
|
|
|
The high point of a wave.
|

Crest
|
|
|
The low point of a wave.
|

Trough
|
|
|
The maximum distance that the particles of the medium carrying them from their rest position.
|

Amplitude
|
|
|
The distance between two corresponding parts of a wave.
|
Wave length
|
|
|
When an object or wave bounces back off a surface through it cannot pass.
|

Reflection
|
|
|
All waves obey this. This states that the angle of incidence equals the angle of the reflection.
|

Law of Reflection
|
|
|
A mirror with a surface that curves inward like the inside of a bowl.
(curves in like a cave) |

Concave mirror
|
|
|
A mirror with a surface that curves outward.
|

Convex mirror
|
|
|
The bending of light waves due to a change in speed.
|

Refraction
|
|
|
A magnifiying glass is thicker in the center than at the edges.
|

Convex lens
|
|
|
A lens that is thinner in the middle than at the edges.
|
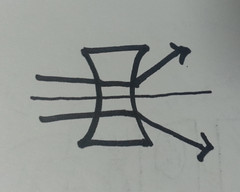
Concave lens
|
|
|
The complete range of the electromagnetic wave placed in their order of frequency.
|

Electromagnetic spectrum
|
|
|
Material that transmits most of the light that strikes it.
|

Transparent
|
|
|
Material that scatters light as it passes through. ( smoke, fog, or clouds.)
|

Translucent
|
|
|
Material that absorbs all the light that strikes it.
|

Opaque
|
|
|
A short thick nerve in the eye.
|

Optic nerve
|
|
|
The circular structure that surrounds the pupil and regulates the amount of light entering the eye.
|

Iris
|
|
|
A layer of cells that lines the inside of the eyeball.
|
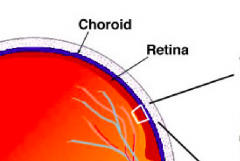
Retina
|
|
|
A small depression in the retina of the eye where visual acuity is highest.
|
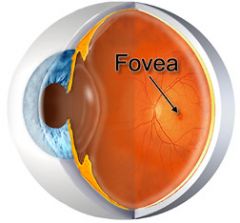
Fovea
|
|
|
Light enter the eye through the transparent front surface.
|
Cornea
|
|
|
An opening through which light enters the inside of the eye.
|

Pupil
|
|
|
A curved piece of glass or other transparent material that refracts light.
|

Lens
|
|
|
The white outer layer of the eyeball. At the front of the eye it is continuous with the cornea.
|

Sclera
|
|
|
The pigmented vascular layer of the eyeball between the retina and the sclera.
|

Choroid
|
|
|
The transparent jellylike tissue filling the eyeball behind the lens.
|

Vitreous humor
|
|
|
The clear fluid filling the space in the front of the eyeball between the lens and the cornea.
|
Aqueous Humor
|

