![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
82 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Is the sudden shaking or movement of the crust. |
Earthquake |
|
|
The outermost solid portion of Earth that houses all living things. |
Crust |
|
|
The layer of the atmosphere wherein all weather phenomena occurs. |
Troposphere |
|
|
Is a region that carries the entire crust that extends down to the upper portion of the asthenosphere. |
Lithosphere |
|
|
The lithosphere is _______ _______. The rocks here are elastic but brittle that they deform or fracture as they receive and store stress. |
Elastic Solid |
|
|
Enumerate the 5 layers of the earth. |
Crust, upper and lower mantle, and outer and inner core. |
|
|
The upper mantle is also known as..? |
The Asthenosphere |
|
|
The Greek word asthenēs means what? |
Weak |
|
|
The Asthenosphere is ___-___ km deep. |
100-650 km |
|
|
The lithosphere is elastic solid, and the Asthenosphere is ______ ______. |
Plastic solid |
|
|
Nearly 90% of the world's strongest earthquakes, and more than 80% of the strongest ones occur here. |
Pacific Ring of Fire |
|
|
Fractures or breaks in Earth's crust are called.... |
Faults |
|
|
Occurs when there is movement or displacement of rock masses along a fault. |
Faulting |
|
|
*True or false* There are 5 types of tectonic plates. |
False, only 3 |
|
|
A type of tectonic force that pushes rocks in the crust to each other. |
Compressional Force |
|
|
A type of tectonic force which pulls crustal rocks away from each other. |
Tensional Force. |
|
|
A type of tectonic force which enables rocks in the crust to slide past each other. |
Shearing Force |
|
|
What type of fault is formed when a rock mass in the crust is pushed up relative to the other rock mass due to compressional force? |
Reverse fault |
|
|
What type of fault is formed when a tensional force acts on rock masses in the crust, and one rock mass moves downward relative to the other? |
Normal fault |
|
|
What type of fault is formed when a rock mass on one side of a fault slides past the other? |
Transform fault/Strike-slip fault |
|
|
Faults in which all shallow earthquakes occur. |
Active Faults |
|
|
Areas that have not displayed seismic activity for a long time. (Thousands of years) |
Inactive faults *In spite of being inactive, these faults are believed to be able to produce strong earthquakes.* |
|
|
Which fault system is Cavite part of? |
West Valley Fault System |
|
|
Which is directly above the hypocenter/focus? |
Epicenter |
|
|
Pertains to the strength and size of an earthquake. |
Magnitude |
|
|
Magnitude is measured by what scale? |
The Richter Scale |
|
|
Measures the observed effects of an earthquake. |
Intensity |
|
|
Intensity is measured by what scale? |
Modified Mercalli Scale |
|
|
Series of huge waves caused by an earthquake that occurs underneath or near the ocean. |
Tsunami |
|
|
Tsunami is a Japanese term that means... |
“Harbor waves” |
|
|
*True or false* Tsunamis and Tidal waves are the same thing. |
False, tidal waves are caused by the moon's gravity, unlike tsunamis. |
|
|
For an underwater earthquake to cause tsunamis, its magnitude should be over ____ on the Richter Scale. |
6.75 |
|
|
The _________ phenomenon causes high-intensity underwater earthquakes that move a colossal volume of water. |
Subduction |
|
|
Released outward from the focus and travel horizontally and vertically in different directions across Earth's interior. |
Seismic waves |
|
|
*True or False* Seismologists identified 4 types of seismic waves. |
True |
|
|
These waves travel across the earth's interior. |
Body waves |
|
|
Which 2 waves are classified as body waves? |
P- and S-waves |
|
|
The vibrations we feel when an earthquake strikes. |
Surface waves |
|
|
Which 2 waves are classified as Surface waves? |
L- and R-waves |
|
|
P-waves are also called what? |
Primary waves |
|
|
The seismic waves that are the first to be recorded by a seismograph. |
P-waves or Primary waves |
|
|
*True or False* P-waves can only move through one medium. |
False. P-waves travel in all types of medium: solid, liquid, and gas. |
|
|
S-waves are also called what? |
Secondary waves |
|
|
The seismic waves that are the second to be detected by a seismograph. |
S-waves or Secondary waves |
|
|
S-waves only travel in ______ medium. |
Solid |
|
|
L-waves are also known as Love waves, named after who? |
Augustus Edward Hough Love |
|
|
*True of False* L-waves are of high frequency. |
False. L-waves are of LOW frequency. |
|
|
The seismic waves that are the third to be detected by a seismograph. |
L-waves or Love waves |
|
|
R-waves are also known as? |
Rayleigh waves |
|
|
The slowest travelling seismic wave. |
R-waves |
|
|
Most destructive waves. |
Surface waves |
|
|
Used to detect, measure, and record seismic waves generated by earthquakes. |
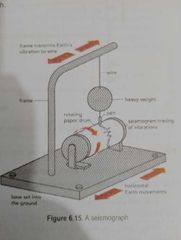
Seismograph |
|
|
A seismograph produces what? |
Seismogram |
|
|
Scientists that study seismic waves. |
Seismologists |
|
|
On _____ observations, scientists have a direct hand in gathering data. |
Direct |
|
|
*Concept question* It was found from the analysis of a seismogram that S-waves cannot travel into the inner core of the earth, even though P-waves are perfectly capable of it. Why is that? |
Because the outer core of the earth was discovered to be liquid. Since S-waves can only travel in solid mediums, it cannot even pass through the outer core, let alone the inner core. P-waves on the other hand, can travel in all medium, and passed through the core with no problems. |
|
|
The point at which an earthquake originates. |
Focus |
|
|
Determines the epicenter of an earthquake. |
Triangulation |
|
|
The troposphere begins from the surface up to a height of _ to __ km above sea level. |
7 to 20 km |
|
|
The department that monitors seismic activity. |
PHIVOLCS - Philippine Institute of Volcanology and Seismology |
|
|
Enumerate the three basic stages in the development of a tropical cyclone. |
Origin or Formative stage, Mature stage, and Dissipation stage. |
|
|
This stage pertains to the state in which a tropical cyclone begins to develop when the conditions for its formation are met. |
Formative stage |
|
|
The stage when a tropical cyclone is already packed with raging winds and swirling towering clouds. |
Mature stage |
|
|
The stage when it is weak and can disappear anytime with lack of moisture. |
Dissipation stage |
|
|
*True or False* For a tropical cyclone to form, it needs large, still, and warm water. |
True |
|
|
The surface temperature needed for warm air to develop typically ranges from ___ to ___° Celsius. |
26 to 30° Celsius |
|
|
As warm air develops on the ocean's surface, it expands and rises to the atmosphere creating a..... |
Low-pressure area |
|
|
The force rendered by the Earth's rotation due to its tilted axis. |
Coriolis Force |
|
|
The Coriolis force affects the rising air from the surface to spiral around the center of the thick clouds, forming a vortex called ____. |
Eye or the “eye of the storm” |
|
|
*True or false* The eye is an area of calm air. |
True |
|
|
For a tropical cyclone to survive, it needs what? |
A constant supply of warm water. |
|
|
What sector of the government is responsible for monitoring typhoons? |
PAGASA - Philippine Atmospheric Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration |
|
|
If the winds of a typhoon are lower, or at 61 km/h, what is the classification? |
Tropical Depression |
|
|
If the winds of a typhoon are 62 to 88 km/h, what is the classification? |
Tropical storm |
|
|
If the winds of a typhoon are 89 to 117 km/h, what is the classification? |
Severe Tropical Storm |
|
|
If the winds of a typhoon are 118 to 184 km/h, what is the classification? |
Typhoon |
|
|
If the winds of a typhoon are 185 km/h or higher, what is the classification? |
Super Typhoon |
|
|
A mass of swirling towering clouds that carried surging winds and rainfalls. |
Tropical cyclone |
|
|
The Philippines is prone to earthquakes because of what? |
It's geographic location |
|
|
Surrounding the equator is the ____________, an area where tropical cyclones form. |
The ITCZ - Intertropical Convergence Zone |
|
|
PAGASA uses what term concerning the weather disturbances that periodically hit the country? |
PAR - Philippine Area of Responsibility |
|
|
*True or False* Tropical cyclones that traverse the PAR follows a constant track or movement. |
False |

