![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
53 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Important component of earths litosphere. Building blocks of rocks. |
Minerals |
|
|
Naturally Occurring and inorganic in nature |
minerals |
|
|
Objects made of minerals |
jewelries, toothpaste, make up, and mirror. |
|
|
Eight classes of minerals |
silicates, oxides, sulphides, halides, sulfates, carbonates, phosphates, and mineraloids |
|
|
Jewelries |
gold and silver |
|
|
make up |
talc |
|
|
mirror |
quartz |
|
|
electricity |
copper |
|
|
pencil |
graphite |
|
|
salt |
halite |
|
|
kitchen |
granite |
|
|
What are the characteristics of minerals? |
Define the 4 characteristics |
|
|
Refers to the overall shape pr growth pattern of the mineral |
Crystal Habit |
|
|
3D of mineral, have about same length like a cube or sphere |
Equant |
|
|
Forms or prism like crystal that are thicker that a needle |
elongate |
|
|
Looks like a flattened and thin crystal |
Platy |
|
|
Describe the appearance of mineral when a light is reflected from its surface, can be described as opaque, transparent, dull, or shiny |
Luster |
|
|
Tendency of minerals to break along gery smooth, flat, and shiny surface |
Cleavage |
|
|
Described as irregular, random surfaces |
Fracture |
|
|
Is a measure of the minerals residtance to scratching, harder minerals will scratch harder |
hardness |
|
|
Arranged in an orderly and repeating patterns |
orderly crystaline structures |
|
|
Who created the various hardness level |
Friedrich Mohs |
|
|
Has a hardness level of 1 |
Talc |
|
|
Hardness level 2 |
gypsum |
|
|
hardness level 9 |
corundum (Ruby) |
|
|
Hardness level 10 |
Diamond |
|
|
Reaction to stress |
Tenacity |
|
|
Minerals turns into powder |
Brittleness |
|
|
Mineral can be flattened by pounding with a hammer |
melleability |
|
|
Elastic and inelastic |
Flexible |
|
|
Goes back to the same shape |
elastic |
|
|
Ability of minerals to be sliced by a knife |
sectility |
|
|
Classified as metals, semi-metals, and non metals |
native elements |
|
|
Minerals are attracted to a hand magnet |
magnetism |
|
|
Thin, parallel groove or streaks |
striation |
|
|
more reliable property than color as streak shows the true color of minerals |
streak |
|
|
Weight of that mineral divided by the weight of an equal volume of water |
specifc gravity |
|
|
some minerals have distinctive taste, odor, and feel |
taste, odor, feel |
|
|
Created DANA system |
James Dwight Dana |
|

|
Native elements |
|

magnesium, iron and calcium |
silicates |
|
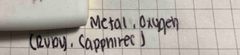
Metallic materials such as hemalite, chrysoberyl, and spinel. Formed by percipitation or weathering
|
oxides |
|
|
Important metals such as copper, lead, and silver used in cosntructions
|
sulphide |
|

found in areas with high evaporation rates and where salty waters slowly evaporate
|
sulphates |
|
|
contains natural salt. Found in lakes, ponds, dead seas and great salt lake. Poor conductor of heat and electricity, low specific gravity
|
halide |
|
|
found in deposited marine environment, also found in caves, places with high evaporation rates formed from the shells of deadl plankton and othe rmarine organisms
|
carbonate |
|
|
found in teeths and bones of many animals |
phospate |
|
|
contains metals and internetallis elements, semi metals, non-metals or natural alloys
|
natuve element |
|
|
Form regular and repeating three dimensional crystal structure |
Crystal Solid |
|
|
Forms aggregates that have no particular order or arrangement |
amorphous solid |
|
|
Allows most light to pass through undistorted such as calcite |
Transparent |
|
|
Light passes through but it is bent and you cannot resolve images such as muscovite |
translucent |
|
|
no light passes through even the thinnest slice such as cinnbar |
opaque |

