![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
11 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Electrolyte
|
An electrolyte is a substance that ionizes when dissolved in suitable ionizing solvents such as water. This includes most soluble salts, acids, and bases. |
NaCl, HNO3, HClO3, CaCl2
|
|
|
independent variable
|
not change
|
|
|
|
Substrate
|
a substance or layer that underlies something, or on which some process occurs, in particular.
the surface or material on or from which an organism lives, grows, or obtains its nourishment. the substance on which an enzyme acts. |
|
|
|
Photosynthesis
|
the process by which green plants and some other organisms use sunlight to synthesize foods from carbon dioxide and water. Photosynthesis in plants generally involves the green pigment chlorophyll and generates oxygen as a byproduct.
|
|
|
|
troposphere
|
lower atmosphere almost all weather occurs in this region. The troposphere begins at the Earth's surface
As the density of the gases in this layer decrease with height, the air becomes thinner. Therefore, the temperature in the troposphere also decreases with height in response. As one climbs higher, the temperature drops from an average around 62°F (17°C) to -60°F (-51°C) at the tropopause. |
|
|
|
Stratosphere
|
This layer holds 19 percent of the atmosphere's gases but very little water vapor.
In this region the temperature increases with height. Heat is produced in the process of the formation of Ozone This increase in temperature with height means warmer air is located above cooler air. This prevents "convection" |
|
|
|
mesosphere
|
The gases, including the oxygen molecules, continue to become more dense as one descends. As such, temperatures increase as one descends rising to about 5°F (-15°C) near the bottom of this layer.
The gases in the mesosphere are now thick enough to slow down meteors hurtling into the atmosphere, where they burn up, leaving fiery trails in the night sky. Both the stratosphere (next layer down) and the mesosphere are considered the middle atmosphere. The transition boundary which separates the mesosphere from the stratosphere is called the stratopause. |
|
|
|
Glycolysis or Glucose
|
Each molecules of glucose is broken down into 2 molecules of pyruvic acid , 2 APT molecules, 2 hydrogen atoms NOT CO
|
|
|
|
inertia
|
Inertia is the resistance of any physical object to any change in its state of motion, including changes to its speed and direction. It is the tendency of objects to keep moving in a straight line at constant velocity.
|
|
|
|
Momentum
|
the quantity of motion of a moving body, measured as a product of its mass and velocity.
the impetus gained by a moving object. "the vehicle gained momentum as the road dipped" |
|
|
|
layers
|
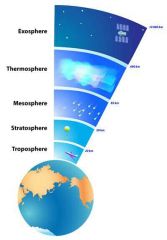
|
|

