![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
16 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
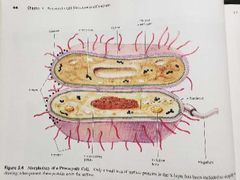
Plasma membrane (functions of prokaryotic structures) |
Selectively permeable barrier, mechanical boundary of cell, nutrient and waste transport, location of many metabolic processes (respiration, photosynthesis) detection of environmental cues for chemotaxis |
|
|
Chemotaxis |
Pattern of microbial behavior in which the microorganism moves toward chemical attractants and/ or away from repellents. |
|
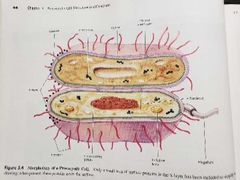
Gas vacuole (functions of prokaryotic structures) |
Buoyancy for floating in aquatic environments |
|
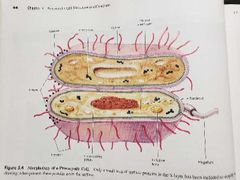
Ribosomes (functions of prokaryotic structures) |
Protein synthesis |
|
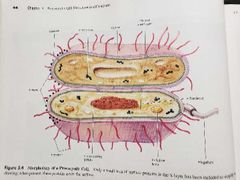
Inclusion bodies (functions of prokaryotic structures) |
Storage of carbon, phosphate and other substances |
|
|
Nucleoid (functions of prokaryotic structures) |
Localization of genetic material (DNA) |
|
|
Periplasmic space (functions of prokaryotic structures) |
Contains hydrolytic enzymes and binding proteins for nutrient processing and uptake |
|
|
Cell wall (functions of prokaryotic structures) |
Gives bacteria shape and protection from lysis in dilute solutions |
|
|
Capsules & Slime layers (functions of prokaryotic structures) |
Resistance to phagocytosis, adherence to surfaces |
|
|
Fimbriae & Pili (functions of prokaryotic structures) |
Attachment to surfaces, bacterial mating |
|
|
Flagella (functions of prokaryotic structures) |
Movement |
|
|
Endospore (functions of prokaryotic structures) |
Survival under harsh environmental conditions |
|
|
What two substances do prokaryotic cell membranes contain? |
Proteins and lipids |
|
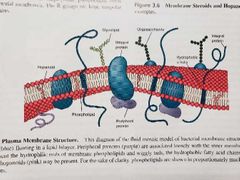
What are amphipathic lipids? |
Have polar and nonpolar ends structurally asymmetric; polar end interacts w/ h2o is hydrophilic; nonpolar end insoluble in h2o is hydrophobic. |
|
|
[Who and] What is the Gram stain? |
Christian Gram; divides cells into 2 classes - gram negative (lose violet & become colorless) / positive (retain violet stain). There's a reason for retention/ loss. |
|

2 areas bound within the interior of cell |
Cytoplasmic matrix & protoplast |

