![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
58 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Why are Aristotle and Ptolemy significant to you? |
Logic based approach; not keen on experiment |
|
|
What is science? |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
How old is the earth? |
4.6 billion years old |
|
|
Can you feel speed? |
No but you can feel acceleration and deceleration |
|
|
How fast does the earth orbits around the sun? |
66,000 mph |
|
|
How fast does the sun orbit the galaxy? |
500,000 mph |
|
|
Where is the Basin and Range Province? |
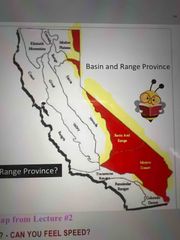
Back (Definition) |
|
|
The basin range is extensional and inflational |
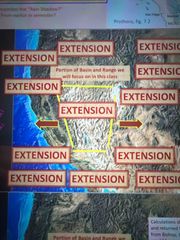
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Are basin and range hot? |
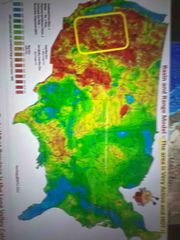
YES! Very active and hot! |
|
|
In what province is the long valley caldera? |
It is in the basin and range province |
|
|
Typical Morphology of Basin and Range |
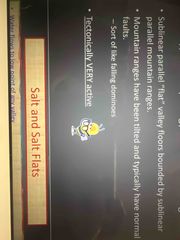
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Why is this an important societal concept for California? |
Since humans put dams into the river systems to store water and prevent flooding the Central Valley and Imperial Valley have both become internal-drainage valleys. Consequently, salt is building up in both valleys. |
|
|
Does Death Valley have volcanoes? |
Yes! |
|
|
What kind of transportation would you need if you travel to Death Valley during the Paleozoic era? |
A boat |
|
|
Where is Klamath mountains? |
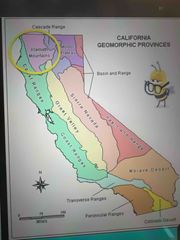
Back (Definition) |
|
|
What is Orogeny? |
When two tectonic plates collide |
|
|
Accretionary wedge |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
Coral |
Early Paleozoic Appeared appropriately 500 mya |
|
|
Klamath mountains |
They represent part of an amazingly complex suite of accretionary terrains inducted into the North American plate platform |
|
|
Do we see modern converging subduction zones? |
Philippines and Taiwan |
|
|
Where are the coast ranges? |
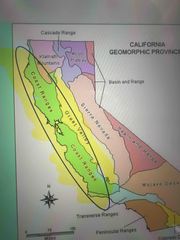
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Is precipitation seasonal? |
Yes, falling almost entirely between October and April |
|
|
Sacramento Valley superstorm of 1861/62 |
Rained for 28 days 37 inches in San Francisco 102 inches in Sonora |
|
|
Is water recycled? |
All water is recycled over geological time |
|
|
CA overall developed water use |
75% of water comes from Northern California 80% of demand comes from southern 2/3rds 70-80% of water used for agriculture Urban user around 10% Most Californians use about 60% of their residential water on outdoor landscaping |
|
|
Is groundwater in Bakersfield good? |
Yes it is generally excellent quality and comes out almost clear |
|
|
Is precipitation seasonal? |
Yes, falling almost entirely between October and April |
|
|
Sacramento Valley superstorm of 1861/62 |
Rained for 28 days 37 inches in San Francisco 102 inches in Sonora |
|
|
Is water recycled? |
All water is recycled over geological time |
|
|
CA overall developed water use |
75% of water comes from Northern California 80% of demand comes from southern 2/3rds 70-80% of water used for agriculture Urban user around 10% Most Californians use about 60% of their residential water on outdoor landscaping |
|
|
Is groundwater in Bakersfield good? |
Yes it is generally excellent quality and comes out almost clear |
|
|
What way does water flow in Bakersfield campus |
Groundwater flow to southwest in 2017 |
|
|
What happens when we over draft aquifers? |
They tend to compact (collapse) and the porosity is NEVER EVER restored. The damage is permanent |
|
|
Unlocked and unattended wells |
Can become conducts for groundwater contamination and become targets for accidental or intentional illegal dumping |
|
|
Major points to know about California water |
• "Most of the state is a semi-desert naturally unsuitable for agriculture or major cities." • "The [natural] water in California is not found where most of the people live." • "Years of drought and years of flood are part of the normal, natural pattern." California survives on a complex infrastructure of dams (1,300 of them!), canals, aqueducts, wells, and pipes. 39+ million people are thirsty - the population expands faster than the supply-infrastructure. As a rest seem to spend a lot of time on the edge of disaster. - All of those people and their activities create huge amounts of pollution and threats to ground water. |
|
|
Basin and Range Province earthquake |
• Earthquakes - Owen's Valley, March 1872 estimated at 7.8 • Shifted block 1-2 meters vertically and 6 meters horizontally - Dixie Valley Nevada, 1954, shifted block 5 meters |
|
|
Eras |
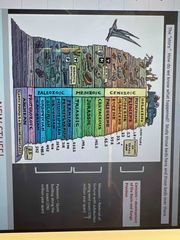
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Cenozoic era |
Cenozoic Era: extension of the Basin Range Province as North American Plate slides over the hot spreading center |
|
|
Mesozoic era |
• Mesozoic Era: reversal of fortune as divergent margin began REALLY enlarging the Atlantic Ocean and subcluction began on the Pacific margins - on huge scale |
|
|
Paleozoic era |
• Paleozoic Era + older time: Passive margin and carbonate platform along western margin of NA. Most of the planet's land mass was in one supercontinent. |
|
|
What caused Klamath mountains? |
• How did that happen - what are the theories? - For some reason, that is part of an area where oceanic terrains smashed into the western North American continent and some terrains did not go under - MOST DID, but SOME DID NOT. The technical jargon is that during subduction of oceanic terrains, portions were obducted (or accreted) onto the western north American Continent. |
|
|
Klamath Mountains Lithologies greatly simplified |
• Sub parallel packages of rock types separated by big faultsEastern Klamath belt has "McCloud" carbonates included in them which include Permian-age fossils suggesting an assemblage more indicative of coming from across the ocean (Asia). They don't look like North American fossils of equivalent age. Theory is LONG distance transport prior. to accretion. |
|
|
Porosity |
Porosity: % of void (empty) space in sediment or rock to store water; the volume of aquifer that consists of empty space - this empty space is used to store water - tells us how much water we have. |
|
|
Permeability |
Permeability: measures the interconnection of pores in a rock material ("efficiency of flow"), allows water to move through the aquifer and into the well. |
|
|
From where do we get our groundwater? |
- Subsurface sediments are usually layered and not homogenous. - In many places, the subsurface has layers of porous/permeable sand full of water; these are called aquifers. |
|
|
From where do we get our groundwater? |
- Subsurface sediments are usually layered and not homogenous. - In many places, the subsurface has layers of porous/permeable sand full of water; these are called aquifers. |
|
|
What is a cement seal? |
The cement seal prevents contaminants from migrating downward because it "binds" or "secures" the casing to the rock and sand. It's essential. Remember, that it's not unusual for wells to be caught in floods and for periods of time end up underwater land everything else that is included in floodwaters). |
|
|
Mexican American war |
• Mexican-American War in the Territories (1846 to 1848) President Polk and "Manifest Destiny" coupled with skirmishes along the Rio Grande .. |
|
|
1848 |
1848 - US acquires California from Mexico under the terms and conditions of the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo. All property rights (including water rights) under Mexican law are protected. At least the US said they would be protected and there are disputes to this day. |
|
|
Surface water rights |
- Surface water rights are primarily based on miner's practices • Riparian - If you own the beach-front property you own rights to that water Appropriated - "first in time, first in right" - They diverted (appropriated) rivers and streams and brought water to where THEY needed the water. Remember, this was literally the wild west. |
|
|
For decades the governing bodies of the US and California ignored the events transpiring on the public lands of California |
About 64 years! Dingi Dingl Dingl Ding! |
|
|
1877 to 1879 |
• 1877 to 1879 - The Constitutional Convention produces California's second Constitution and lengthy. This is when "Water" first appears as a Constitutional title. It is now known as Article X. |
|
|
1911 event |
• 1911 - The legislature placed "Proposition 7" on the ballot proposing to amend the California Constitution to incorporate the right of "ballot initiative." It was approved by the voters. - As an aside, Prop 4 was passed too and that gave women the right to vote |
|
|
1911 event |
• 1911 - The legislature placed "Proposition 7" on the ballot proposing to amend the California Constitution to incorporate the right of "ballot initiative." It was approved by the voters. - As an aside, Prop 4 was passed too and that gave women the right to vote |
|
|
1914 event |
1914 - California voters passed a referendum enacting the "Water Commission Act" which eventually led to today's "Water Code." The "People" decided a regulatory and permit system was needed. |
|
|
Riparian water rights |
California "developed" a unique system of water rights laws that are incompatible and lead to conflict which end up in court. They are RIPARIAN RIGHTS and APPROPRIATIVE RIGHTS Riparian Water Rights (property-based rights): • From English common law and used in the early colonies (which had a lot of water but Riparian Rights may not work so well in an arid climate) If there is a conflict with other holders of Riparian Rights then they have to determine what is 'reasonable." Good luck with that. |
|
|
WATER IS "OWNED" BY THE PEOPLE |
Ding! Ding! Ding! Ding! "The people of California own all the water in the state. Water rights provide the right to reasonab and beneficial use of the water, not ownership of the water. Public interests are thus involved at ev level of water management in California." (Ca Water Plan Update, 2009, vol 4 - Reference Guide, p. "All water within the State is the property of the people of the State, but the right to the use of wat may be acquired by appropriation in the manner provided by law." (Ca Water Code, Chapter 1, Secti 102) |
|
|
PUBLIC TRUST DOCTRINE LOOMS - This is a big deal |
A legal theory that began to make its presence felt in California water litigation beginning in 1970 following an article published by UC Berkeley School of Law. The theory says that the government is a trustee of certain things for the benefit of the people. In plainer terms, certain things should not be owned by private parties because those things are foundational to life and as such should be held by the government so that all may benefit. Legal concept that goes back to Roman law; Justinian wrote that the air, the sea, and running water belong to all mankind. Anticipate that in a drought the combination of the "Public Trust Doctrine" and what is "reasonable" will get the attention o the California courts. The first US case was an 1821 court decision titled Arnold y. Mundy where a dispute arose in New Jersey regarding access to oyster beds. Mundy wanted to harvest oysters in a bay and Arnold said "no" because he owned property on the shore and his ownership extended into the bay. The court invoked the public trust doctrine and saying Arnold could not lay claim to the bay. |

