![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
32 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
cell |
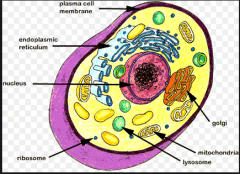
the smallest unit of life |
|
|
cell membrane |
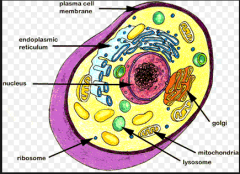
membrane that separates the interior of all cells from the outside environment |
|
|
nucleus |
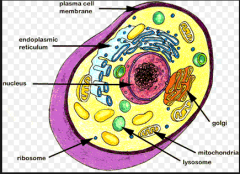
a dense organelle present in most eukaryotic cells, typically a single rounded structure bounded by a double membrane, containing the genetic material |
|
|
cytoplasm |
is that part of the cell between the cell membrane and the nuclear envelope |
|
|
tissue |
a cellular organizational level intermediate between cells and a complete organ |
|
|
muscle tissue |
a soft tissue found in most animals |
|
|
nerve tissue |
the main component of the two parts of the nervous system |
|
|
connective tissue |
tissue that connects, supports, binds, or separates other tissues or organs, typically having relatively few cells embedded in an amorphous matrix, often with collagen or other fibers, and including cartilaginous, fatty, and elastic tissues |
|
|
epithelial tissue |
covers the whole surface of the body |
|
|
organ |
a group of tissues in a living organism that have been adapted to perform a specific function |
|
|
organ system |
a group oforgans that work together to perform one or more functions |
|
|
homeostasis |
the ability to maintain a constant internal environment in response to environmental changes |
|
|
stress |
a body's method of reacting to a challenge |
|
|
vertebra |
each of the series of small bones forming the backbone, having several projections for articulation and muscle attachment, and a hole through which the spinal cord passes |
|
|
marrow |
a soft fatty substance in the cavities of bones, in which blood cells are produced (often taken as typifying strength and vitality |
|
|
cartilage |
firm, whitish, flexible connective tissue found in various forms in the larynx and respiratory tract, in structures such as the external ear, and in the articulating surfaces of joints. It is more widespread in the infant skeleton, being replaced by bone during growth
|
|
|
joint |
a structure in the human or animal body at which two parts of the skeleton are fitted together |
|
|
ligament |
a short band of tough, flexible, fibrous connective tissue that connects two bones or cartilages or holds together a joint |
|
|
osteoporosis |
a medical condition in which the bones become brittle and fragile from loss of tissue, typically as a result of hormonal changes, or deficiency of calcium or vitamin D |
|
|
involuntary muscle |
a muscle that contracts without conscious control (ACTS ON ITS OWN) |
|
|
voluntary muscle |
muscle whose action is normally controlled by an individual's will (DOES NOT ACT ON ITS OWN) |
|
|
skeletal muscle |
a muscle that is connected to the skeleton to form part of the mechanical system that moves the limbs and other parts of the body |
|
|
tendon
|
a flexible but not stretchy cord of strong fibrous collagen tissue attaching a muscle to a bone |
|
|
smooth muscle |
muscle tissue in which the contractile fibrils are not highly ordered, occurring in the gut and other internal organs and not under voluntary control |
|
|
cardiac muscle |
the muscular tissue of the heart |
|
|
epidermis |
the outer layer of cells covering an organism, in particular |
|
|
melanin |
a dark brown to black pigment occurring in the hair, skin, and iris of the eye in people and animals. It is responsible for tanning of skin exposed to sunlight |
|
|
dermis |
the thick layer of living tissue below the epidermis that forms the true skin, containing blood capillaries, nerve endings, sweat glands, hair follicles, and other structures |
|
|
pore |
One of the minute orifices in an animal or vegetable membrane, for transpiration, absorption, etc. |
|
|
follicle |
a small secretory cavity, sac, or gland, in particular` |
|
|
cancer |
disease caused by an uncontrolled division of abnormal cells in a part of the body |
|
|
acne |
the occurrence of inflamed or infected sebaceous glands in the skin; in particular, a condition characterized by red pimples on the face, prevalent chiefly among teenagers |

