![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
51 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
General features of Bacillus antracis
|
Non-motile, Spore forming, Gram +, rod
Aerobic Large, boxcar-like spore forming rods Poly-D-Glutamate capsule (UNIQUE!!!) |
|
|
|
Anthrax toxin three protein components
|
Protective Ag--mediate entry of LF or EF in eukaryotic cells
Lethal factor--kills cells Edema Factor--is an adenylate cyclase (activated by calmodulin) |
|
|
|
DOC for Anthrax
|
Cipro or Doxy
|
|
|
|
S/S of cutaneous Anthrax
|
Black eschar
--No Pus --No Pain Edema |
|
|
|
General features of Clostridium perfringens
|
Large Gram +, spore-forming rods
nonmotile Anaerobic Double zone of hemolysis |
|
|
|
Medically important
Gram positive rods |
Bacillus
Clostridium Cornyebacterium Listeria |
|
|
|
Cat scratch fever:
Bug & its characteristics |
Bartonella Henselae
Fastidious, Gram (-) rods |
|
|
|
General characteristics of listeria
|
Non-spore forming, Gram + rod
Aerobic motile INTRACELLULAR produces no exotoxin |
|
|
|
Difference between Bacillus anthracis and cereus
|
Cereus is motile
|
|
|
|
MOA of tetanospasmin (neurotoxin)
|
Binds to ganglioside receptors
Inhibits release of inhibitory NT Causes convulsive contractions of voluntary mm |
|
|
|
MOA of Botulinum toxin
|
Blocks release of ACH from presynaptic vesicle
flaccid paralysis |
|
|
|
These two bugs use alpha toxin?
How does it work in each? |
C. perfringens (enzymatic lysis)
S. Aureus (pore formation) |
|
|
|
Exotoxin A:
MOA? Which bug uses this? |
P. Aeruginosa
ADP ribosyl transferase; inactivates EF-2. Inhibits Eukaryotic protein synthesis. |
|
|
|
Skin infection that was initially vesicular but with longer lasting bullae;
catalase-positive organism. DX? |
Impetigo
due to S. aureus |
|
|
|
Skin infection; skin erosion; honey-crusted;
catalase-negative organism. DX? |
Impetigo
Due to S. pyogenes (Gr. A) |
|
|
|
General Features of Strep. pyogenes.
(GAS) (5) |
Gram + cocci in chains
Catalase negative M protein Beta hemolytic Bacitracin Sensitive |
Gram
Catalase Serological ID Hemolysis Sensitivity |
|
|
Tx of S. pyogenes
|
Penicillin
(if allergic use Macrolide) |
|
|
|
Distinguishing features of S. Aureus
|
Small, yellow colonies on blood agar
Gram positive cocci clusters Catalase positive ß-hemolytic Coagulase positive Ferments mannitol |
Positive x3
|
|
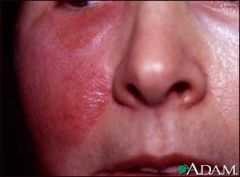
Border is raised and surface appears like an orange peel
Can also occur on extremities. DX? Etiology? Tx? |
Erysipelas
S. pyogenes If on face: Vanc If on extremities: IV Pen G |
|
|
|
Most common causes of Cellulitis
|
S. aureus
S. pyogenes |
|
|
|
Furuncles/Carbuncles on: Neck, face, axillae, or buttocks.
Bug? |
S. aureus
|
|
|
|
Furuncles/Carbuncles on: Inflamed follicles from neck down.
Bug? |
Pseudomonas aeruginosa (hot tub folliculitis)
|
|
|
|
Inflammation of follicles and sebaceous glands
Bug and Dx |
Propionibacterium acnes
Acne Vulgaris |
|
|
|
Vesicular lesions sometimes preceded by neurologic pain.
|
Herpes
|
|
|
|
Bug and toxin causing Scalded skin syndrome
|
S. aureus--->Exfoliatin toxin
|
|
|
|
Most common causes of fasciitis
|
Streptococcus pyogenes
C. perfringens |
|
|
|
DOC for C. perfringens
|
Pen G +/- Clindamycin
PLUS debridement |
|
|
|
General characteristics of C. perfringens (3 big ones)
|
GRAM (+) RODS
SPORE FORMING NON-MOTILE Stormy fermentation Egg yolk agar Double zone of hemolysis Phospholipase C |
|
|
|
Nocardia brasiliensis characteristics
|
Aerobic
Gram (+) branching rods Partially Acid Fast Intracellular |
|
|
|
Corynebacterium diphtheriae Characteristics
|
Aerobic
Non-motile Gram (+) non-spore forming rods Pleomorphic Tellurite medium |
|
|
|
#1 burn infection
|
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
|
|
|
|
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
|
Aerobic
Gram (-) Rod Motile Pyocyanin pigment Oxidase Positive Grape-like odor slime layer (glycocalyx) Non-lactose fermenter on MacConkey |
|
|
|
Where is Borrelia burgdorferi commonly found?
When? Vector? |
Northeast, Midwest, & West coast
Late spring/Early summer Ixodes sp. (tick) |
|
|
|
Characteristics of:
Borrelia Burgdorferi TX? |
Spirochetes
Gram neg. (note: spiros don't gram stain) Difficult to culture Tx: Doxy |
|
|
|
Hunter with ulceroglandular dz, atypical pneumonia, or GI dz
Arkansas/Missouri DX |
Tularemia
|
|
|
|
Vector of Tularemia
Reservoir |
Dermacentor (Tick)
Rodents |
|
|
|
Francisella tularensis Characteristics
|
Gram (-) small rods
Intracellular, parasitize reticuloendothelial system |
|
|
|
Tx of Tularemia
|
Streptomycin
|
|
|
|
Vector of Yersinia pestis
|
Xeopsylla cheopsis (rat flea)
|
|
|
|
Characteristics of Yersinia pestis
|
"Safety pin" staining
Gram (-) rods with bipolar staining |
|
|
|
Tx of Yersinia pestis
|
Streptomycin and/or Penicillin
|
|
|
|
Pt with influenza-like s/s and petechial rash that begins on ankles and wrists and moves to trunk. Went camping in Virginia mountains.
Intracellular, Gram(-) bacilli |
Rickettsia rickettsii
Rocky Mtn Spotted Fever |
|
|
|
Vectors of Rickettsia
|
Dermacentor in most places
Amblyomma americanum (lone star tick) in the Southwest |
|
|
|
Tx of Rocky mountain spotted fever
|
Doxycycline
|
|
|
|
Similar to Rocky Mtn Spotted Fever, but no rash.
+Thrombocytopenia +Leukopenia +Morulae inside cells |
Ehrlichiosis
|
|
|
|
Tx of Ehrlichiosis
|
Doxycycline
(begin before Lab confirmation) |
|
|
|
Leptospira interrogans
characteristics Tx? |
Tightly coiled spirochetes
Flagellated (2 flagella) Penicillin/Tetracycline |
|
|
|
Brucellosis Characteristics
|
Gram (-) Coccobacilli
Non-motile Intracellular parasite |
|
|
|
Tx of Brucellosis
|
Tetracycline/Streptomycin
|
|
|
|
Pt with acute septicemia; exposure to animals or unpasteurized dairy;
California/Texas or travel to Mexico |
Brucellosis
|
|
|
|
Three types of Brucella sp. and their reservoirs
|
B. abortus: Cattle
B. melitensis: Goats B. suis: Pigs |
|

