![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
16 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
INTEGUMENTARY MEDS |
CHAPTER 42- SAUNDERS 5TH EDITION |
|
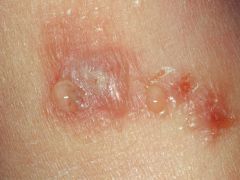
POISON IVY
|
Tx of lesions: calamine lotion, Burrow's soln, Aveeno baths
Tx of inflammation: topical corticosteriods
Tx severe reactions: PO corticosteriods and sedative (diphenhydramine/Benadryl) |
|
|
POISON IVY TREATMENT PRODUCTS |
1. bentoquatam- for preventive use (Ivy block) 2. Calamine lotion (Caladryl lotion) 3. hydrocortisone (Ivy soothe, Ivy stat) 4. isopropanol: cetyl alchohol (Ivy Cleanse) 5. Zinc acetate: isopropanol (Ivy Dry) 6. Zinc acetate: isopropanol, benzyl alcohol (Ivy Super Dry) |
|
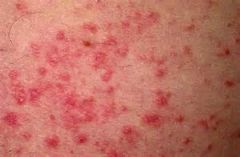
ATOPIC DERMATITITS
|
1. moisturizers 2. topical glucocorticoids 3.SYSTEMIC IMMUNOSUPRESSANTS: methotrexate, cyclosporine (Sandimmune), or azathioprine (Imuran) and oral glucocorticoids 4. TOPICAL IMMUNOSUPPRESSANTS: a. tacrolimus (protopic) -increases risk of varicella zoster infection in children, may cause skin cancer and lymphoma b. Pimecrolimus 1% cream (Eldidel) c. side effects: redness, burning, itching, sensitization of skin to sunlight |
|
|
TOPICAL GLUCOCORTICOIDS |
1. have anti-inflammatory, antipruritic and vasoconstrictive actions 2. preps vary in potency and depend on the concnetration and type of prep, method of application (occlusive dressings enhance absorption, increasing effects 3. systemic effects occur with prolonged therapy and extensive skin surfaces are treated 4. absorbed greater in permeable skin areas (scalp, axilla, face and neck, eyelids, perineum) and less in areas where permeability is poor (palms, soles, back) |
|
|
GLUCOCORTICOIDS CONTRAINDICATION |
1. previous sensitivity to corticosteriods 2. current systemic fungal, viral, or bacterial infection 3. current complications related to glucocorticoid therapy |
|
|
GLUCOCORTICOIDS ADVERSE EFFECTS (SYSTEMIC) |
1. growth retardation (children) 2. adrenal suppression 3. Cushing's syndrome 4. Striae, skin atrophy 5. Ocular effects (glaucoma, cataracts) |
|
|
GLUCOCORTICOIDS ADVERSE EFFECTS (LOCAL) |
1. burning, dryness, irritation, itching 2. skin atrophy 3. thinning of the skin, striae, purpura, telangiectasia 4. acneiform eruptions 5. hypopigmentation 6. overgrowth of bacteria, fungi, and viruses |
|
|
GLUCOCORTICOIDS INTERVENTIONS |
1. monitor plasma cortisol levels may be prescribed if prolonged therapy is necessary 2. wash the area just before application to increase medication penetration 3. apply sparingly in a thin film, rubbing gently 4. avoid the use of a dry occulsive dressing unless specifically prescribed by HCP 5. Instruct client to report signs of adverse effects to HCP |
|
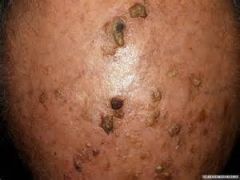
WHAT IS ACTINIC KERATOSIS
|
1. caused by chronic exposure to the sun 2. rough, scaly, red or brown lesions 3. usually found on the face, scalp, arms, and back of hands 4. can progress to squamous cell carcinoma |
|
|
MEDS TO TREAT ACTINIC KERATOSIS |
1. Flurorouracil (Carac, Efudex, Fluoroplex) 2. Diclofenac sodium (Solaraze) 3. Imiquimod 5 % cream (Aldara) 4. Aminolevulinic acid (Levulan kerastick) |
|
|
FLUROURACIL (CARAC, EFUDEX, FLUOROPLEX) |
1. topical mediation 2. affects DNA and RNA synthesis and causes a seq of response that results in healing 3. results usually seen in 2-6 weeks, but may take 1-2 months longer for complete healing 4. side effects: itching, burning, inflammation, rash, increased sensitivity to sunlight 5. used to treat actinic keratosis |
|
|
Diclofenac sodium (Solarize) |
1. nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory topical drug 2. used to treat actinic keratosis 3. may take 3 months to be effective 4. side effects: dry skin, itching, redness, and rash |
|
|
Imiquimod 5% cream (Aldara) |
1. topical medication 2. used to treats actinic keratosis and venereal warts 3. takes up to 4 months to be effective 4. side effects: redness, skin swelling, itching, burning, sores, blisters, scabbing, and crusting of the skin |
|
|
SUNSCREENS |
1. UV light damages skin, causes actinic keratosis and skin cancer 2. sunscreen prevents penetration of UV light and protects skin 3. organic (chemical) sunscreen absorbs UV light 4. inorganic (physical) reflect and scatter UV light 5. a sunscreen that protects against both UVB and UVA rays and one that has a sun protection factor (SPF) of at least 15 should be used
|
|
|
SUNSCREEN APPLICATION |
1. most effective when applied at least 30 minutes before exposure to the skin however, sunscreens that contain para-aminobenzoic acid [PABA] or padimate O require application 2 hours prior to sun exposure. 2. |

