![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
43 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the 4 levels in which data access is configured? |
1. Organization 2. Objects 3. Fields 4. Records |
|
|
True/False: Data security and sharing model are implemented at the API level. |
True. Permissions specified for objects, records, and fields apply even if you query or update the data via API calls. |
|
|
What are 4 ways to secure access to your organization? |
1. Maintaining a list of authorized users 2. Setting password policies 3. Limiting login access to certain hours 4. Limiting login access to certain locations (IPs) |
|
|
What are 4 object-level security settings? |
1. Create 2. View 3. Edit 4. Delete |
|
|
True/False: You can use field-level security to restrict access to certain fields, but only if the user has access to that object. |
True. If the user doesn't have access to the object, there is no need for field-level security. |
|
|
What are the 4 ways in which record-level access is managed? |
1. Organization-wide defaults 2. Role hierarchies 3. Sharing rules 4. Manual sharing |
|
|
True/False: Organization-wide defaults are used to specify the most common level of access users have to each others' records. |
False. Organization-wide defaults specify the default level and should be used to lock down data to the most restrictive level. |
|
|
How do role hierarchies affect record-level access? |
Role hierarchies open up record-level access to those higher in the hierarchy so they inherit access to all records owned by users below them in the hierarchy. |
|
|
True/False: Role hierarchies should match your organization chart exactly. |
False. Each role in the hierarchy should represent a level of data access that a user or group of users needs. |
|
|
How do sharing rules affect record-level access? |
Sharing rules make automatic exceptions to organization-wide defaults for particular group of users, to give them access to records they don't own or can't normally see. |
|
|
True/False: Sharing rules can be stricter than the organization-wide default settings. |
False: Sharing rules are only used to give additional users access to records. |
|
|
True/False: Role hierarchies are only used to open up access to records they don't own or can't normally see. |
True. Role hierarchies can't be stricter than the organization-wide default settings. |
|
|
How does manual sharing affect record-level access? |
Manual sharing allows owners of particular records to share them with other users. |
|
|
True/False: Manual sharing is automated. |
False. Manual sharing isn't automated like organization-wide sharing settings, role hierarchies, or sharing rules, it can be useful in some one-off situations. |
|
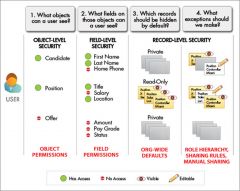
|
A table used to help set up the security model, which contains the various types of users in the organization, the level of access each types of user needs for each object and for fields and records within the object. |
|
|
True/False: Auditing features does not secure the organization by itself. |
True. However, it does provide important information about system usage, which can be useful in diagnosing potential or real security issues. |
|
|
What are 4 auditing features that Salesforce provides? |
1. Record modification fields 2. Login history 3. Field history tracking 4. Setup audit trail |
|
|
What information do record modification fields show? |
All objects include record modification fields that store the name of the user who created the record and when, and who last modified the record and when. |
|
|
What does the login history show? |
Login history lists successful and failed login attempts for the past six months and includes API access logins. |
|
|
How many attempts does the login history page show? |
The most recent 20,000 attempts. |
|
|
True/False: It is possible to see more than the most recent 20,000 login attempts. |
True. You can download the login history to see more than 20,000 attempts and up to 6 months of history. |
|
|
True/False: Single Sign-On with SAML does not appear in the login history. |
False. If your organization uses SAML single sign-on identity provider certificates, single sign-on logins appear in the history. |
|
|
True/False: My Domain URLs do not appear in the login history. |
False. If you are using My Domain, you can identify which users are logging in with the new login URL and when. |
|
|
What is field history tracking? |
Field history tracking is auditing enabled for individual fields, which will automatically track any changes in the values of selected fields. |
|
|
True/False: Field history tracking is available for all custom and standard objects. |
False. Although field history tracking is available for all custom objects, only some standard objects allow field-level auditing. |
|
|
How long is field history data retained? |
For orgs created before June 2011 with field history limits that remain static, Salesforce commits to retain field history without limit. For orgs created after June 2011 and the Field Audit Trail add-on is not purchased, field history is retained for a maximum of 18 months. For orgs created after June 2011 and the Field Audit Trail add-on is purchased, field history is retained based on the retention policy associated with the offering. |
|
|
Which standard objects allow field-level auditing? |
- Accounts - Articles - Assets - Cases - Contacts - Contracts - Contract line items - Entitlements - Leads - Opportunities - Orders - Order Products - Products - Service Contracts - Solutions |
|
|
What information do field history tracking entries show? |
The date, time, nature of the change, and how made the change. |
|
|
True/False: All field types are available for historical trend reporting. |
False. Not all field types are available for historical trend reporting. |
|
|
True/False: Field history tracking always records old and new values. |
False: Changes to fields with more than 255 characters are tracked as edited, and their old and new values are not recorded. |
|
|
True/False: A field that has been enabled for field history tracking will always be tracked. |
False. If a trigger causes a change on an object the current user doesn’t have permission to edit, that change is not tracked because field history honors the permissions of the current user. |
|
|
What does the setup audit trail do? |
The setup audit trail history tracks the recent setup changes that administrators have made to the org. |
|
|
How many changes does the setup audit trail history page show? |
The 20 most recent setup changes. |
|
|
True/False: It is possible to see more than the most recent 20 setup changes. |
True. You can download the org's full setup history for the past 180 days. |
|
|
What information is displayed for each setup change? |
It lists the date of the change, who made it, and what the change was. |
|
|
True/False: If a delegate makes a setup change on behalf of an end user, the history will only show the end user. |
False. The Delegate User column will show the delegate’s username. |
|
|
What changes are tracked in the administration type of setup audit trail history? |
- Company information, default settings such as language or locale, and company message changes - Multiple currency setup changes - User, portal user, role, permission set, and profile changes - Email address changes for any user - Deleting email attachments sent as links - Creating, editing, or deleting email footers - Record type changes, including creating or renaming record types and assigning record types to profiles - Changes to divisions, including creating and editing divisions, transferring divisions, and changing users' default division - Adding or deleting certificates - Domain name changes - Enabling or disabling Salesforce as an identity provider |
|
|
What changes are tracked in the customization type of setup audit trail history? |
-Changes to user interface settings, such as collapsible sections, Quick Create, hover details, or the related list hover links - Page layout, action layout, and search layout changes - Changes to compact layoutsChanges to the Salesforce1 navigation menu - Changes made using inline editing - Custom field and field-level security changes, including changes to formulas, picklist values, and custom field attributes, like the format of auto-number fields, manageability, or masking of encrypted fields - Changes to lead settings, lead assignment rules, and lead queues - Changes to activity settings - Changes to support settings, business hours, case assignment and escalation rules, and case queues - Any changes made by Salesforce Customer Support at your request - Changes to tab names, including tabs that you reset to the original tab name - Changes to custom apps (including Salesforce console apps), custom objects, and custom tabs - Changes to contract settingsChanges to forecast settings - Enabling or disabling Email-to-Case or On-Demand Email-to-Case - Changes to custom buttons, links, and s-controls, including standard button overrides - Enabling or disabling drag-and-drop scheduling - Enabling, disabling, or customizing similar opportunities - Enabling or disabling quotes - Changes to data category groups, data categories, and category-group assignments to objects - Changes to article types - Changes to category groups and categories - Changes to Salesforce Knowledge settings - Changes to ideas settings - Changes to answers settings - Changes to field tracking in feeds - Changes to campaign influence settings - Activating or deactivating critical updates - Enabling or disabling Chatter email notifications - Enabling or disabling Chatter new user creation settings for invitations and email domains - Changes to validation rules |
|
|
What changes are tracked in the security and sharing type of setup audit trail history? |
- Public groups, sharing rule changes, and org-wide sharing, including the Grant Access Using Hierarchies option - Password policy changes - Password resets - Session settings changes, such as changing the session timeout setting - Changes to delegated administration groups and the items delegated administrators can manage. Setup changes made by delegated administrators are tracked as well. - How many records a user emptied from their Recycle Bin and from the org’s Recycle Bin - Changes to SAML (Security Assertion Markup Language) configuration settings - Changes to Salesforce certificates - Enabling or disabling identity providers - Changes to named credentials - Changes to service providers - Changes to Shield Platform Encryption setup |
|
|
What changes are tracked in the data management type of setup audit trail history? |
- Mass delete use, including when a mass delete exceeds the user’s Recycle Bin limit of 5,000 deleted records. The oldest excess records are permanently removed from the Recycle Bin within two hours of the mass delete transaction time. - Data export requests - Mass transfer use - Changes to reporting snapshots, including defining, deleting, or changing the source report or target object on a reporting snapshot - Use of the Data Import WizardSandbox deletions |
|
|
What changes are tracked in the development type of setup audit trail history? |
- Changes to Apex classes and triggers - Changes to Visualforce pages, custom components, or static resources - Changes to Lightning Pages - Changes to action link templates - Changes to custom settings - Changes to custom metadata types and records - Changes to remote access definitions - Changes to Force.com Sites settings |
|
|
What changes are tracked in the various setup type of setup audit trail history? |
- Creation of an API usage metering notification - Changes to territories - Changes to process automation settings - Changes to approval processes - Creation and deletion of workflow actions - Changes to Visual Workflow files - Packages from Force.com App - Exchange that you installed or uninstalled |
|
|
What changes are tracked in the using the application type of setup audit trail history? |
- Changes to account team and opportunity team selling settings - Activation of Google Apps services - Changes to mobile configuration settings, including data sets, mobile views, and excluded fields - A user with the “Manage External Users” permission logging into the partner portal as a partner user - A user with the “Edit Self-Service Users” permission logging into the Salesforce Customer Portal as a Customer Portal user - Enabling or disabling a partner portal account - Disabling a Salesforce Customer Portal account - Enabling or disabling a Salesforce Customer Portal and creating multiple Customer Portals - Creating and changing entitlement processes and entitlement templates - Enabling or disabling self-registration for a Salesforce Customer Portal - Enabling or disabling Customer Portal or partner portal users |

